共计 11828 个字符,预计需要花费 30 分钟才能阅读完成。
MySQL 提供了多种数据类型,主要包括数值型、字符串型和日期时间类型。本次博客就来谈谈 MySQL 中常用的数据类型吧(版本:mysql-5.7.19)!
数值类型
MySQL 支持所有标准 SQL 中数值类型,具体见下表:
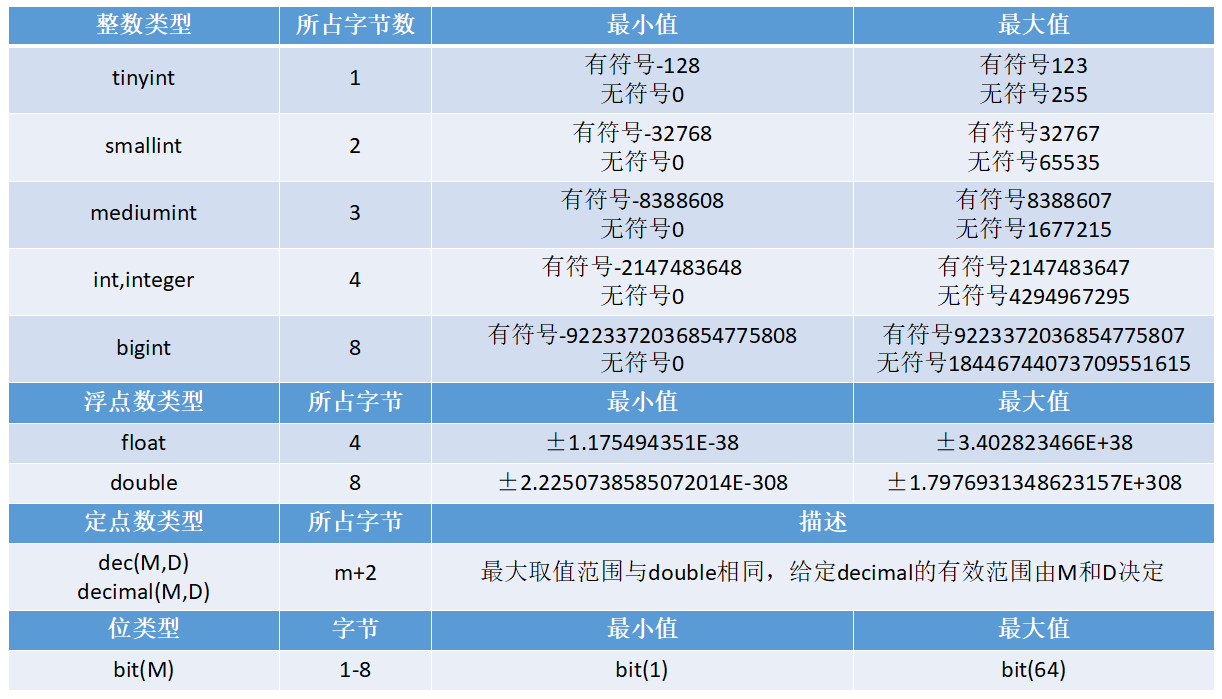
数值类型是由范围的,如果超出数值的范围就会发生“out of range”的错误提示,所以在选择数值类型的时候,一定要结合实际的情况去选择。
1. 整数类型
| mysql> create table t1(num1 int(5),num2 int); | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) | |
| mysql> desc t1; | |
| +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | | |
| +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| | num1 | int(5) | YES | | NULL | | | |
| | num2 | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | |
| +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| 2 rows in set (0.01 sec) | |
| mysql> insert into t1 values(1,1); | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> select * from t1; | |
| +------+------+ | |
| | num1 | num2 | | |
| +------+------+ | |
| | 1 | 1 | | |
| +------+------+ | |
| 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
| mysql> alter table t1 modify num1 int(5) zerofill; | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected (0.07 sec) | |
| Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 | |
| mysql> alter table t1 modify num2 int zerofill; | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected (0.08 sec) | |
| Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 | |
| mysql> select * from t1; | |
| +-------+------------+ | |
| | num1 | num2 | | |
| +-------+------------+ | |
| | 00001 | 0000000001 | | |
| +-------+------------+ | |
| 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
当为一个列指定为 zerofill 的时候,则 MySQL 自动为该列添加无符号属性,那么就可以取得较大的上限值,可以见前面的表格。
| mysql> insert into t1 values(111111,1); | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> select * from t1; | |
| +--------+------------+ | |
| | num1 | num2 | | |
| +--------+------------+ | |
| | 00001 | 0000000001 | | |
| | 111111 | 0000000001 | | |
| +--------+------------+ | |
| 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> desc t1; | |
| +-------+---------------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | | |
| +-------+---------------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| | num1 | int(5) unsigned zerofill | YES | | NULL | | | |
| | num2 | int(10) unsigned zerofill | YES | | NULL | | | |
| +-------+---------------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
如上面的例子,即使我们插入的数值为 111111,也没有报错,且默认的显示长度变为了 10,这里一定要注意的是,括号内的只是显示长度,无符号的 int 的最大值为 4294967295,我们来测试一下就知道了:
| mysql> insert into t1 values(4294967295,4294967295); | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> select * from t1; | |
| +------------+------------+ | |
| | num1 | num2 | | |
| +------------+------------+ | |
| | 00001 | 0000000001 | | |
| | 111111 | 0000000001 | | |
| | 4294967295 | 4294967295 | | |
| +------------+------------+ | |
| 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> insert into t1 values(4294967296,4294967295); | |
| ERROR 1264 (22003): Out of range value for column 'num1' at row 1 | |
| mysql> insert into t1 values(4294967295,4294967296); | |
| ERROR 1264 (22003): Out of range value for column 'num2' at row 1 |
当数值超过 4294967295 的时候就会报错了。
整数类型还有另外一个属性:anto_increment,在需要产生唯一的标识符的时候,可以利用这个属性,这个属性只属于整数类型,默认情况下,anto_increment 的值从 1 开始,每次增加一,一个表中最多只能有一个 auto_incerment 列,对于任何想要使用 auto_incerment 的列,应该定义为 not null,并且定义为 primary key,定义方式如下:
create table tablename(id int auto_increment not null primary key);
举例:
| mysql> create table t2(id int auto_increment not null primary key,name varchar(10)); | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) | |
| mysql> insert into t2(name) values('Frank'),('Rose'); | |
| Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec) | |
| Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 | |
| mysql> select * from t2; | |
| +----+-------+ | |
| | id | name | | |
| +----+-------+ | |
| | 1 | Frank | | |
| | 2 | Rose | | |
| +----+-------+ | |
| 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> desc t2; | |
| +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | |
| | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | | |
| +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | |
| | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | |
| | name | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | | | |
| +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | |
| 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
2. 小数类型
| mysql> create table t3(num1 float(4,2),num2 double(4,2),num3 decimal(4,2)); | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.43 sec) | |
| mysql> insert into t3(num1,num2,num3) values(1.26,1.26,1.26); | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> select * from t3; | |
| +------+------+------+ | |
| | num1 | num2 | num3 | | |
| +------+------+------+ | |
| | 1.26 | 1.26 | 1.26 | | |
| +------+------+------+ | |
| 1 row in set (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> insert into t3(num1,num2,num3) values(1.266,1.266,1.266); | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> show warnings; | |
| +-------+------+-------------------------------------------+ | |
| | Level | Code | Message | | |
| +-------+------+-------------------------------------------+ | |
| | Note | 1265 | Data truncated for column 'num3' at row 1 | | |
| +-------+------+-------------------------------------------+ | |
| 1 row in set (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> select * from t3; | |
| +------+------+------+ | |
| | num1 | num2 | num3 | | |
| +------+------+------+ | |
| | 1.26 | 1.26 | 1.26 | | |
| | 1.27 | 1.27 | 1.27 | | |
| +------+------+------+ | |
| 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
| mysql> alter table t3 modify num1 float; | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) | |
| Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 | |
| mysql> alter table t3 modify num2 double; | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) | |
| Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 | |
| mysql> alter table t3 modify num3 decimal; | |
| Query OK, 4 rows affected, 4 warnings (0.12 sec) | |
| Records: 4 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 4 | |
| mysql> desc t3; | |
| +-------+---------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | | |
| +-------+---------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| | num1 | float | YES | | NULL | | | |
| | num2 | double | YES | | NULL | | | |
| | num3 | decimal(10,0) | YES | | NULL | | | |
| +-------+---------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> select * from t3; #会发现浮点型存储的值没有发生改变,而 decimal 的直接就被截断了,因为浮点型如果不写精度和标度,则会安装实际精度显示。+------+------+------+ | |
| | num1 | num2 | num3 | | |
| +------+------+------+ | |
| | 1.26 | 1.26 | 1 | | |
| | 1.27 | 1.27 | 1 | | |
| | 1.27 | 1.27 | 1 | | |
| | 1.27 | 1.27 | 1 | | |
| +------+------+------+ | |
| 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
3. 位类型
用于存放位字段值,bit(M)可以存放多位二进制,M 的范围为 1 -64,对于位字段,直接使用 select 是看不到结果的,可以使用 bin()或者 hex()函数读取。
| mysql> create table t4(id bit(1)); | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) | |
| mysql> desc t4; | |
| +-------+--------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | | |
| +-------+--------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| | id | bit(1) | YES | | NULL | | | |
| +-------+--------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| 1 row in set (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> | |
| mysql> insert into t4 values(1); | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> select * from t4; | |
| +------+ | |
| | id | | |
| +------+ | |
| | | | |
| +------+ | |
| 1 row in set (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> select bin(id),hex(id) from t4; | |
| +---------+---------+ | |
| | bin(id) | hex(id) | | |
| +---------+---------+ | |
| | 1 | 1 | | |
| +---------+---------+ | |
| 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
我们来试试插入数值 2:
| mysql> insert into t4 values(2); | |
| ERROR 1406 (22001): Data too long for column 'id' at row 1 |
出错了,因为 2 的二进制码是 ”10″,必须有 2bit 才能存储,修改过后查看:
| mysql> alter table t4 modify id bit(2); | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected (0.08 sec) | |
| Records: 1 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 | |
| mysql> insert into t4 values(2); | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> select bin(id),hex(id) from t4; | |
| +---------+---------+ | |
| | bin(id) | hex(id) | | |
| +---------+---------+ | |
| | 1 | 1 | | |
| | 10 | 2 | | |
| +---------+---------+ | |
| 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
字符串类型
MySQL 提供了多种字符数据的存储类型,具体见下表:
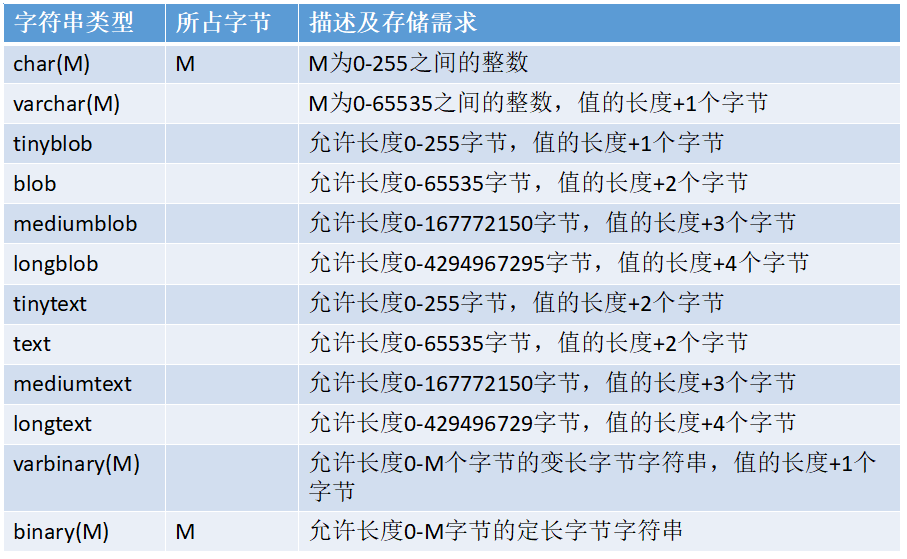
1.char 和 varchar 类型
char 和 varchar 主要是用来存储较短的字符串,二者的主要区别在于存储方式的不同,char 列的长度为创建表时声明的长度,而 varchar 列中的值为可变长字符串。在检索的时候,char 会删除尾部的空格,而 varchar 则保留这些空格。
举个例子:
| mysql> create table space(s1 varchar(4),s2 char(4)); | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) | |
| mysql> insert into space values('aa ','aa '); | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) | |
| mysql> select length(s1),length(s2) from space; | |
| +------------+------------+ | |
| | length(s1) | length(s2) | | |
| +------------+------------+ | |
| | 4 | 2 | | |
| +------------+------------+ | |
| 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
根据以上例子可以看到,char 列在检索的时候已经被删除了。
对比:
char 存储定长的数据很方便且索引的效率很好,比如定义了 char(4),那么不论你的数据是否达到了 4 个字节,都要占用 4 个字节的 1 空间;
varchar,存储变长的数据,但存储的效率没有 char 高且检索的效率也会低很多,varchar 类的实际长度 +1,原因是这一个字节用于保存实际使用了多大的长度。
总结:从节约空间的角度去看使用 varchar 更好,但是如果从存储效率和索引效率上来看,char 更合适。
2.enum 类型
enum 也叫枚举类型,它的值范围需要在创建表时通过枚举方式显示指定,最多允许有 65535 个成员:
举例:
| mysql> create table t6(g enum('green','red','blue','yellow')); | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) | |
| mysql> insert into t6 values('Green'),('red'),('hello'); | |
| ERROR 1265 (01000): Data truncated for column 'g' at row 3 | |
| mysql> | |
| mysql> insert into t6 values('Green'),('red'),('blue'),(NULL); | |
| Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.00 sec) | |
| Records: 4 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 | |
| mysql> select * from t6; | |
| +-------+ | |
| | g | | |
| +-------+ | |
| | green | | |
| | red | | |
| | blue | | |
| | NULL | | |
| +-------+ | |
| 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
3.set 类型
set 和 enum 类似,里面最多可以有 64 个成员。但是 set 和 enum 不同的之处就是,set 一次可以选取多个成员。
| mysql> create table t7(s set('green','red','blue','yellow')); | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) | |
| mysql> desc t7; | |
| +-------+------------------------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | | |
| +-------+------------------------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| | s | set('green','red','blue','yellow') | YES | | NULL | | | |
| +-------+------------------------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| 1 row in set (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> | |
| mysql> insert into t7 values('Green,red'),('yellow,blue,red'); | |
| Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec) | |
| Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 | |
| mysql> | |
| mysql> select * from t7; | |
| +-----------------+ | |
| | s | | |
| +-----------------+ | |
| | green,red | | |
| | red,blue,yellow | | |
| +-----------------+ | |
| 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> insert into t7 values('yellow,red,red'); | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> select * from t7; | |
| +-----------------+ | |
| | s | | |
| +-----------------+ | |
| | green,red | | |
| | red,blue,yellow | | |
| | red,yellow | | |
| +-----------------+ | |
| 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
通过以上例子可以看出,set 也是不区分大小写的,如果在插入信息的有重复的值,将只取一次。成员范围外的值在插入表的时候会报错。
时间和日期类型
MySQL 有很多的数据类型用于表示时间和日期,见下表:
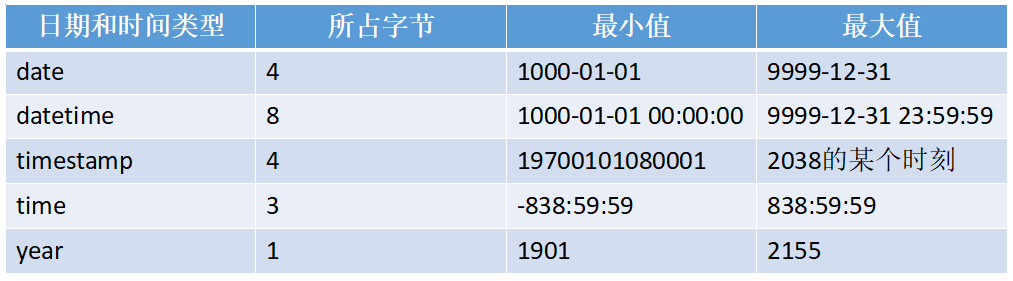
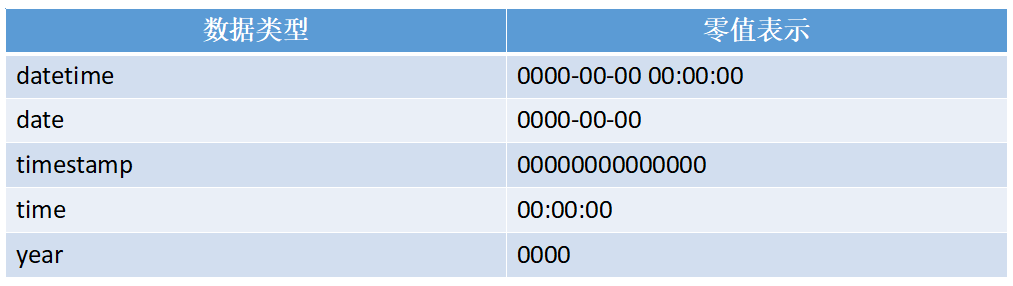
每一个时间和日期的数据类型都有其范围,如果超出其范围,系统会提示错误,并以零值来存储。不同日期的零值的表示如下表:
1.date、time 和 datetime
最常见的三种时间和日期的数据类型了。
举例:
| mysql> create table t8(d date,t time,dt datetime); | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) | |
| mysql> insert into t8 values(now(),now(),now()); #使用 now 函数插入当前的时间和日期 | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> select * from t8; | |
| +------------+----------+---------------------+ | |
| | d | t | dt | | |
| +------------+----------+---------------------+ | |
| | 2017-09-17 | 21:06:59 | 2017-09-17 21:06:59 | | |
| +------------+----------+---------------------+ | |
| 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
通过上面的例子可以看出,datetime 是 date 和 time 的组合。
timestamp 也是用来表示日期和时间的,但是和 datetime 是有所不同的,我们一起看一下吧!
| mysql> create table t1(ts timestamp); | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec) | |
| mysql> desc t1; | |
| +-------+-----------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+ | |
| | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | | |
| +-------+-----------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+ | |
| | ts | timestamp | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | | |
| +-------+-----------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+ | |
| 1 row in set (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> insert into t1 values(null); | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> select * from t1; | |
| +---------------------+ | |
| | ts | | |
| +---------------------+ | |
| | 2017-09-17 21:23:59 | | |
| +---------------------+ | |
| 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
系统给 timestamp 自动创建了默认值 CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(系统时间),当插入了一个 null 的时候,t1 中正确的插入当前的系统时间。一个表中只允许存在一个 timestamp 字段。
timestamp 还有一个重要的特性就是与时区相关:
| mysql> create table t2 (ts timestamp,t datetime); | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) | |
| mysql> show variables like 'time_zone'; #查看当前的时区 | |
| +---------------+--------+ | |
| | Variable_name | Value | | |
| +---------------+--------+ | |
| | time_zone | SYSTEM | | |
| +---------------+--------+ | |
| 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.01 sec) | |
| mysql> insert into t2 values(now(),now()); | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> select * from t2; | |
| +---------------------+---------------------+ | |
| | ts | t | | |
| +---------------------+---------------------+ | |
| | 2017-09-17 21:31:15 | 2017-09-17 21:31:15 | | |
| +---------------------+---------------------+ | |
| 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
SYSTEM 为当前的时区,也就东八区,现在将时区改为东九区试试:
| mysql> set time_zone='+9:00'; | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> select * from t2; | |
| +---------------------+---------------------+ | |
| | ts | t | | |
| +---------------------+---------------------+ | |
| | 2017-09-17 22:31:15 | 2017-09-17 21:31:15 | | |
| +---------------------+---------------------+ | |
| 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
结果发现使用 timestamp 比使用 datetime 快一个小时,这一点是需要注意的,另外,timestamp 的最大取值也就到 2038 年的某有天,所以不建议存放比较久远的日期和时间。
3.year
year 主要是用来记录年份,当时间只需要记录年的时候,year 比 date 更节省空间,year 的范围为 1901-2155 年。
| mysql> create table t3 (y year); | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) | |
| mysql> desc t3; | |
| +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | | |
| +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| | y | year(4) | YES | | NULL | | | |
| +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | |
| 1 row in set (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> insert into t3 values(2017); | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> insert into t3 values(20); | |
| Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) | |
| mysql> select * from t3; | |
| +------+ | |
| | y | | |
| +------+ | |
| | 2017 | | |
| | 2020 | | |
| +------+ | |
| 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
| "00" ~ "69" 范围被转换成 2000 ~ 2069 年 | |
| "70" ~ "99" 范围被转换成 1970 ~ 1999 年 |
总结:在学习 MySQL 的时候,应该对数据类型的用途、占用空间、表示范围等都要有一定的了解,这样才能在实际运用中选择适合的数据类型,用较小的存储空间换来较高的数据库的性能。
参考书籍:《深入浅出 MySQL》,写的非常不错,推荐!
《深入浅出 MySQL》PDF 文字版(全)PDF 下载 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2016-05/130922.htm
本文永久更新链接地址:http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2017-09/146952.htm
















