共计 2876 个字符,预计需要花费 8 分钟才能阅读完成。
数据控制语言 (Data Control Language) 在 SQL 语言中,是一种可对数据访问权进行控制的指令,它可以控制特定用户账户对数据表、查看表、存储程序、用户自定义函数等数据库对象的控制权。由 GRANT 和 REVOKE 两个指令组成。
一、DCL 概述
1.1、什么是 DCL
DCL 语句主要是 DBA 用来管理系统中的对象权限时所使用,一般的开发人员很少使用。
DCL 中主要包括创建用户、给用户授权、对用户撤销授权、查询用户授权和删除用户等操作。
1.2、为什么学习 DCL
在一个企业里面的数据库服务器上面可能同时运行着很多个项目的数据库。所以,我们应该可以根据不同的项目建立不同的用户,分配不同的权限来管理和维护数据库。
二、用户管理
mysql 数据库的用户都在 mysql 数据库下面的 user 表中
2.1、查看用户
格式:select * from user;
案例:
| mysql> select * from user; | |
| mysql> select user,host,plugin,authentication_string from user; |

2.2、创建用户
格式:create user '用户名'@'主机名' identified by '密码';
注意:
用户名: 新用户的名字
主机名: 指定该用户在哪个主机上可以登陆,如果是本地用户可用 localhost,如果想让该用户可以从任意远程主机登陆,可以使用通配符 %
密码: 密码可以为空,如果为空则该用户可以不需要密码登陆服务器
案例:
创建一个用户 root1,只能在本机登录(localhost)
| mysql> create user 'root1'@'localhost' identified by '123'; | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 秒) | |
| mysql> select user,host,plugin,authentication_string from user; |
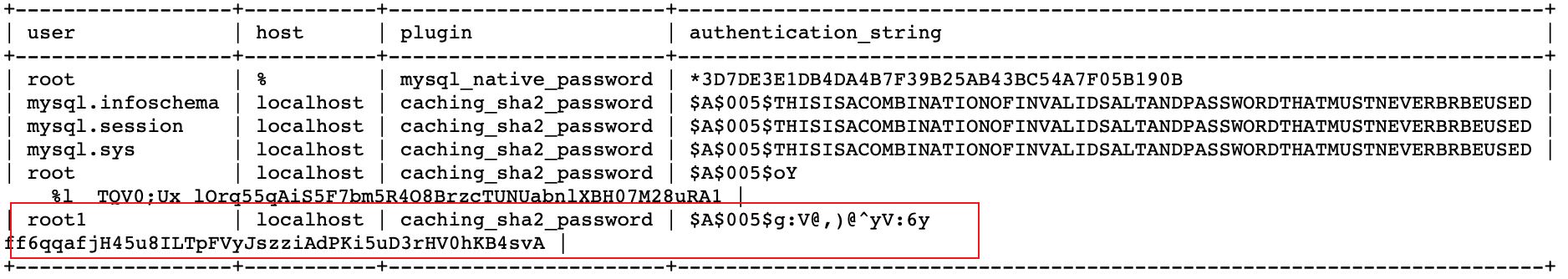
创建一个用户 root2,可以在任何主机(%)登录
| mysql> create user 'root2'@'%' identified by '123'; | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 秒) | |
| mysql> select user,host,plugin,authentication_string from user; |
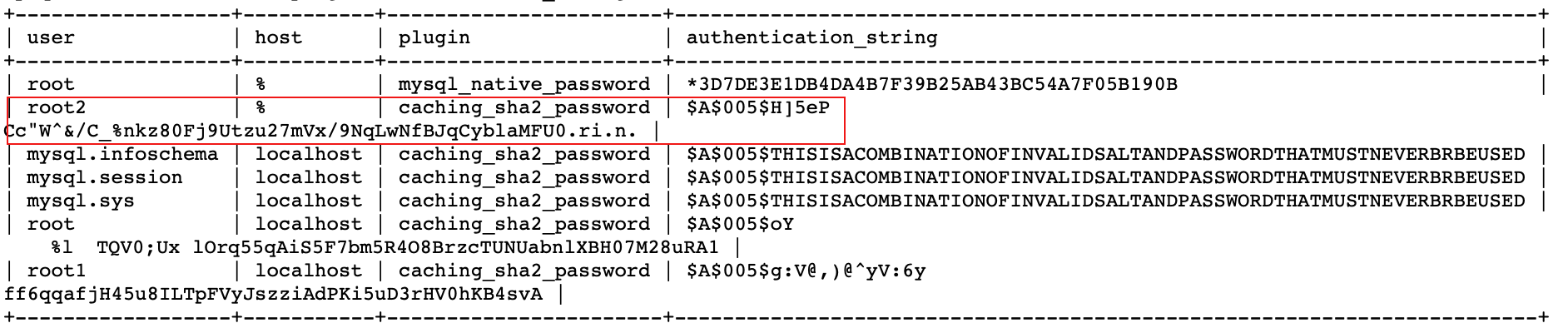
注意:
指定加密方式,增加用户
| mysql> create user 'root3'@'%' identified with mysql_native_password by '123'; | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 秒) | |
| mysql> select user,host,plugin,authentication_string from user; |

2.3、删除用户
drop user '用户名'@'主机名';
案例:
删除 root1
| mysql> drop user root1@localhost; | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 秒) | |
| mysql> select user,host,plugin,authentication_string from user; |
三、密码管理
3.1、修改用户密码
格式:alter user '用户名'@'主机名' identified by '密码';
案例:
修改 root2 的密码
| mysql> alter user 'root2'@'%' identified by '456'; | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 秒) |
注意:
如果想用该 root2 用户连接上 mysql 服务端的话,我们的密码修改时应该是:
| mysql> alter user 'root2'@'%' identified with mysql_native_password by '456'; | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 秒) |
3.2、设置管理员(root)密码
清空密码
| use mysql; | |
| update user set authentication_string=''where user='root';# 设置提 root 用户的密码为‘’,本地,远程 |
设置密码
| alter user 'root'@'%' identified by 'Root12345'; | |
| alter user 'root'@'localhost' identified by 'Root12345'; |
四、权限管理
4.1、查看用户权限
格式:show grants for '用户名'@'主机名';
案例:
查看’root2’,’root3’及’root’权限
| mysql> show grants for 'root2'@'%'; | |
| +-----------------------------------+ | |
| | Grants for root2@% | | |
| +-----------------------------------+ | |
| | GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO `root2`@`%` | | |
| +-----------------------------------+ | |
| 1 行于数据集 (0.01 秒) | |
| mysql> show grants for 'root3'@'%'; | |
| +-----------------------------------+ | |
| | Grants for root3@% | | |
| +-----------------------------------+ | |
| | GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO `root3`@`%` | | |
| +-----------------------------------+ | |
| 1 行于数据集 (0.02 秒) | |
| mysql> show grants for 'root'@'%' |
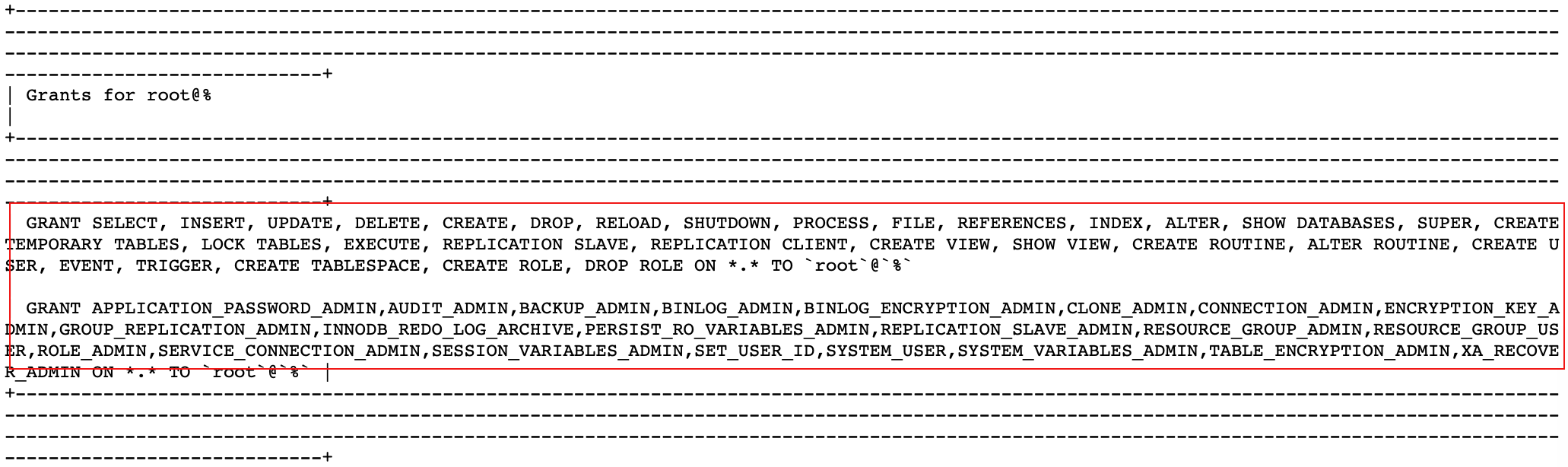
4.2、授权
格式:grant 权限 1, 权限 2... on 数据库名. 表名 to '用户名'@'主机名';
注意:
**grant… on …to:** 授权关键字
权限: 如 select\insert\update\delete 等,如果是所有用 all
数据库名. 表名: 该用户可以操作哪个数据库的哪些表。如果要授予该用户对所有数据库和表的相应操作权限则可用 * 表示,如 *.*
’用户名’@‘主机名’: 注意单引号不能省略
案例:
给’root2’分配,增加、删除、修改、查询表的权限
mysql> grant insert,delete,update,select on zutuanxue.* to 'root2'@'%';
给’root3’分配所有权限
mysql> grant all on *.* to 'root3'@'%';
4.3、撤销授权
格式:revoke 权限 1, 权限 2... on 数据库名. 表名 from '用户名'@'主机名';
注意:
revoke… on …from: 撤消授权关键字
权限: 如 select\insert\update\delete 等,如果是所有用 all
数据库名. 表名: 该用户可以操作哪个数据库的哪些表。如果要撤消授予该用户对所有数据库和表的相应操作权限则可用 * 表示,如 *.*
’用户名’@‘主机名’: 注意单引号不能省略
案例:
撤消’root2’的权限
| mysql> revoke all on zutuanxue.* from 'root2'@'%'; | |
| Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) |















