共计 7045 个字符,预计需要花费 18 分钟才能阅读完成。
SpringBoot 集成 Redis 的三种方式:
- AutoConfig 加载
- 自己写代码加载
- xml 加载
使用这三种方式都需要:
1. 添加依赖
2. 写配置信息
spring.redis.database=0
spring.redis.host=localhost
spring.redis.port=6379
# 连接超时时间 单位 ms(毫秒)
spring.redis.timeout=3000
# 连接池中的最大空闲连接,默认值也是 8。
spring.redis.pool.max-idle=8
# 连接池中的最小空闲连接,默认值也是 0。
spring.redis.pool.min-idle=0
# 如果赋值为 -1,则表示不限制;如果 pool 已经分配了 maxActive 个 jedis 实例,则此时 pool 的状态为 exhausted(耗尽)。
spring.redis.pool.max-active=8
# 等待可用连接的最大时间,单位毫秒,默认值为 -1,表示永不超时。如果超过等待时间,则直接抛出 JedisConnectionException
spring.redis.pool.max-wait=-1
方式一:使用 Autoconfiguration 自动加载。
因为上面引入了 spring-boot-start-data-redis,所以可以使用 RedisAutoConfiguration 类加载 properties 文件的配置。
**
* Standard Redis configuration.
*/
@Configuration
protected static class RedisConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = “redisTemplate”)
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory)
throws UnknownHostException {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<Object, Object>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(StringRedisTemplate.class)
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory)
throws UnknownHostException {
StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
}
此种方式会默认加载 applicaiton 中的 redis 配置,提供了以下两种 bean
RedisTemplate<Object,Object> 可以对 Redis 中 key 和 value 都为 object 类型的数据进行操作, 默认会将对象使用 JdkSerializationRedisSerializer 进行序列化
StringRedisTemplate 可以对 Redis 中 key 和 value 都是 String 类型的数据进行操作。
方式二:自己写代码加载。
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig{
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Value(“${spring.redis.host}”)
private String host;
@Value(“${spring.redis.port}”)
private int port;
@Value(“${spring.redis.timeout}”)
private int timeout;
@Value(“${spring.redis.password}”)
private String password;
@Value(“${spring.redis.database}”)
private int database;
@Value(“${spring.redis.pool.max-idle}”)
private int maxIdle;
@Value(“${spring.redis.pool.min-idle}”)
private int minIdle;
/**
* redis 模板,存储关键字是字符串,值是 Jdk 序列化
* @Description:
* @param factory
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String,Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String,Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(factory);
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
//JdkSerializationRedisSerializer 序列化方式;
JdkSerializationRedisSerializer jdkRedisSerializer=new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer();
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jdkRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(jdkRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
}
方式三:使用 xml 加载。
在程序入口添加:
@ImportResource(locations={“classpath:spring-redis.xml”})
在 resource 文件夹下新建文件 spring-redis.xml
<beans xmlns=”http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans”
xmlns:xsi=”http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance” xmlns:cache=”http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache”
xmlns:context=”http://www.springframework.org/schema/context”
xsi:schemaLocation=”http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd”>
<bean id=”jedisPoolConfig” class=”redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig”>
<property name=”minIdle” value=”${redis.pool.minIdle}” />
<property name=”maxIdle” value=”${redis.pool.maxIdle}” />
<property name=”maxWaitMillis” value=”${redis.pool.maxWaitMillis}” />
</bean>
<bean id=”jedisConnectionFactory”
class=”org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory”>
<property name=”usePool” value=”true”></property>
<property name=”hostName” value=”${redis.ip}” />
<property name=”port” value=”${redis.port}” />
<property name=”password” value=”${redis.password}” />
<property name=”timeout” value=”${redis.timeout}” />
<property name=”database” value=”${redis.default.db}”></property>
<constructor-arg ref=”jedisPoolConfig” />
</bean>
<bean id=”redisTemplate” class=”org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate”>
<property name=”connectionFactory” ref=”jedisConnectionFactory” />
<property name=”KeySerializer”>
<bean
class=”org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer”></bean>
</property>
<property name=”ValueSerializer”>
<bean
class=”org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.JdkSerializationRedisSerializer”></bean>
</property>
<property name=”HashKeySerializer”>
<bean
class=”org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer”></bean>
</property>
<property name=”HashValueSerializer”>
<bean
class=”org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.JdkSerializationRedisSerializer”></bean>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
使用:
用注解注入 Template,直接调用就好了。
@Repository
public class RedisService {
@Autowired
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
public void add(String key, User user, Long time) {
Gson gson = new Gson();
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, gson.toJson(user), time, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}
public void add(String key, List<User> users, Long time) {
Gson gson = new Gson();
String src = gson.toJson(users);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, src, time, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}
public User get(String key) {
String source = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(source)) {
return new Gson().fromJson(source, User.class);
}
return null;
}
public List<User> getUserList(String key) {
String source = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(source)) {
return new Gson().fromJson(source, new TypeToken<List<User>>() {
}.getType());
}
return null;
}
public void delete(String key) {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().getOperations().delete(key);
}
}
���果是测试的话:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class RedisTest {
@Autowired
RedisService redisService;
@Before
public void setUp() {
}
@Test
public void get() {
User user = new User();
user.setName(“wangjianfeng”);
user.setAge(22);
redisService.add(“userByName:” + user.getName(), user, 10L);
List<User> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(user);
redisService.add(“list”, list, 10L);
User user1 = redisService.get(“userByName:wangjianfeng”);
Assert.notNull(user1, “user is null”);
List<User> list2 = redisService.getUserList(“list”);
Assert.notNull(list2, “list is null”);
}
}
SpringBoot 使用 Redis 缓存:
Springboot 提供了很多缓存管理器,比如:
- SimpleCacheManager
- EhCacheManager
- CaffeineCacheManager
- GuavaCacheManager
- CompositeCacheManager
SpringData 提供了缓存管理器:RedisCacheManager
在 SpringBoot 中,在程序入口,加上 @EnableCaching 注解自动化配置合适的管理器。
然后我们使用自己写代码配置的方式,修改 RedisConfig 添加 @EnableCaching 注解,并继承 CachingCongigurerSupport
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport{
…
}
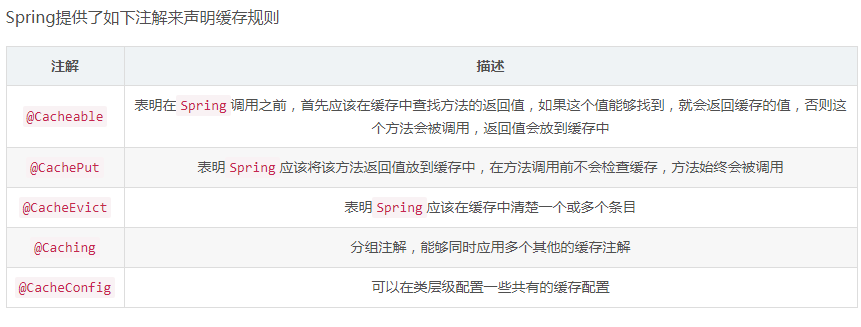
:
















