共计 8937 个字符,预计需要花费 23 分钟才能阅读完成。
Nginx 从入门到放弃 02-Nginx 基本命令和新建 WEB 站点
通过上一篇文章我们知道了的一些基础知识还有在 centos7 上安装 nginx,yum 源或者通过编译,但是通过两种方式安装后的 nginx 的目录结构略有不同,默认提供的资源与配置略有不同,我们暂且先以编译安装的方式进行介绍。
笔者把自己总结的文档分为几遍,合集在 https://g.xgss.net/nginx/

一、Nginx 的常用命令
查看 nginx 编译过后的目录结构:
# ll /data/nginx
total 0
drwx------ 2 nobody root 6 Jun 23 11:16 client_body_temp
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 333 Jun 23 13:20 conf # 存放了 nginx 相关的配置文件
drwx------ 2 nobody root 6 Jun 23 11:16 fastcgi_temp
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 40 Jun 23 11:15 html # 默认提供的 web 服务的”根目录”
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 58 Jun 23 13:31 logs # logs 目录是 nginx 日志的存放目录
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 135 Jun 23 11:15 modules # 存放了一些模块会用到的库
drwx------ 2 nobody root 6 Jun 23 11:16 proxy_temp
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 19 Jun 23 11:15 sbin # 存放了 nginx 的二进制文件
drwx------ 2 nobody root 6 Jun 23 11:16 scgi_temp
drwx------ 2 nobody root 6 Jun 23 11:16 uwsgi_temp
nginx path prefix:“/data/nginx”
nginx binary file:“/data/nginx/sbin/nginx”
nginx modules path:“/data/nginx/modules”
nginx configuration prefix:“/data/nginx/conf”
nginx configuration file:“/data/nginx/conf/nginx.conf”
nginx pid file:“/data/nginx/logs/nginx.pid”
nginx error log file:“/data/nginx/logs/error.log”
nginx http access log file:“/data/nginx/logs/access.log”常用命令
1. 启动 nginx
/data/nginx/sbin/nginx2. 获取帮助
/data/nginx/sbin/nginx-h/data/nginx/sbin/nginx-?
例如:
#/data/nginx/sbin/nginx-?
nginx version: nginx/1.22.0
Usage: nginx [-?hvVtTq] [-s signal] [-p prefix]
[-e filename] [-c filename] [-g directives]
Options:
-?,-h : this help
-v : show version and exit
-V : show version and configure options then exit
-t : test configuration and exit
-T : test configuration, dump it and exit
-q : suppress non-error messages during configuration testing
-s signal : send signal to a master process: stop, quit, reopen, reload
-p prefix : set prefix path (default: /data/nginx/)
-e filename : set error log file (default: logs/error.log)
-c filename : set configuration file (default: conf/nginx.conf)
-g directives : set global directives out of configuration file
3. 查看 nginx 版本
使用”-v”选项 (小写 v) 可以查看 nginx 的版本信。
使用”-V”选项 (大写 V) 可以查看当前 nginx 的编译信息。
/data/nginx/sbin/nginx-V/data/nginx/sbin/nginx-v
例如
#/data/nginx/sbin/nginx-V
nginx version: nginx/1.22.0
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-36) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
TLS SNI support enabled
configure arguments: --prefix=/data/nginx --with-file-aio --with-http_auth_request_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_addition_module --with-http_xslt_module=dynamic --with-http_geoip_module=dynamic --with-http_sub_module --with-http_dav_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_mp4_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_random_index_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_degradation_module --with-http_slice_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_perl_module=dynamic --with-pcre --with-pcre-jit --with-stream=dynamic --with-stream_ssl_module
[root@node3 nginx]#/data/nginx/sbin/nginx-v
nginx version: nginx/1.22.0
3. 检查配置文件是否错误
这个命令是非常有用的,在修改配置之后查看自己是否配置成功,如果有错误,而未修改重启 nginx 可能会出现 nginx 无法服务的问题。
#/data/nginx/sbin/nginx-t
nginx: the configuration file /data/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /data/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
#/data/nginx/sbin/nginx-T 测试配置, 显示并退出
4. 重载、关闭 nginx
”-s”选项的作用就是向正在运行的 nginx 进程发送信号,信号的可用值有 stop, quit, reopen, reload
/data/nginx/sbin/nginx-s stop/data/nginx/sbin/nginx-s reload
pkill nginx #杀死 nginx/data/nginx/sbin/nginx-s start # 错误的命令
”/data/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop”命令表示向 nginx 进程发送 stop 信号,“-s reload”重载配置文件。
quit 信号:与 stop 信号的作用类似,quit 信号作用也是用于停止 nginx 服务,quit 信号和 stop 信号的区别在于,nignx 进程收到 stop 信号以后会立即停止服务,而收到 quit 信号后,不会再接收新的请求,但是会先处理完已经接受的链接请求,处理完这些请求之后再停止服务,这种停止方式被称之为”优雅的停止”。reload 信号:reload 信号的作用就是在不停止服务的情况下重载配置文件,比如,nginx 正在正常的提供服务,此时,管理员修改了 nginx.conf 文件中的配置指令,管理员希望新的配置立刻生效,但是又不希望重启 nginx 服务,此时就可以使用”nginx -s reload”命令重载配置文件,以便在不重启 nginx 的情况下载入新的配置,同时避免了因重启而造成的服务中断。reopen 信号:利用 reopen 信号可以使 nignx 进程重新打开日志文件,以便实现日志分割的效果,关于日志切割的话题会单独总结一片文章,reopen 信号也会在届时进行演示,此处不用纠结。二、Nginx 配置一个 WEB 站点
启动 nginx 之后,通过浏览器访问 IP,我们可以访问默认的 HTTP 服务。
虚拟主机 就是把一台物理服务器划分成多个“虚拟”的服务器,每一个虚拟主机都可以有独立的域名和独立的目录,可以独立发布一个网站。
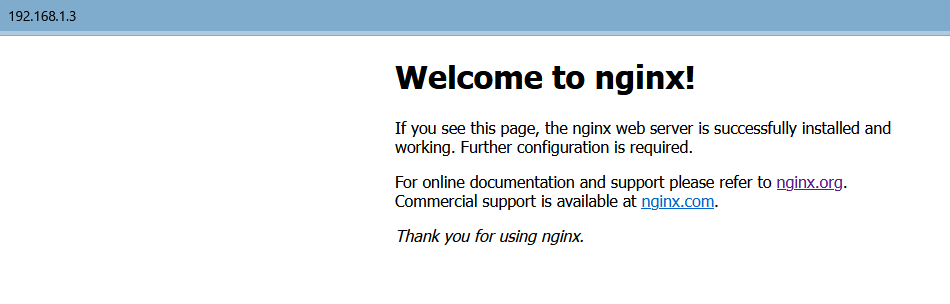
默认的首页为 /data/nginx/html/index.html
# ll /data/nginx/html/
total 8
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 497 Jun 23 11:15 50x.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 615 Jun 23 11:15 index.html默认情况下,nginx.conf 文件中会有很多注释的行,我们把注释去掉
# sed -i '/^[[:space:]]*#/'d conf/nginx.conf
# cat conf/nginx.conf
worker_processes 1;
events {worker_connections 1024;}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {root html;}
}
}先来说说最常用到的配置语法,示例如下:
http {
...
...
server {
...
...
location ... {
...
...
}
}
server {
...
...
}
}从上述语法配置示例可以看出,上述示例可以分为几个逻辑部分,http 部分、server 部分、location 部分,每个”配置块”都是使用大括号”{}”作为分界线的,而且,从缩进可以看出,它们是有层级关系的,http 中可以配置多个 server,一个 server 中可以配置多个 location,我们知道,nginx 最基础的功能就是用来提供 http 服务,所以,跟 http 有关的公共配置,可以放置在 http 块中,http 块中又可以配置多个 server,那么 server 代表了什么呢?我们在一台主机中安装了 nginx,那么能不能让这台 nginx 主机同时提供多个 web 服务呢?答案是肯定的,每一个 server 就代表一个 http 服务,我们可以同时配置多个 server,以便同时提供多个 http 服务,不同的 server 可以使用不同的配置,写入到某个 server 块中的配置只对对应的 http 服务生效,如果多个 server 存在共同的公用配置,则可以将共同的配置写在 http 块中,以便多个 server 共享这些配置,一个 server 块中又可以有一个或多个 location,location 又是什么意思呢?当我们访问一个网络上的资源时,都是通过 url 访问的,你可以把 location 当做 url 的一部分。
笔者的 nginx 配置
vim /data/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
填写以下配置:#user nobody;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /data/wwwroot/log/nginx_error.log crit;
# 用来指定进程 id 的存储文件位置
#pid /var/run/nginx.pid; # yum 安装的 pid
pid logs/nginx.pid;
# 用于绑定 worker 进程和 CPU,该值必须和 Linux 内核打开文件数关联起来,如将该值设置为 65535 就必须在 Linux 命令行中执行 ulimit -HSn 65535
worker_rlimit_nofile 65535;
events {
use epoll;
worker_connections 65535;
multi_accept on;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local]"$request"''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent""$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /data/wwwroot/log/nginx_access.log main;
#获取真实 IP 地址
map $http_x_forwarded_for $clientRealIp {
"" $remote_addr;
~^(?P<firstAddr>[0-9\.]+),?.*$ $firstAddr;
}
### 自定义访问日志类型
#log_format main_aliyun '$clientRealIp - $remote_user [$time_local]"$request"$status $body_bytes_sent"$http_referer""$http_user_agent" "$request_time"';
#log_format main_zdy '$request_time IP:$http_x_forwarded_for - RealIP:$clientRealIp - [$time_local] $request - $status - $http_user_agent - $host - from:$http_referer - POST:$request_body - COOKIE:$http_cookie';
log_format main_aliyun '$clientRealIp - $remote_user [$time_local]"$request"$status $body_bytes_sent"$http_referer""$http_user_agent" "$request_time"';
log_format main_zdy '$clientRealIp - $remote_user [$time_local]"$request"$status $body_bytes_sent"$http_referer""$http_user_agent" "$request_time"';
# 是否开启高效文件传输模式,将 tcp_nopush 和 tcp_nodelay 两个指令设置为 on 用于防止网络阻塞
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
# 隐藏 nginx 的版本显示,增强安全性
server_tokens off;
# 用于设置客户端连接保持活动的超时时间,单位为秒,默认为 75s
keepalive_timeout 30;
# 用于指定响应客户端的超时时间,这个超时仅限于两个连接活动之间的时间,默认为 60s
send_timeout 30;
# 下面是 FastCGI 的优化指令
# 连接到后端 FastCGI 的超时时间
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
# 向 FastCGI 传送请求的超时时间
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
# 接收 FastCGI 应答的超时时间
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
# 指定读取 FastCGI 应答第一部分需要多大的缓冲区
fastcgi_buffer_size 64k;
fastcgi_buffers 4 64k;
# 默认值是 fastcgi_buffers 的两倍
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 128k;
# 表示在写入缓存文件时使用多大的数据块,默认为 fastcgi_buffers 的两倍
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 128k;
# 为 FastCGI 缓存指定一个文件路径、目录结构等级、关键字区域存储时间和非活动删除时间
#fastcgi_cache_path /usr/local/nginx/fastcgi_cache levels=1:2 keys_zone=TEST:10m inactive=5m;
# 开启 FastCGI 缓存并为其设定一个名称。开启缓存可以有效降低 CPU 的负载,并且防止 502 错误的发生。# 但是同时也会引起很多问题,要视具体情况而定
#fastcgi_cache TEST;
# 用来指定应答代码的缓存时间,下面三条指令表示将 200 和 303 应答缓存 1 小时,301 应答缓存 1 天,其他应答缓存 1 分钟。#fastcgi_cache_valid 200 302 1h;
#fastcgi_cache_valid 301 1d;
#fastcgi_cache_valid any 1m;
# 配置 Nginx 的 HttpGzip 模块,开通的前提是安装的时候启用了该模块,使用 /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -V 来查看安装的信息(大写的 V)# 是否开通 gzip
gzip on;
# 允许压缩的页面最小字节数
gzip_min_length 1k;
gzip_buffers 4 16k;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
# 压缩比,从 1 到 9,越大压缩率越高但越占资源,默认为 1
gzip_comp_level 4;
# 指定压缩的类型,text/html 总是被压缩
gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css application/xml;
# 是否让浏览器缓存压缩过的数据,默认为 off
gzip_vary on;
client_max_body_size 20m;
proxy_buffer_size 128k;
proxy_buffers 32 32k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 128k;
# server 用于对虚拟主机的设置,建议每个站点的设置放到外部配置文件中,然后使用 include 进行引用
# 这里设置一个默认的主机,当默认访问的时候返回 403 错误
server {
listen 80 default;
server_name _;
# 也可以修改成 404 或者 500,根据自身情况进行设置
return 403;
}
include /data/conf/sites-available/nginx_*;
}每次只需要在 /data/conf/sites-available/ 新增 nginx_web01.conf 文件即可
# vim /data/conf/sites-available/nginx_web01.conf
添加
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.nginx01.com;
root /data/wwwroot/web/www.nginx01.com/;
access_log /data/wwwroot/log/www.nginx01.com-access.log main_aliyun;
error_log /dev/null;
location / {index index.html index.htm index.php;}
}
# mkdir -p /data/wwwroot/web/www.nginx01.com/
# echo 'hello nginx!' > /data/wwwroot/web/www.nginx01.com/index.html
# /data/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
在客户端的 hosts 文件中添加
192.168.1.3 www.nginx01.com
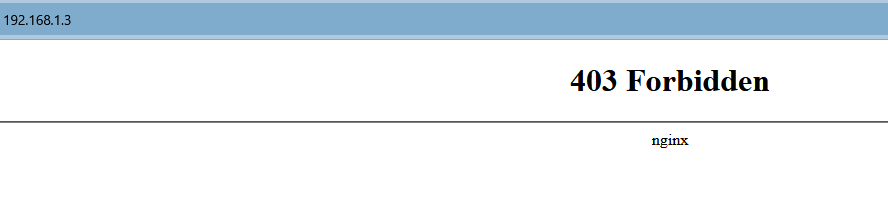
默认站点(通过 IP 访问)访问为 403,如果要修改则修改以下配置。
server {
listen 80 default;
server_name _;
# 也可以修改成 404 或者 500,根据自身情况进行设置
return 403;
}
访问 www.nginx01.com 站点

服务器查看 nginx 日志:
cat /data/wwwroot/log/www.nginx01.com-access.log
192.168.1.164 - - [23/Jun/2022:15:24:55 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 13 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:101.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/101.0" "0.000"
192.168.1.164 - - [23/Jun/2022:15:24:55 +0800] "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 146 "http://www.nginx01.com/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:101.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/101.0" "0.000"至此 配置一个 WEB 站点成功,下一篇文章来讲解 nginx 的调优和常用配置。
















