共计 19342 个字符,预计需要花费 49 分钟才能阅读完成。
| 导读 | 由于 Nginx 本身的一些优点,轻量,开源,易用,越来越多的公司使用 nginx 作为自己公司的 web 应用服务器,本文详细介绍 nginx 源码安装的同时并对 nginx 进行优化配置。 |

[root@linuxprobe ~]# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.10.1.tar.gz
[root@linuxprobe ~]# tar xvf nginx-1.10.1.tar.gz -C /usr/local/src/
[root@linuxprobe ~]# cd /usr/local/src/nginx-1.10.1/编译前的优化主要是用来修改程序名等等,例如:
[root@linuxprobe nginx-1.10.1]# curl -I http://www.baidu.com
……
Server: bfe/1.0.8.14
……
[root@linuxprobe nginx-1.10.1]# curl -I http://www.sina.com.cn
……
Server: nginx
……[root@linuxprobe nginx-1.10.1]# curl -I https://www.linuxprobe.com
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.10.1 #我们目标是将 nginx 更改名字
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Connection: keep-alive
X-Powered-By: PHP/5.6.29
Set-Cookie: PHPSESSID=smm0i6u4f9v7bj0gove79ja1g7; path=/
Cache-Control: no-cache
Date: Mon, 07 Seq 2016 06:09:11 GMT[root@linuxprobe nginx-1.10.1]# vim src/core/nginx.h
#define NGINX_VERSION “nginx_stable” #此行修改的是你想要的版本号
#define NGINX_VER “linuxprobe/” NGINX_VERSION #此行修改的是你想修改的软件名称
[root@linuxprobe nginx-1.10.1]# vim +49 src/http/ngx_http_header_filter_module.c
拓展:通用 http 头域
通用头域包含请求和响应消息都支持的头域,通用头域包含 Cache-Control、Connection、Date、Pragma、Transfer-Encoding、Upgrade、Via。对通用头域的扩展要求通讯双方都支持此扩展,如果存在不支持的通用头域,一般将会作为实体头域处理。那么也就是说有部分设备,或者是软件,能获取到 connection,部分不能,要隐藏就要彻底!
static char ngx_http_server_string[] = “Server: LinuxprobeWeb” CRLF;
[root@linuxprobe nginx-1.10.1]# vim +29 src/http/ngx_http_special_response.c
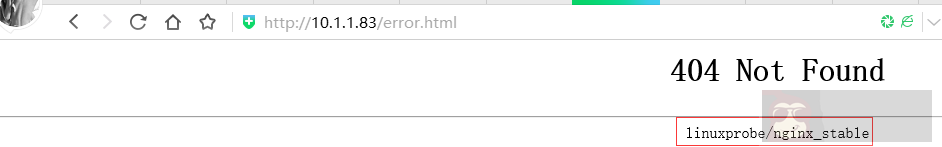
有时候我们页面程序出现错误,Nginx 会代我们返回相应的错误代码,回显的时候,会带上 nginx 和版本号,我们把他隐藏起来
static u_char ngx_http_error_full_tail[] =
"<hr><center>" NGINX_VER "</center>" CRLF
"</body>" CRLF
"</html>" CRLF
;修改后
static u_char ngx_http_error_tail[] =
"<hr><center>LinuxprobeWeb</center>" CRLF
"</body>" CRLF
"</html>" CRLF
;[root@linuxprobe nginx-1.10.1]# yum install gcc gcc-c++ autoconf automake zlib zlib-devel openssl openssl-devel -y# 本地下载 pcre 上传到服务器
[root@linuxprobe]# tar zxvf /usr/local/src/pcre-8.36.tar.gz -C /usr/local/src/
[root@linuxprobe nginx-1.10.1]# cd /usr/local/src/pcre-8.36
[root@linuxprobe nginx-1.10.1]# ./configure && make && make install
[root@linuxprobe nginx-1.10.1]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_dav_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_addition_module --with-http_sub_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_mp4_module --with-pcre=/usr/local/src/pcre-8.36 --with-openssl=/usr/include/openssl 注意:TCP_FASTOPEN 只在 3.7.1 以及更新的 Linux 内核版本才支持
--with-http_dav_module #启用支持(增加 PUT,DELETE,MKCOL:创建集合,COPY 和 MOVE 方法)默认关闭,需要编译开启
--with-http_stub_status_module #启用支持(获取 Nginx 上次启动以来的工作状态)--with-http_addition_module #启用支持(作为一个输出过滤器,支持不完全缓冲,分部分相应请求)--with-http_sub_module #启用支持(允许一些其他文本替换 Nginx 相应中的一些文本)--with-http_flv_module #启用支持(提供支持 flv 视频文件支持)--with-http_mp4_module #启用支持(提供支持 mp4 视频文件支持,提供伪流媒体服务端支持)--with-pcre=/usr/local/src/pcre-8.36 #需要注意,这里指的是源码, 用 #./configure --help |grep pcre 查看帮助 [root@linuxprobe nginx-1.10.1]# make && make install#Nginx 安装路径。如果没有指定,默认为 /usr/local/nginx。--prefix=PATH #Nginx 可执行文件安装路径。只能安装时指定,如果没有指定,默认为 PATH/sbin/nginx。--sbin-path=PATH #在没有给定 - c 选项下默认的 nginx.conf 的路径。如果没有指定,默认为 PATH/conf/nginx.conf。--conf-path=PATH #在 nginx.conf 中没有指定 pid 指令的情况下,默认的 nginx.pid 的路径。如果没有指定,默认为 PATH/logs/nginx.pid。--pid-path=PATH #nginx.lock 文件的路径。--lock-path=PATH #在 nginx.conf 中没有指定 error_log 指令的情况下,默认的错误日志的路径。如果没有指定,默认为 PATH/logs/error.log。--error-log-path=PATH #在 nginx.conf 中没有指定 access_log 指令的情况下,默认的访问日志的路径。如果没有指定,默认为 PATH/logs/access.log。--http-log-path=PATH #在 nginx.conf 中没有指定 user 指令的情况下,默认的 nginx 使用的用户。如果没有指定,默认为 nobody。--user=USER #在 nginx.conf 中没有指定 user 指令的情况下,默认的 nginx 使用的组。如果没有指定,默认为 nobody。--group=GROUP #指定编译的目录
--builddir=DIR #启用 rtsig 模块
--with-rtsig_module #允许或不允许开启 SELECT 模式,如果 configure 没有找到合适的模式,比如,kqueue(sun os)、epoll(linux kenel 2.6+)、rtsig(实时信号)
--with-select_module(--without-select_module) #允许或不允许开启 POLL 模式,如果没有合适的,则开启该模式。--with-poll_module(--without-poll_module) #开启 HTTP SSL 模块,使 NGINX 可以支持 HTTPS 请求。这个模块需要已经安装了 OPENSSL,在 DEBIAN 上是 libssl-dev
--with-http_ssl_module #启用 ngx_http_ssl_module
--with-http_realip_module #启用 ngx_http_realip_module
--with-http_addition_module #启用 ngx_http_addition_module
--with-http_sub_module #启用 ngx_http_sub_module
--with-http_dav_module #启用 ngx_http_dav_module
--with-http_flv_module #启用 ngx_http_flv_module
--with-http_stub_status_module #启用 "server status" 页
--without-http_charset_module #禁用 ngx_http_charset_module
--without-http_gzip_module #禁用 ngx_http_gzip_module. 如果启用,需要 zlib。--without-http_ssi_module #禁用 ngx_http_ssi_module
--without-http_userid_module #禁用 ngx_http_userid_module
--without-http_access_module #禁用 ngx_http_access_module
--without-http_auth_basic_module #禁用 ngx_http_auth_basic_module
--without-http_autoindex_module #禁用 ngx_http_autoindex_module
--without-http_geo_module #禁用 ngx_http_geo_module
--without-http_map_module #禁用 ngx_http_map_module
--without-http_referer_module #禁用 ngx_http_referer_module
--without-http_rewrite_module #禁用 ngx_http_rewrite_module. 如果启用需要 PCRE。--without-http_proxy_module #禁用 ngx_http_proxy_module
--without-http_fastcgi_module #禁用 ngx_http_fastcgi_module
--without-http_memcached_module #禁用 ngx_http_memcached_module
--without-http_limit_zone_module #禁用 ngx_http_limit_zone_module
--without-http_empty_gif_module #禁用 ngx_http_empty_gif_module
--without-http_browser_module #禁用 ngx_http_browser_module
--without-http_upstream_ip_hash_module #禁用 ngx_http_upstream_ip_hash_module
--with-http_perl_module - #启用 ngx_http_perl_module
--with-perl_modules_path=PATH #指定 perl 模块的路径
--with-perl=PATH #指定 perl 执行文件的路径
--http-log-path=PATH #Set path to the http access log
--http-client-body-temp-path=PATH #Set path to the http client request body temporary files
--http-proxy-temp-path=PATH #Set path to the http proxy temporary files
--http-fastcgi-temp-path=PATH #Set path to the http fastcgi temporary files
--without-http #禁用 HTTP server
--with-mail #启用 IMAP4/POP3/SMTP 代理模块
--with-mail_ssl_module #启用 ngx_mail_ssl_module
--with-cc=PATH #指定 C 编译器的路径
--with-cpp=PATH #指定 C 预处理器的路径
--with-cc-opt=OPTIONS #
--with-ld-opt=OPTIONS #Additional parameters passed to the linker. With the use of the system library PCRE in FreeBSD, it is necessary to indicate --with-ld-opt="-L /usr/local/lib".
--with-cpu-opt=CPU #为特定的 CPU 编译,有效的值包括:pentium, pentiumpro, pentium3, pentium4, athlon, opteron, amd64, sparc32, sparc64, ppc64
--without-pcre #禁止 PCRE 库的使用。同时也会禁止 HTTP rewrite 模块。在 "location" 配置指令中的正则表达式也需要 PCRE。--with-pcre=DIR #指定 PCRE 库的源代码的路径。--with-pcre-opt=OPTIONS #设置 PCRE 的额外编译选项。--with-md5=DIR #使用 MD5 汇编源码。--with-md5-opt=OPTIONS #Set additional options for md5 building.
--with-md5-asm #Use md5 assembler sources.
--with-sha1=DIR #Set path to sha1 library sources.
--with-sha1-opt=OPTIONS #Set additional options for sha1 building.
--with-sha1-asm #Use sha1 assembler sources.
--with-zlib=DIR #Set path to zlib library sources.
--with-zlib-opt=OPTIONS #Set additional options for zlib building.
--with-zlib-asm=CPU #Use zlib assembler sources optimized for specified CPU, valid values are: pentium, pentiumpro
--with-openssl=DIR #Set path to OpenSSL library sources
--with-openssl-opt=OPTIONS #Set additional options for OpenSSL building
--with-debug #启用调试日志
--add-module=PATH #Add in a third-party module found in directory PATH[root@linuxprobe nginx-1.10.1]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
[root@linuxprobe nginx-1.10.1]# netstat -antup | grep nginx
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 52553/nginx测试是否隐藏了版本和软件名
[root@linuxprobe nginx-1.10.1]# cd
[root@linuxprobe ~]# curl -I http://127.0.0.1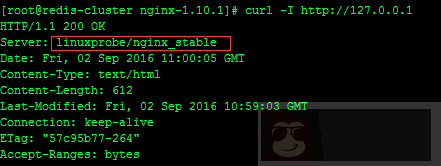
错误代码测试(尽量使用 firefox 或者类 360 浏览器)
 Nginx 运行用户
Nginx 运行用户
[root@linuxprobe~]# useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin nginx // 修改 nginx 默认运行用户
[root@linuxprobe ~]# ps -aux | grep nginx // 默认是 nobody 用户
nobody 52554 0.0 0.1 22660 1568 ? S 14:39 0:00 nginx: worker process
[root@linuxprobe ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
user nginx;
[root@linuxprobe ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
[root@linuxprobe ~]# ps -aux | grep nginx
nginx 52555 0.0 0.1 22660 1568 ? S 14:39 0:00 nginx: worker process在这里我们还可以看到在查看的时候,work 进程是 nginx 用户了,但是 master 进程还是 root
其中,master 是监控进程,也叫主进程,work 是工作进程,部分还有 cache 相关进程,关系如图:
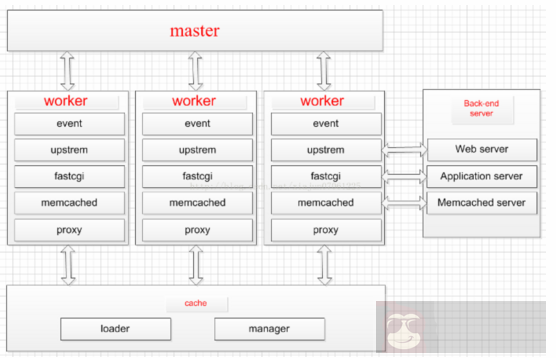
所以我们可以 master 监控进程使用 root,可以是降级使用普通用户,如果都是用普用户,注意编译安装的时候,是用普通用户执行,sudo 方式操作!可以直接理解为 master 是管理员,work 进程才是为用户提供服务的!
Nginx 运行进程个数,一般我们设置 CPU 的核心或者核心数 x2, 如果你不了解,top 命令之后按 1 也可以看出来(一般直接追到线程即可)
[root@linuxprobe ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
worker_processes 2;
[root@linuxprobe ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
[root@linuxprobe ~]# ps -axu | grep nginx
nginx 52686 0.0 0.1 22668 1300 ? S 15:10 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 52687 0.0 0.1 22668 1376 ? S 15:10 0:00 nginx: worker processNginx 运行 CPU 亲和力 (这个要根据你的 CPU 线程数配置)
比如 4 核 4 线程配置
[root@linuxprobe ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
worker_processes 4;
worker_cpu_affinity 0001 0010 0100 1000;比如 8 核 8 线程配置
worker_processes 8;
worker_cpu_affinity 00000001 00000010 00000100 00001000 00010000 00100000 01000000 10000000;那么如果我是 4 线程的 CPU,我只想跑两个进程呢?
worker_processes 2;
worker_cpu_affinity 0101 1010;意思就似乎我开启了第一个和第三个内核,第二个和第四个内核,两个进程分别在这两个组合上轮询!worker_processes 最多开启 8 个,8 个以上性能提升不会再提升了,而且稳定性变得更低,所以 8 个进程够用了。
Nginx 最多可以打开文件数 worker_rlimit_nofile 65535;
这个指令是指当一个 nginx 进程打开的最多文件描述符数目,理论值应该是最多打开文件数(ulimit -n)与 nginx 进程数相除,但是 nginx 分配请求并不是那么均匀,所以最好与 ulimit - n 的值保持一致。
Nginx 事件处理模型
events {
use epoll;
worker_connections 1024;
}知道在 linux 下 nginx 采用 epoll 事件模型,处理效率高,关于 epoll 的时间处理其他只是,可以自行百度,了解即可!
Work_connections 是单个进程允许客户端最大连接数,这个数值一般根据服务器性能和内存来制定,也就是单个进程最大连接数,实际最大值就是 work 进程数乘以这个数,如何设置,可以根据设置一个进程启动所占内存,top -u nginx,但是实际我们填入一个 65535,足够了,这些都算并发值,一个网站的并发达到这么大的数量,也算一个大站了!
开启高效传输模式
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
……
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
……
Include mime.types; 媒体类型
default_type application/octet-stream; 默认媒体类型足够
sendfile on;开启高效文件传输模式,sendfile 指令指定 nginx 是否调用 sendfile 函数来输出文件,对于普通应用设为 on,如果用来进行下载等应用磁盘 IO 重负载应用,可设置为 off,以平衡磁盘与网络 I / O 处理速度,降低系统的负载。注意:如果图片显示不正常把这个改成 off。tcp_nopush on;必须在 sendfile 开启模式才有效,防止网路阻塞,积极的减少网络报文段的数量 连接超时时间
主要目的是保护服务器资源,CPU,内存,控制连接数,因为建立连接也是需要消耗资源的,TCP 的三次握手四次挥手等,我们一般断掉的是那些建立连接但是不做事儿,也就是我建立了链接开始,但是后续的握手过程没有进行,那么我们的链接处于等待状态的,全部断掉!
同时我们也希望 php 建议短链接,消耗资源少
Java 建议长链接,消耗资源少
keepalive_timeout 60;
tcp_nodelay on;
client_header_timeout 15;
client_body_timeout 15;
send_timeout 15;
keepalived_timeout 客户端连接保持会话超时时间,超过这个时间,服务器断开这个链接
tcp_nodelay;也是防止网络阻塞,不过要包涵在 keepalived 参数才有效
client_header_timeout 客户端请求头读取超时时间,如果超过这个时间没有发送任何数据,nginx 将返回 request time out 的错误
client_body_timeout 客户端求主体超时时间,超过这个时间没有发送任何数据,和上面一样的错误提示
send_timeout 响应客户端超时时间,这个超时时间仅限于两个活动之间的时间,如果超哥这个时间,客户端没有任何活动,nginx 关闭连接 文件上传大小限制
我们知道 PHP 可以修改上传文件大小限制,nginx 也可以修改
http {
……
client_max_body_size 10m;Nginx 没有配置 factcgi,你使用 nginx 是一个失败的方法,配置之前。了解几个概念:
Cache:写入缓存区
Buffer:读取缓存区
Fastcgi 是静态服务和动态服务的一个接口
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300; #指定链接到后端 FastCGI 的超时时间。fastcgi_send_timeout 300; #向 FastCGI 传送请求的超时时间,这个值是指已经完成两次握手后向 FastCGI 传送请求的超时时间。fastcgi_read_timeout 300; #指定接收 FastCGI 应答的超时时间,这个值是指已经完成两次握手后接收 FastCGI 应答的超时时间。fastcgi_buffer_size 64k; #指定读取 FastCGI 应答第一部分需要用多大的缓冲区,这个值表示将使用 1 个 64KB 的缓冲区读取应答的第一部分(应答头),可以设置为 gastcgi_buffers 选项指定的缓冲区大小。fastcgi_buffers 4 64k; #指定本地需要用多少和多大的缓冲区来缓冲 FastCGI 的应答请求,如果一个 php 脚本所产生的页面大小为 256KB,那么会分配 4 个 64KB 的缓冲区来缓存,如果页面大小大于 256KB,那么大于 256KB 的部分会缓存到 fastcgi_temp 指定的路径中,但是这并不是好方法,因为内存中的数据处理速度要快于磁盘。一般这个值应该为站点中 php 脚本所产生的页面大小的中间值,如果站点大部分脚本所产生的页面大小为 256KB,那么可以把这个值设置为“8 16K”、“4 64k”等。fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 128k; #建议设置为 fastcgi_buffer 的两倍,繁忙时候的 buffer
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 128k; #在写入 fastcgi_temp_path 时将用多大的数据库,默认值是 fastcgi_buffers 的两倍,设置上述数值设置小时若负载上来时可能报 502Bad Gateway
fastcgi_cache aniu_ngnix; #表示开启 FastCGI 缓存并为其指定一个名称。开启缓存非常有用,可以有效降低 CPU 的负载,并且防止 502 的错误放生,但是开启缓存也可能会引起其他问题,要很据具体情况选择
fastcgi_cache_valid 200 302 1h; #用来指定应答代码的缓存时间,实例中的值表示将 2000 和 302 应答缓存一小时,要和 fastcgi_cache 配合使用
fastcgi_cache_valid 301 1d; #将 301 应答缓存一天
fastcgi_cache_valid any 1m; #将其他应答缓存为 1 分钟
fastcgi_cache_min_uses 1; #请求的数量
fastcgi_cache_path #定义缓存的路径 修改 nginx.conf 配置文件,在 http 标签中添加如下:
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
fastcgi_buffer_size 64k;
fastcgi_buffers 4 64k;
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 128k;
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 128k;
#fastcgi_temp_path /data/ngx_fcgi_tmp;
fastcgi_cache_path /opt/ngx_fcgi_cache levels=2:2
keys_zone=ngx_fcgi_cache:512m
inactive=1d max_size=40g;缓存路径,levels 目录层次 2 级,定义了一个存储区域名字,缓存大小,不活动的数据在缓存中多长时间,目录总大小
在 server location 标签添加如下:
location ~ .*\.(php|php5)?$
{
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi.conf;
fastcgi_cache ngx_fcgi_cache;
fastcgi_cache_valid 200 302 1h;
fastcgi_cache_valid 301 1d;
fastcgi_cache_valid any 1m;
fastcgi_cache_min_uses 1;
fastcgi_cache_use_stale error timeout invalid_header http_500;
fastcgi_cache_key http://$host$request_uri;
}fastcgi cache 官方文档:http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_fastcgi_module.html#fastcgi_cache
使用 gzip 压缩功能,可能为我们节约带宽,加快传输速度,有更好的体验,也为我们节约成本,所以说这是一个重点
Nginx 启用压缩功能需要你来 ngx_http_gzip_module 模块,apache 使用的是 mod_deflate
一般我们需要压缩的内容有:文本,js,html,css,对于图片,视频,flash 什么的不压缩,同时也要注意,我们使用 gzip 的功能是需要消耗 CPU 的!
gzip on; #开启压缩功能
gzip_min_length 1k; #设置允许压缩的页面最小字节数,页面字节数从 header 头的 Content-Length 中获取,默认值是 0,不管页面多大都进行压缩,建议设置成大于 1K,如果小与 1K 可能会越压越大。gzip_buffers 4 32k; #压缩缓冲区大小,表示申请 4 个单位为 32K 的内存作为压缩结果流缓存,默认值是申请与原始数据大小相同的内存空间来存储 gzip 压缩结果。gzip_http_version 1.1; #压缩版本(默认 1.1,前端为 squid2.5 时使用 1.0)用于设置识别 HTTP 协议版本,默认是 1.1,目前大部分浏览器已经支持 GZIP 解压,使用默认即可
gzip_comp_level 9; #压缩比例,用来指定 GZIP 压缩比,1 压缩比最小,处理速度最快,9 压缩比最大,传输速度快,但是处理慢,也比较消耗 CPU 资源。gzip_types text/css text/xml application/javascript; #用来指定压缩的类型,‘text/html’类型总是会被压缩。gzip_vary on; #vary header 支持,改选项可以让前端的缓存服务器缓存经过 GZIP 压缩的页面,例如用 Squid 缓存经过 nginx 压缩的数据 那么配置压缩的过程中,会有一下参数
gzip on;
gzip_min_length 1k;
gzip_buffers 4 32k;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_comp_level 9;
gzip_types text/plain application/javascript application/x-javascript text/javascript text/css application/xml application/xml+rss;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_proxied expired no-cache no-store private auth;
gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\.";缓存,主要针对于图片,css,js 等元素更改机会比较少的情况下使用,特别是图片,占用带宽大,我们完全可以设置图片在浏览器本地缓存 365d,css,js,html 可以缓存个 10 来天,这样用户第一次打开加载慢一点,第二次,就非常快乐!缓存的时候,我们需要将需要缓存的拓展名列出来!
Expires 缓存配置在 server 字段里面
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf)$
{expires 3650d;}
location ~ .*\.(js|css)?$
{expires 30d;}同时也可以对目录及其进行判断:
location ~ ^/(images|javascript|js|css|flash|media|static)/ {expires 360d;}
location ~(robots.txt) {
expires 7d;
break;
}expire 功能优点
(1)expires 可以降低网站购买的带宽,节约成本
(2)同时提升用户访问体验
(3)减轻服务的压力,节约服务器成本,甚至可以节约人力成本,是 web 服务非常重要的功能。
expire 功能缺点:
被缓存的页面或数据更新了,用户看到的可能还是旧的内容,反而影响用户体验。
解决办法:
第一个 缩短缓存时间,例如:1 天,不彻底,除非更新频率大于 1 天
第二个 对缓存的对象改名
a. 图片,附件一般不会被用户修改,如果用户修改了,实际上也是更改文件名重新传了而已
b. 网站升级对于 js,css 元素,一般可以改名,把 css,js,推送到 CDN。
网站不希望被缓存的内容
1)广告图片
2)网站流量统计工具
3)更新频繁的文件(google 的 logo)
[root@linuxprobe ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/logs/日志优化的目的,是为了一天日志一压缩,焚天存放,超过 10 天的删除
// 每天日志分割脚本
[root@linuxprobe logs]# vim cut_nginx_log.sh
#!/bin/bash
######################################
#function:cut nginx log files
#author: shaon
######################################
#set the path to nginx log files
log_files_path="/usr/local/nginx/logs"
log_files_dir=${log_files_path}/$(date -d "yesterday" +"%Y")/$(date -d "yesterday" +"%m")
log_files_dir=${log_files_path}/$(date -d "yesterday" +"%Y")/$(date -d "yesterday" +"%m")
#set nginx log files you want to cut
log_files_name=(access error)
#set the path to nginx.
nginx_sbin="/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx"
#Set how long you want to save
save_days=30
############################################
#Please do not modify the following script #
############################################
mkdir -p $log_files_dir
log_files_num=${#log_files_name[@]}
#cut nginx log files
for((i=0;i<$log_files_num;i++));do
mv ${log_files_path}/${log_files_name[i]}.log ${log_files_dir}/${log_files_name[i]}_$(date -d "yesterday" +"%Y%m%d").log
done ays -exec rm -rf {}
#delete 30 days ago nginx log files
find $log_files_path -mtime +$save_days -exec rm -rf {} \;健康检查的日志,不输入到 log 中,这些日志没有意义,我们分析的话只需要分析访问日志,看看一些页面链接,如 200,301,404 的状态吗,在 SEO 中很重要,而且我们统计 PV 是页面计算,这些都没有意义,反而消耗了磁盘 IO,降低了服务器性能,我们可以屏蔽这些如图片,js,css 这些不宜变化的内容
[root@linuxprobe ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
location ~ .*\.(js|jpg|jpeg|JPG|JPEG|css|bmp|gif|GIF)$ {access_log off;}日志目录权限优化
[root@linuxprobe ~]# chown -R root:root /usr/local/nginx/logs
[root@linuxprobe ~]# chmod 700 /usr/local/nginx/logs日志格式优化
#vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
log_format access‘$remote_addr – $remote_user [$time_local]“$request”‘‘$status $body_bytes_sent“$http_referer”‘‘”$http_user_agent”$http_x_forwarded_for’;其中,各个字段的含义如下:
1.$remote_addr 与 $http_x_forwarded_for 用以记录客户端的 ip 地址;2.$remote_user:用来记录客户端用户名称;3.$time_local:用来记录访问时间与时区;4.$request:用来记录请求的 url 与 http 协议;5.$status:用来记录请求状态;成功是 200,6.$body_bytes_s ent:记录发送给客户端文件主体内容大小;7.$http_referer:用来记录从那个页面链接访问过来的;8.$http_user_agent:记录客户端浏览器的相关信息;目录文件访问控制
主要用在禁止目录下指定文件被访问,当然也可以禁止所有文件被访问!一般什么情况下用?比如是有存储共享,这些文件本来都只是一下资源文件,那么这些资源文件就不允许被执行,如 sh.py,pl,php 等等
例如:禁止访问 images 下面的 php 程序文件
location ~ ^/images/.*\.(php|php5|.sh|.py|.py)$ {deny all;}[root@linuxprobe ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
[root@linuxprobe ~]# mkdir /usr/local/nginx/html/images
[root@linuxprobe ~]# echo "" > /usr/local/nginx/html/images/index.php 测试访问

多目录组合配置方法
location ~ ^/images/(attachment|avatar)/.*\.(php|php5|.sh|.py|.py)$ {deny all;}配置 nginx 禁止访问 *.txt 文件
[root@linuxprobe ~]# echo "hello,linuxprobe" > /usr/local/nginx/html/test.txt
配置规则,禁止访问
[root@linuxprobe ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf //server 字段中
location ~* \.(txt|doc)$ {if ( -f $request_filename) {
root /usr/local/nginx/html;
break;
}
deny all;
}
[root@linuxprobe ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
当然,可以重定向到某一个 URL
[root@linuxprobe ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
location ~* \.(txt|doc)$ {if ( -f $request_filename) {
root /usr/local/nginx/html;
rewrite ^/(.*)$ https://www.linuxprobe.com last;
break;
}
}对目录进行限制的方法
[root@linuxprobe ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/nginx/html/{linuxprobe,1mcloud}
[root@linuxprobe ~]# echo linuxprobe > /usr/local/nginx/html/linuxprobe/index.html
[root@linuxprobe ~]# echo 1mcloud > /usr/local/nginx/html/1mcloud/index.html
[root@linuxprobe ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
location /linuxprobe/ {return 404 ;}
location /1mcloud/ {return 403 ;}
测试返回结果 

上面是直接给了反馈的状态吗,也可以通过匹配 deny all 方式做
[root@linuxprobe ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
location ~ ^/(linuxprobe)/ {deny all;}
[root@linuxprobe ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
来源访问控制
这个需要 ngx_http_access_module 模块支持,不过,默认会安装
[root@linuxprobe ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf // 写法类似 Apache
location ~ ^/(linuxprobe)/ {
allow 192.168.1.0/24;
deny all;
}
接着上面的实验,就可以访问了,下面是针对整个网站的写法,对 / 限制就 OK
location / {
allow 192.168.1.0/24;
deny all;
}当然可以写 IP,可以写 IP 段,但是注意次序,上下匹配
同时,也可以通过 if 语句控制,给以友好的错误提示
if ($remote_addr = 10.1.1.55) {return 404;}# 此处 remote_addr 地址为当前编辑文档的系统 ip 地址
有时候,我们发现访问网站的时候,使用 IP 也是可以得,我们可以把这一层给屏蔽掉,让其直接反馈给 403, 也可以做跳转
跳转的做法:
server {
listen 80 default_server;
server_name _;
rewrite ^ https://www.linuxprobe.com$request_uri?;
}403 反馈的做法
server {
listen 80 default_server;
server_name _;
return 403;
}301 跳转的做法
# 如我们域名一般在解析的过程中,linuxprobe.com 一般会跳转到 www.linuxprobe.com, 记住修改本地 hosts
server {
listen 80;
root /usr/share/nginx/html/;
server_name www.linuxprobe.com linuxprobe.com;
if ($host = 'a.com') {rewrite ^/(.*)$ www.linuxprobe.com/$1 permanent;
}防止别人直接从你网站引用图片等链接,消耗了你的资源和网络流量,那么我们的解决办法由几种:
1:水印,品牌宣传,你的带宽,服务器足够
2:防火墙,直接控制,前提是你知道 IP 来源
3:防盗链策略
下面的方法是直接给予 404 的错误提示
location ~* \.(jpg|gif|png|swf|flv|wma|wmv|asf|mp3|mmf|zip|rar)$ {
valid_referers none blocked *.linuxprobe,com linuxprobe.com;
if ($invalid_referer) {return 404;}同时,我们也可以设置一个独有的,图片比较小的,来做 rewrite 跳转
location ~* \.(jpg|gif|png|swf|flv|wma|wmv|asf|mp3|mmf|zip|rar)$ {
valid_referers none blocked *.a.com a.com;
if ($invalid_referer) {rewrite ^/ https://www.linuxprobe.com/img/nolink.png;}错误页面的提示
对于自定义的错误页面,我们只需要将 errorpage 写入到配置文件
error_page 404 /404.html;内部身份验证
[root@linuxprobe ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
location /linuxprobe/ {
auth_basic "haha";
auth_basic_user_file /usr/local/nginx/conf/passwd;
}用户创建
[root@linuxprobe ~]# yum -y install httpd-tools
[root@linuxprobe ~]# htpasswd -cb /usr/local/nginx/conf/passwd linuxprobe 211212
[root@linuxprobe ~]# chmod 400 /usr/local/nginx/conf/passwd
[root@linuxprobe ~]# chown nginx /usr/local/nginx/conf/passwd
[root@linuxprobe ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload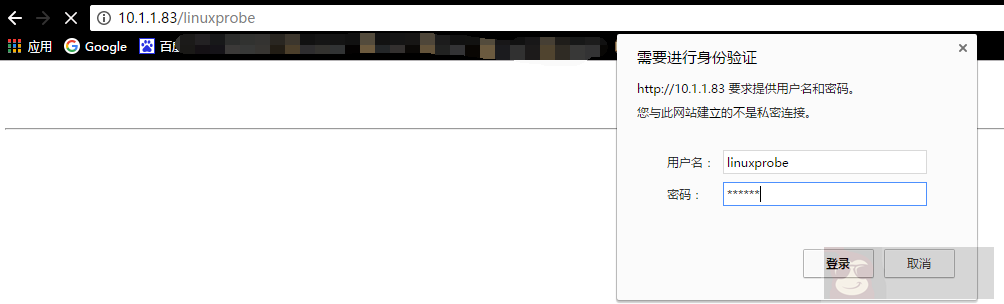
通过使用 limit_conn_zone 进行控制单个 IP 或者域名的访问次数
[root@linuxprobe ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.confhttp 字段中配置
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:10m;server 的 location 字段配置
location / {
root html;
limit_conn addr 1;# 在其他机器上面进行并发测试
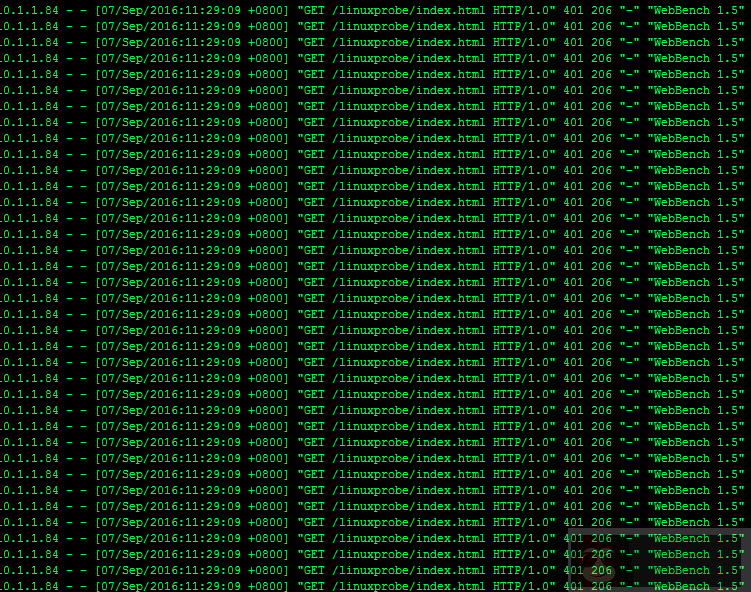
[root@linuxprobe ~]# webbench -c 5000 -t 120 http://10.1.1.83/linuxprobe/index.html#webbench 安装请参考 http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_87113ac20102wag5.html
#nginx 匹配符介绍
= 开头表示精确匹配
^~ 开头表示 uri 以某个常规字符串开头,理解为匹配 url 路径即可。nginx 不对 url 做编码,因此请求为 /static/20%/aa,可以被规则 ^~ /static/ /aa 匹配到(注意是空格)。~ 开头表示区分大小写的正则匹配
~* 开头表示不区分大小写的正则匹配
!~ 和!~* 分别为区分大小写不匹配及不区分大小写不匹配的正则
/ 通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到。多个 location 配置的情况下匹配顺序为(参考资料而来,还未实际验证,试试就知道了,不必拘泥,仅供参考):
首先匹配 =,其次匹配 ^~, 其次是按文件中顺序的正则匹配,最后是交给 / 通用匹配。当有匹配成功时候,停止匹配,按当前匹配规则处理请求。
















