共计 8158 个字符,预计需要花费 21 分钟才能阅读完成。
生命周期概念
Vue 的生命周期就是 vue 实例从创建到销毁的全过程,也就是 new Vue() 开始就是 vue 生命周期的开始。Vue 实例有⼀个完整的⽣命周期,也就是 从开始创建、初始化数据、编译模版、挂载 Dom-> 渲染、更新 -> 渲染、卸载 等⼀系列过程,称这是 Vue 的⽣命周期。钩子函数是 Vue 生命周期中每个阶段对外开放让程序员操作 Vue 的接口。Vue 有 8 个钩子函数。
每个 vue 实例从创建到销毁的过程都是一个生命周期,也会运行对应的钩子函数,下图为 Vue 生命周期示意图:
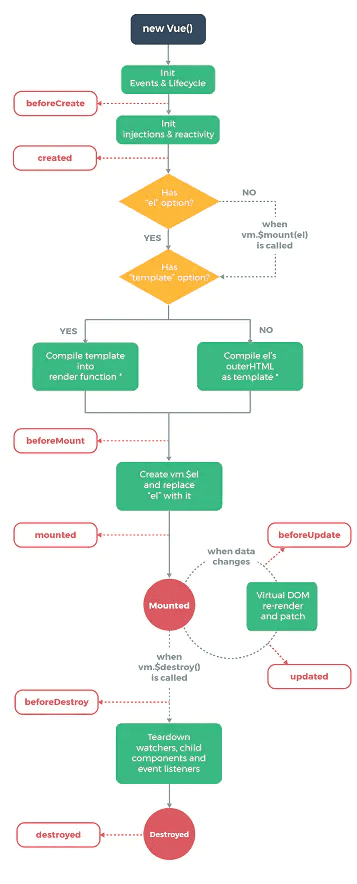
8 个钩子函数
1. beforeCreate
官方解释: 在实例初始化之后,数据观测 (data observer) 和event/watcher事件配置之前被调用。
说明:这个时候 this 还不能使用,data 中的数据、methods 中的方法,以及 watcher 中的事件都不能获得。
| var vm = new Vue({ | |
| el: '#app', | |
| data: { | |
| message: '今天是周一!!!' | |
| }, | |
| beforeCreate(){ | |
| console.group('beforeCreate 创建前状态 ==========>>'); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //undefined | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //undefined | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); //undefined | |
| }, | |
| //... |
2. created
官方解释: 实例已经创建完成之后被调用。在这一步,实例已完成以下的配置:数据观测(data observer),属性和方法的运算,watch/event 事件回调。然而,挂载阶段还没开始,$el 属性目前不可见。
说明:这个时候可以操作 vue 中的数据和方法,但是还不能对 dom 节点进行操作。
| //... | |
| created(){ | |
| console.group('created 创建完毕状态 ==========>>'); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //undefined | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //[object Object] | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); // 今天是周一!!! | |
| }, | |
| //... |
3. beforeMount
官方解释: 在挂载开始之前被调用:相关的 render 函数首次被调用。
说明:$el属性已存在,是虚拟 dom,只是数据未挂载到模板中。
| //... | |
| beforeMount(){ | |
| console.group('beforeMount 挂载前状态 ==========>>'); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //[object HTMLDivElement] | |
| console.log(this.$el); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //[object Object] | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); // 今天是周一!!! | |
| }, | |
| //... |
4. mounted
官方解释: el 被新创建的 vm.$el 替换,并挂载到实例上去之后调用该钩子。如果 root 实例挂载了一个文档内元素,当 mounted 被调用时 vm.$el 也在文档内。
注意 mounted 不会承诺所有的子组件也都一起被挂载。如果你希望等到整个视图都渲染完毕,可以用 vm.$nextTick 替换掉 mounted
说明:挂载完毕,这时 dom 节点被渲染到文档内,dom 操作在此时能正常进行
| //... | |
| mounted(){ | |
| console.group('mounted 挂载结束状态 ==========>>'); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //[object HTMLDivElement] | |
| console.log(this.$el); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //[object Object] | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); // 今天是周一!!! | |
| }, | |
| //... |

点击页面中的元素执行相应的事件,并触发 beforeUpdate 和 updated 钩子函数。
5. beforeUpdate
官方解释: 数据更新时调用,发生在虚拟 DOM 打补丁之前。这里适合在更新之前访问现有的 DOM,比如手动移除已添加的事件监听器。
说明:beforeUpdate 是指 view 层的数据变化前,不是 data 中的数据改变前触发。因为 Vue 是数据驱动的。
| //... | |
| beforeUpdate(){ | |
| console.group('beforeUpdate 更新前状态 ==========>>'); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //[object HTMLDivElement] | |
| console.log(this.$el); | |
| console.log(this.$el.innerHTML); //<p> 今天是周一!!!</p> | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //[object Object] | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); // 今天周二了!!! | |
| }, | |
| //... |
6. updated
官方解释: 由于数据更改导致的虚拟 DOM 重新渲染和打补丁,在这之后会调用该钩子。
当这个钩子被调用时,组件 DOM 已经更新,所以你现在可以执行依赖于 DOM 的操作。然而在大多数情况下,你应该避免在此期间更改状态。如果要相应状态改变,通常最好使用计算属性或 watcher 取而代之。
注意 updated 不会承诺所有的子组件也都一起被重绘。如果你希望等到整个视图都重绘完毕,可以用 vm.$nextTick 替换掉 updated:
说明:view 层的数据更新后,data 中的数据同 beforeUpdate,都是更新完以后的。
| //... | |
| updated(){ | |
| console.group('updated 更新完成状态 ==========>>'); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //[object HTMLDivElement] | |
| console.log(this.$el); | |
| console.log(this.$el.innerHTML); //<p> 今天周二了!!!</p> | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //[object Object] | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); // 今天周二了!!! | |
| }, | |
| //... |

注意:细心的小伙伴会发现 beforeUpdate 和 updated 钩子函数中的 $el 一样,根据官方理解 beforeUpdate 应该指向虚拟 dom,所以才会一样,而 dom 中的真正内容不一样,但是 beforeMount 和 mouted 钩子函数中为什么又会有区别呢?感觉是设计的不足之处。
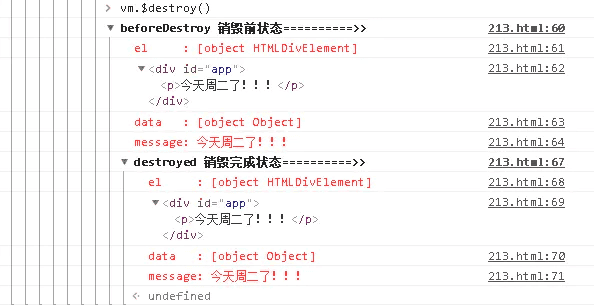
执行 vm.$destroy() 函数触发 beforeDestroy 和 destoryed 钩子函数
7. beforeDestroy
官方解释: 实例销毁之前调用。在这一步,实例仍然完全可用。
说明:
| //... | |
| beforeDestroy(){ | |
| console.group('beforeDestroy 销毁前状态 ==========>>'); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //[object HTMLDivElement] | |
| console.log(this.$el); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //[object Object] | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); // 今天周二了!!! | |
| }, | |
| //... |
8. destroyed
官方解释: Vue 实例销毁后调用。调用后,Vue 实例指示的所有东西都会解绑定,所有的事件监听器会被移除,所有的子实例也会被销毁。
说明:执行 destroy 方法后,对 data 的改变不会再触发周期函数,此时的 vue 实例已经解除了事件监听以及和 dom 的绑定,但是 dom 结构依然存在。
| //... | |
| destroyed(){ | |
| console.group('destroyed 销毁完成状态 ==========>>'); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //[object HTMLDivElement] | |
| console.log(this.$el); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //[object Object] | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); // 今天周二了!!! | |
| }, | |
| //... |
代码如下:
| <!DOCTYPE html> | |
| <html> | |
| <head> | |
| <title></title> | |
| </head> | |
| <body> | |
| <div id="app" ="change"> | |
| <p>{{message}}</p> | |
| </div> | |
| <script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.6.10/vue.min.js"></script> | |
| <script type="text/javascript"> | |
| var vm = new Vue({ | |
| el: '#app', | |
| data: { | |
| message: '今天是周一!!!' | |
| }, | |
| beforeCreate(){ | |
| console.group('beforeCreate 创建前状态 ==========>>'); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //undefined | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //undefined | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); //undefined | |
| }, | |
| created(){ | |
| console.group('created 创建完毕状态 ==========>>'); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //undefined | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //[object Object] | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); // 今天是周一!!! | |
| }, | |
| beforeMount(){ | |
| console.group('beforeMount 挂载前状态 ==========>>'); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //[object HTMLDivElement] | |
| console.log(this.$el); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //[object Object] | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); // 今天是周一!!! | |
| }, | |
| mounted(){ | |
| console.group('mounted 挂载结束状态 ==========>>'); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //[object HTMLDivElement] | |
| console.log(this.$el); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //[object Object] | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); // 今天是周一!!! | |
| }, | |
| beforeUpdate(){ | |
| console.group('beforeUpdate 更新前状态 ==========>>'); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //[object HTMLDivElement] | |
| console.log(this.$el); | |
| console.log(this.$el.innerHTML); //<p> 今天是周一!!!</p> | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //[object Object] | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); // 今天周二了!!! | |
| }, | |
| updated(){ | |
| console.group('updated 更新完成状态 ==========>>'); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //[object HTMLDivElement] | |
| console.log(this.$el); | |
| console.log(this.$el.innerHTML); //<p> 今天周二了!!!</p> | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //[object Object] | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); // 今天周二了!!! | |
| }, | |
| beforeDestroy(){ | |
| console.group('beforeDestroy 销毁前状态 ==========>>'); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //[object HTMLDivElement] | |
| console.log(this.$el); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //[object Object] | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); // 今天周二了!!! | |
| }, | |
| destroyed(){ | |
| console.group('destroyed 销毁完成状态 ==========>>'); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //[object HTMLDivElement] | |
| console.log(this.$el); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //[object Object] | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); // 今天周二了!!! | |
| }, | |
| methods: { | |
| change(){ | |
| this.message = "今天周二了!!!"; | |
| console.group("============== 点击事件执行的方法 ==============>>"); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "el :"+this.$el); //[object HTMLDivElement] | |
| console.log(this.$el); | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "data :"+this.$data); //[object Object] | |
| console.log("%c%s", "color:red", "message:"+this.message); // 今天周二了!!! | |
| } | |
| } | |
| }) | |
| </script> | |
| </body> | |
| </html> |
函数执行顺序
1. 生命周期执行顺序
-
页面初始化时:beforeCreate -> created -> beforeMount -> mounted
-
页面发生修改时:beforeUpdate -> updated
-
页面销毁时:beforeDestroy -> destroyed
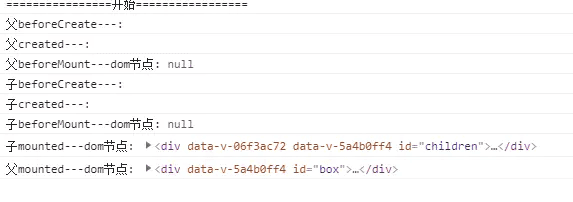
2. 父子组件生命周期执行顺序
-
页面初始化时:父 beforeCreate -> 父 created -> 父 beforeMount -> 子 beforeCreate -> 子 created -> 子 beforeMount -> 子 mounted-> 父 mounted
从图中可以看到,子组件要先于父组件挂载完成。
-
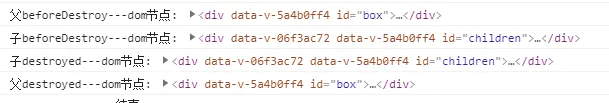
页面发生修改时:beforeUpdate -> updated 父、子组件间的更新互不影响,只更新自己。
-
页面销毁时:父 beforeDestroy -> 子 beforeDestroy -> 子 destroyed-> 父 destroyed 销毁时也是子组件要先于父组件销毁
3. this.$nextTick 在各生命周期的执行顺序
-
nextTick 在各生命周期的执行顺序,nextTick 是指在 dom 渲染完成后执行,结果如图。

-
虽然每个周期使用 $nextTick 都可以获取到 dom,但是还是建议在 mounted 中使用哈,因为 beforeMount/mounted 本来就是挂载 dom 滴~
4. watch、computed、methods 执行顺序
-
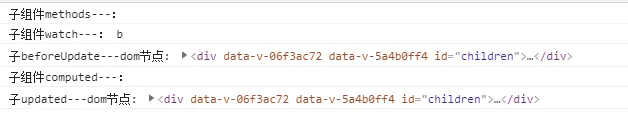
页面初始化时:会执行一次 computed,watch 初始化时不会执行,methods 只有调用的时候才会执行。
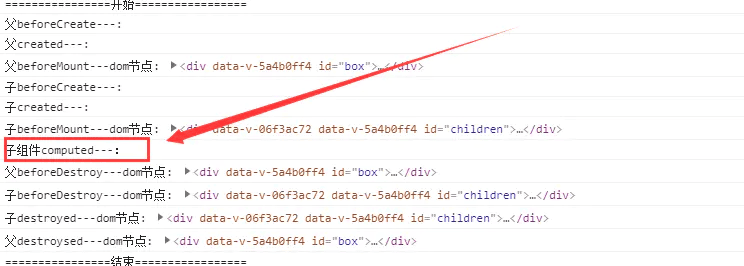
-
渲染完成后,触发 methods:methods -> watch -> computed
总结
-
beforecreate:可以在这加个 loading 事件;
-
created:在这结束 loading,还做一些初始化,实现函数自执行;
-
mounted:在这发起后端请求,拿回数据,配合路由钩子做一些事情;
-
beforeDestory:你确认删除 vue 实例了吗?
-
destoryed















