共计 3681 个字符,预计需要花费 10 分钟才能阅读完成。
1、String 概述
1.1、什么是 String 类
String 类用于比较两个字符串,查找和抽取串中的字符或子串、字符串与其他类型之间相互转换等。String 类是一个常量对象,String 类对象的内容一旦被初始化就不能再被改变。
1.2、String 构造方法
public String():创建一个字符串对象,其字符串值为空。
public String (String value):用字符串对象 value 创建一个新的字符串对象。
public String (char[] value):用字符数组 value 来创建字符串对象。
public String (char[]value,int offset,int count):从字符数组 value 中下标为 offset 的字符开始,创建有 count 个字符的字符串对象()
public String(byte ascII[]):用 byte 型字符串数组 ascII,按缺省的字符编码方案创建字符串对象。
public String(byte ascII[],int offset int count)):从字节型数组 ascII 中下标为 offset 的字符开始,按缺省的字符编码方案创建 count 个字符的串对象。
public String(StringBuffer buffer):用缓冲字符串 buffer 创建一个字符串对象。
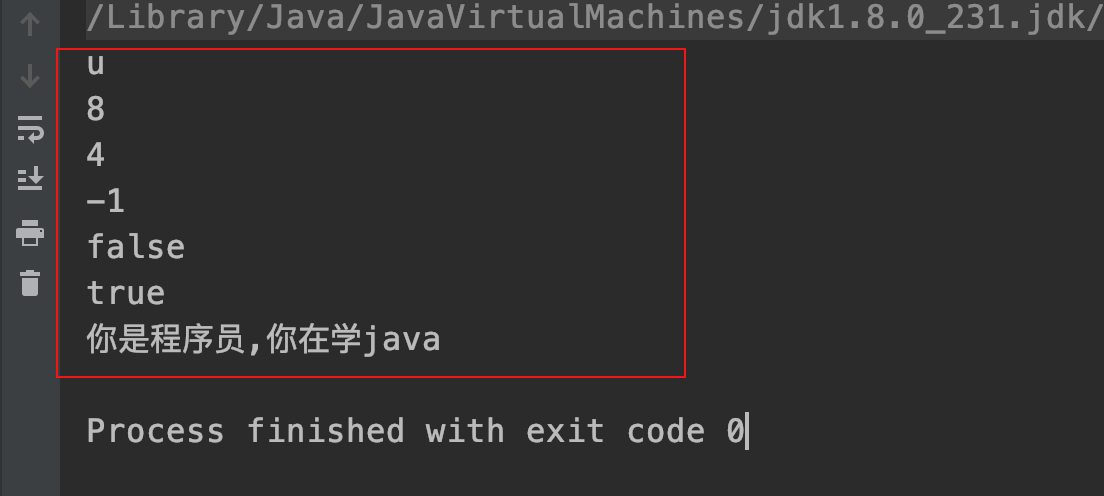
| public class StringDemo01{public static void main(String args[]){String s1="hello"; | |
| String s2="world"; | |
| String s3="hello"; | |
| // 按值比较 | |
| System.out.println(s1==s3); | |
| s1=new String ("hello"); | |
| s2=new String ("hello"); | |
| // 按地址比较 | |
| System.out.println(s1==s2); | |
| // 按值比较 | |
| System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); | |
| char c[]={'s','u','n','','j','a','v','a'}; | |
| // 将一个字符数组,转化为一个字符串 | |
| String s4=new String(c); | |
| // 从下标为 3 的字符开始(包含下标为 3 的位置)取 4 个字符 | |
| String s5=new String(c,3,4); | |
| System.out.println(s4); | |
| System.out.println(s5); | |
| } | |
| } |
运行结果:
2、常用方法
2.1、常用方法 1
public char charAt(int index):返回字符串中第 index 个字符。
public int length():返回字符串的长度。
public int indexOf(String str):返回字符串中出现 str 的第一个下标位置。
public int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex):返回字符串中从 fromIndex 开始出现 str 的第一个位置。
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String another):比较字符串是否与 another 一样。
public String replace(char oldChar,char newChar):字符串中用 newchar 替代 oldChar 字符。
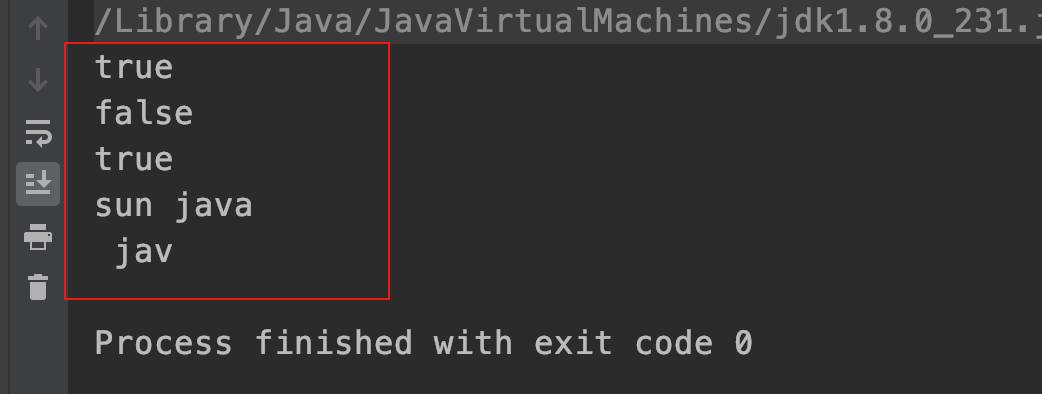
| public class StringDemo02{public static void main(String args[]){String s1="sun java"; | |
| String s2="sun Java"; | |
| // 取出指定下标位置的字符 | |
| System.out.println(s1.charAt(1)); | |
| // 取出字符串长度 | |
| System.out.println(s2.length()); | |
| // 返回字符串中出现 java 的第一个下标位置 | |
| System.out.println(s1.indexOf("java")); | |
| System.out.println(s1.indexOf("Java")); | |
| // 比较二个字符串是否相同,区分大小写 | |
| System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); | |
| // 比较二个字符串是否相同,不区分大小写 | |
| System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2)); | |
| String s="我是程序员, 我在学 java"; | |
| // 将字符串中的我,替换成你 | |
| String sr=s.replace('我','你'); | |
| System.out.println(sr); | |
| } | |
| } |
运行结果:
2.2、常用方法 2
public boolean startsWith(String prefix):判断字符串是否以 prefix 字符串开头。
public boolean endsWith(String suffix):判断字符串是否以 suffix 字符结尾。
public String toUpperCase():返回一个字符串为该字符串的大写形式。
public String toLowerCase():返回一个字符串为该字符串的小写形式。
public String substring(int beginIndex):返回字符串从 beginIndex 开始到结尾的子字符串。
public String substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex):返回字符串从 beginIndex 开始到 endIndex 结尾的子字符串。
public String trim():返回将该字符串去掉开头和结尾空格后的字符串。
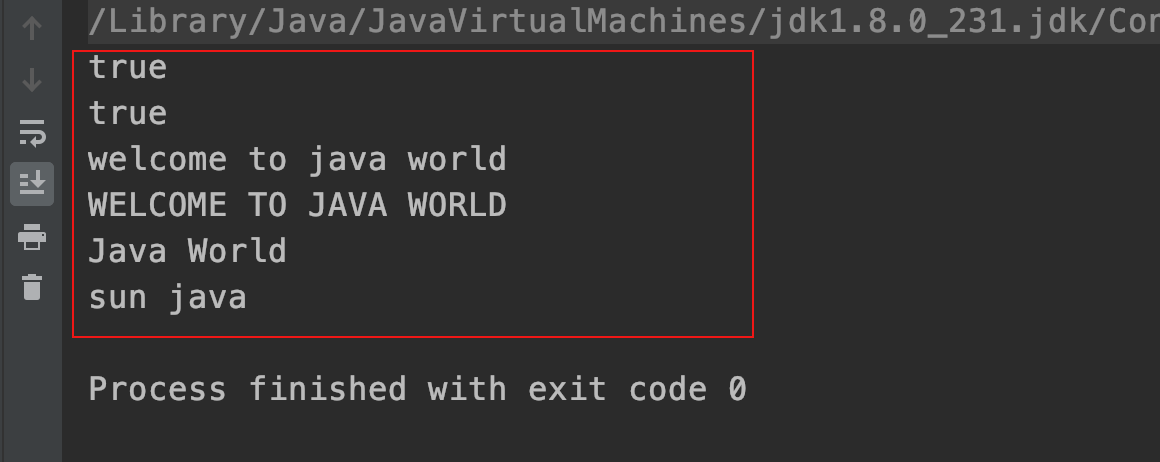
| public class StringDemo03 {public static void main(String args[]){String s="Welcome to Java World"; | |
| String s1="sun java"; | |
| // 判断字符串是否以 Welcome 开始 | |
| System.out.println(s.startsWith("Welcome")); | |
| // 判断字符串是否以 World 结束 | |
| System.out.println(s.endsWith("World")); | |
| // 把字符串全部转换为小写 | |
| String sL=s.toLowerCase(); | |
| // 把字符串全部转换为大写 | |
| String sU=s.toUpperCase(); | |
| System.out.println(sL); | |
| System.out.println(sU); | |
| // 返回从下标 11 开始到结尾的字符串 | |
| String subS=s.substring(11); | |
| System.out.println(subS); | |
| // 去掉字符串头、尾的空格 | |
| String sp=s1.trim(); | |
| System.out.println(sp); | |
| } | |
| } |
运行结果:
2.3、常用方法 3
public static String valueOf(…) 可以将基本类型数据转换为字符串
例如:
public static String valueOf(double d)
public static String valueOf(int i)
…
public String []split(String regex): 可以将一个字符串按照指定的分隔符分隔,返回分隔后的字符串数组。
| public class StringDemo04 {public static void main(String args[]){int j=1234567; | |
| // 将 int 类型,转换成 String 类型 | |
| String sNumber=String.valueOf(j); | |
| System.out.println("j 是"+sNumber.length()+"位数。"); | |
| String s ="Mary,F,1976"; | |
| // 以, 号分隔,将字符串拆分为字符数组 | |
| String sPlit[] =s.split(","); | |
| for(int i=0;i<sPlit.length;i++){System.out.println(sPlit[i]); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
运行结果:

2.4、常用方法 4
concat(String str):把字符串 str 附加在当前字符串的末尾。
如:
| String str="Hello"; | |
| String newStr=str.concat("World"); | |
| System.out.println(str); // 打印 Hello | |
| System.out.println(newStr); // 打印 HelloWorld |
注意:以上 concat() 方法并不会改变字符串 str 本身的内容。
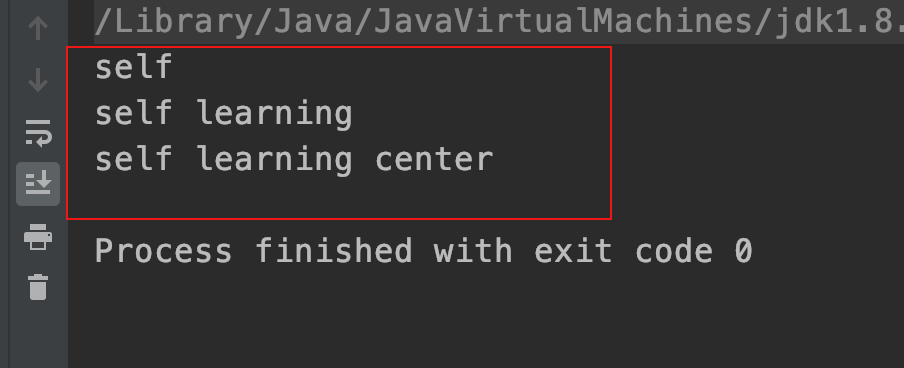
| public class StringDemo05 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 打印 str1 | |
| String str1 = "self"; | |
| System.out.println(str1); | |
| // 打印 str2 连接了 str1 | |
| String str2 = str1.concat("learning"); | |
| System.out.println(str2); | |
| // 打印 str3 连接了 str2 | |
| String str3 = str2.concat("center"); | |
| System.out.println(str3); | |
| } | |
| } |
运行结果: