共计 5165 个字符,预计需要花费 13 分钟才能阅读完成。
一、连接 MySQL 数据库
作用:对数据库进行操作(SQL 语句)
说明:pymysql 是纯用 Python 操作 MySQL 的模块,其使用方法和 MySQLdb 几乎相同
安装:pip install pymysql
| # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- | |
| # 引入 pymysql | |
| import pymysql | |
| # 连接数据库 | |
| # 参数 1:mysql 服务器 IP | |
| # 参数 2:用户名 | |
| # 参数 3:用户密码 | |
| # 参数 4:要连接的数据库名 | |
| db = pymysql.connect("8.8.8.8", "zutuanxue_com", "zutuanxue_com2000", "db1", charset="utf8") | |
| # 创建 cursor 对象 | |
| cursor = db.cursor() | |
| # 执行 SQL 语句 | |
| cursor.execute("select version()") | |
| # 获取返回信息 | |
| data = cursor.fetchone() | |
| print(data) | |
| # 断开数据库连接 | |
| db.close() |
二、执行 SQL 语句
建表语句
| # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- | |
| import pymysql | |
| db = pymysql.connect("8.8.8.8", "zutuanxue_com", "zutuanxue_com2000", "db1", charset="utf8") | |
| cursor = db.cursor() | |
| # 建表之前首先判断表是否存在,存在则删除 | |
| sql1 = "drop table if exists students;" | |
| sql2 = "create table students(id int not null auto_increment primary key,name char(20),passwd char(20)) engine=innodb default charset=utf8;" | |
| cursor.execute(sql1) | |
| cursor.execute(sql2) | |
| cursor.close() | |
| db.close() |
新增语句
| # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- | |
| import pymysql | |
| db = pymysql.connect("8.8.8.8", "zutuanxue_com", "zutuanxue_com2000", "db1", charset="utf8") | |
| cursor = db.cursor() | |
| try: | |
| # 待执行的 SQL 语句 | |
| sql = "insert into students values(0,'lilei','111');" | |
| cursor.execute(sql) | |
| # 提交事物,真正写入数据库 | |
| db.commit() | |
| except: | |
| # 如果提交失败,回滚到上次提交的数据 | |
| db.rollback() | |
| cursor.close() | |
| db.close() |
修改语句
| # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- | |
| import pymysql | |
| db = pymysql.connect("8.8.8.8", "zutuanxue_com", "zutuanxue_com2000", "db1", charset="utf8") | |
| cursor = db.cursor() | |
| try: | |
| sql = "update students set name='li'where id=1" | |
| cursor.execute(sql) | |
| db.commit() | |
| print("------------", cursor.rowcount) | |
| except: | |
| db.rollback() | |
| cursor.close() | |
| db.close() |
删除语句
| # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- | |
| import pymysql | |
| db = pymysql.connect("8.8.8.8", "zutuanxue_com", "zutuanxue_com2000", "db1", charset="utf8") | |
| cursor = db.cursor() | |
| try: | |
| sql = "delete from students where id=1;" | |
| cursor.execute(sql) | |
| db.commit() | |
| except: | |
| db.rollback() | |
| cursor.close() | |
| db.close() |
查询语句
| 方法与属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| fetchone() | 获取下一个查询结果集,结果集是一个对象 |
| fetchall() | 接收全部的返回结果 |
| rowcount | 是一个只读属性,返回执行 execute() 方法后影响的行数 |
| # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- | |
| import pymysql | |
| db = pymysql.connect("8.8.8.8", "zutuanxue_com", "zutuanxue_com2000", "db1", charset="utf8") | |
| # cursor = db.cursor() | |
| # 以字典形式显示 | |
| cursor = db.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) | |
| try: | |
| sql = "select * from students where id>=4;" | |
| cursor.execute(sql) | |
| # 获取所有数据列表 | |
| # reslist = cursor.fetchall() | |
| # print(reslist) | |
| # for row in reslist: | |
| # print(row, type(row)) | |
| # print(cursor.fetchone()) | |
| # print(cursor.fetchone()) | |
| # print(cursor.fetchone()) | |
| for i in range(cursor.rowcount): | |
| res = cursor.fetchone() | |
| print(res) | |
| except: | |
| print("查询有误") | |
| cursor.close() | |
| db.close() |
三、防止 SQL 注入
SQL 注入是一种注入攻击,可以执行恶意 SQL 语句。它通过将任意 SQL 代码插入数据库查询,使攻击者能够完全控制 Web 应用程序后面的数据库服务器。攻击者可以使用 SQL 注入漏洞绕过应用程序安全措施;可以绕过网页或 Web 应用程序的身份验证和授权,并检索整个 SQL 数据库的内容;还可以使用 SQL 注入来添加,修改和删除数据库中的记录
SQL 注入漏洞可能会影响使用 SQL 数据库(如 MySQL,Oracle,SQL Server 或其他)的任何网站或 Web 应用程序。犯罪分子可能会利用它来未经授权访问用户的敏感数据:客户信息,个人数据,商业机密,知识产权等。SQL 注入攻击是最古老,最流行,最危险的 Web 应用程序漏洞之一
如何防止 SQL 注入攻击?
-
不要使用动态 SQL
避免将用户提供的输入直接放入 SQL 语句中;最好使用准备好的语句和参数化查询,这样更安全
-
不要将敏感数据保留在纯文本中
加密存储在数据库中的私有 / 机密数据;这样可以提供了另一级保护,以防攻击者成功地排出敏感数据
-
限制数据库权限和特权
将数据库用户的功能设置为最低要求;这将限制攻击者在设法获取访问权限时可以执行的操作
-
避免直接向用户显示数据库错误
攻击者可以使用这些错误消息来获取有关数据库的信息
-
对访问数据库的 Web 应用程序使用 Web 应用程序防火墙(WAF)
这为面向 Web 的应用程序提供了保护,它可以帮助识别 SQL 注入尝试;根据设置,它还可以帮助防止 SQL 注入尝试到达应用程序(以及数据库)
-
定期测试与数据库交互的 Web 应用程序
这样做可以帮助捕获可能允许 SQL 注入的新错误或回归
-
将数据库更新为最新的可用修补程序
这可以防止攻击者利用旧版本中存在的已知弱点 / 错误
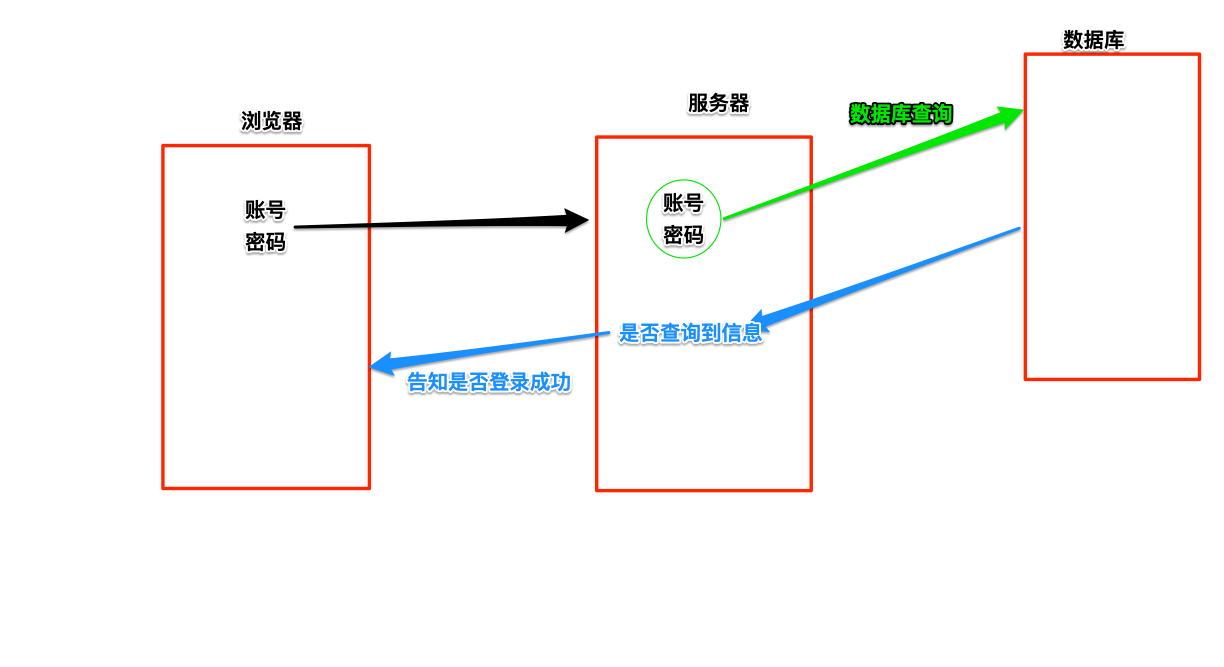
| # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- | |
| import pymysql | |
| name = input("账号:") | |
| passwd = input("密码:") | |
| db = pymysql.connect("8.8.8.8", "zutuanxue_com", "zutuanxue_com2000", "db1", charset="utf8") | |
| cursor = db.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) | |
| try: | |
| sql = "select * from students where name='%s'and passwd='%s';" % (name, passwd) | |
| print("sql 语句:", sql) | |
| cursor.execute(sql) | |
| res = cursor.fetchall() | |
| if res: | |
| print("登陆成功", res) | |
| else: | |
| print("登陆失败") | |
| except: | |
| print("查询有误") | |
| cursor.close() | |
| db.close() |
| SQL 注入代码 | 注意 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
li' -- |
-- 后有一个空格 |
用户存在,但是密码错误也查找成功 |
abc' or 1=1 -- |
-- 后有一个空格 |
用户不存在,但是能查找出所有用户 |
select * from students where name='li' -- 'and passwd='qwe';
select * from students where name='abc' or 1=1 -- 'and passwd='sfeg';
防注入代码书写
-
方式 1
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import pymysql name = input("账号:") passwd = input("密码:") db = pymysql.connect("8.8.8.8", "zutuanxue_com", "zutuanxue_com2000", "db1", charset="utf8") cursor = db.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) try: sql = "select * from students where name=%s and passwd=%s;" cursor.execute(sql, [name, passwd]) res = cursor.fetchall() if res: print("登陆成功", res) else: print("登陆失败") except: print("查询有误") cursor.close() db.close() -
方式 2
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import pymysql name = input("账号:") passwd = input("密码:") db = pymysql.connect("8.8.8.8", "zutuanxue_com", "zutuanxue_com2000", "db1", charset="utf8") cursor = db.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) try: sql = "select * from students where name=%(name)s and passwd=%(passwd)s;" cursor.execute(sql, {"name":name, "passwd":passwd}) res = cursor.fetchall() if res: print("登陆成功", res) else: print("登陆失败") except: print("查询有误") cursor.close() db.close()
四、增加多条数据
| # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- | |
| import pymysql | |
| db = pymysql.connect("8.8.8.8", "zutuanxue_com", "zutuanxue_com2000", "db1", charset="utf8") | |
| cursor = db.cursor() | |
| try: | |
| # 待执行的 SQL 语句 | |
| sql = "insert into students(name,passwd) values(%s,%s);" | |
| cursor.executemany(sql, [("aaa","a"),("bbb","b"),("ccc","c")]) | |
| db.commit() | |
| except: | |
| db.rollback() | |
| cursor.close() | |
| db.close() |
五、新插入数据的自增 ID

需求:在插入一篇文章后需要给文章插入它需要的图片到媒体表,那么在此时就需要这篇文章的 id 值作为外键来使用,需要提取出刚刚插入的文章的自增 id 值
| # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- | |
| import pymysql | |
| db = pymysql.connect("8.8.8.8", "zutuanxue_com", "zutuanxue_com2000", "db1", charset="utf8") | |
| cursor = db.cursor() | |
| try: | |
| # 待执行的 SQL 语句 | |
| sql = "insert into articles(title) values(%s);" | |
| cursor.executemany(sql, ["zutuanxue_com"]) | |
| # 插入对应的媒体需要得到刚才插入的文章的 id 号 | |
| print("------", cursor.lastrowid) | |
| db.commit() | |
| except: | |
| db.rollback() | |
| cursor.close() | |
| db.close() |
















