共计 4336 个字符,预计需要花费 11 分钟才能阅读完成。
| 导读 | 这篇文章主要介绍了 VBA 处理数据与 Python Pandas 处理数据案例比较, 本文通过实例代码给大家介绍的非常详细,具有一定的参考借鉴价值,需要的朋友可以参考下 |
需求:
现有一个 csv 文件,包含 ’CNUM’ 和 ’COMPANY’ 两列,数据里包含空行,且有内容重复的行数据。
要求:
1)去掉空行;
2)重复行数据只保留一行有效数据;
3)修改 ’COMPANY’ 列的名称为 ’Company_New‘;
4)并在其后增加六列,分别为 ’C_col’,‘D_col’,‘E_col’,‘F_col’,‘G_col’,‘H_col’。
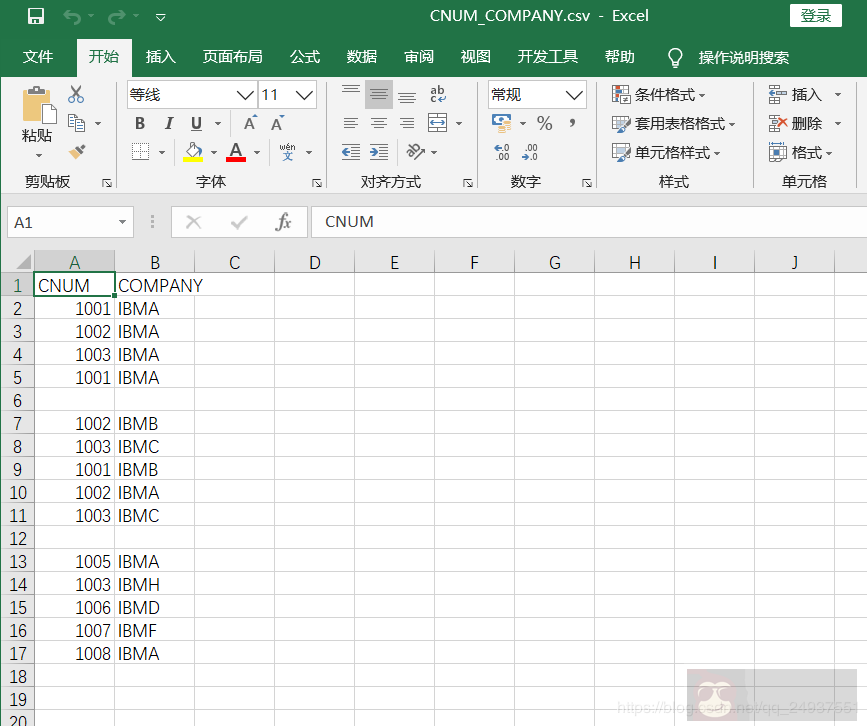
一,使用 Python Pandas 来处理:
| import pandas as pd | |
| import numpy as np | |
| from pandas import DataFrame,Series | |
| def deal_with_data(filepath,newpath): | |
| file_obj=open(filepath) | |
| df=pd.read_csv(file_obj) # 读取 csv 文件,创建 DataFrame | |
| df=df.reindex(columns=['CNUM','COMPANY','C_col','D_col','E_col','F_col','G_col','H_col'],fill_value=None) # 重新指定列索引 | |
| df.rename(columns={'COMPANY':'Company_New'}, inplace = True) # 修改列名 | |
| df=df.dropna(axis=0,how='all') # 去除 NAN 即文件中的空行 | |
| df['CNUM'] = df['CNUM'].astype('int32') # 将 CNUM 列的数据类型指定为 int32 | |
| df = df.drop_duplicates(subset=['CNUM', 'Company_New'], keep='first') # 去除重复行 | |
| df.to_csv(newpath,index=False,encoding='GBK') | |
| file_obj.close() | |
| if __name__=='__main__': | |
| file_path=r'C:\Users\12078\Desktop\python\CNUM_COMPANY.csv' | |
| file_save_path=r'C:\Users\12078\Desktop\python\CNUM_COMPANY_OUTPUT.csv' | |
| deal_with_data(file_path,file_save_path) |
二,使用 VBA 来处理:
| Option Base 1 | |
| Option Explicit | |
| Sub main() | |
| On Error GoTo error_handling | |
| Dim wb As Workbook | |
| Dim wb_out As Workbook | |
| Dim sht As Worksheet | |
| Dim sht_out As Worksheet | |
| Dim rng As Range | |
| Dim usedrows As Byte | |
| Dim usedrows_out As Byte | |
| Dim dict_cnum_company As Object | |
| Dim str_file_path As String | |
| Dim str_new_file_path As String | |
| 'assign values to variables: | |
| str_file_path = "C:\Users\12078\Desktop\Python\CNUM_COMPANY.csv" | |
| str_new_file_path = "C:\Users\12078\Desktop\Python\CNUM_COMPANY_OUTPUT.csv" | |
| Set wb = checkAndAttachWorkbook(str_file_path) | |
| Set sht = wb.Worksheets("CNUM_COMPANY") | |
| Set wb_out = Workbooks.Add | |
| wb_out.SaveAs str_new_file_path, xlCSV 'create a csv file | |
| Set sht_out = wb_out.Worksheets("CNUM_COMPANY_OUTPUT") | |
| Set dict_cnum_company = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary") | |
| usedrows = WorksheetFunction.Max(getLastValidRow(sht, "A"), getLastValidRow(sht, "B")) | |
| 'rename the header'COMPANY'to'Company_New',remove blank & duplicate lines/rows. | |
| Dim cnum_company As String | |
| cnum_company = ""For Each rng In sht.Range("A1","A" & usedrows) | |
| If VBA.Trim(rng.Offset(0, 1).Value) = "COMPANY" Then | |
| rng.Offset(0, 1).Value = "Company_New" | |
| End If | |
| cnum_company = rng.Value & "-" & rng.Offset(0, 1).Value | |
| If VBA.Trim(cnum_company) "-" And Not dict_cnum_company.Exists(rng.Value & "-" & rng.Offset(0, 1).Value) Then | |
| dict_cnum_company.Add rng.Value & "-" & rng.Offset(0, 1).Value, "" | |
| End If | |
| Next rng | |
| 'loop the keys of dict split the keyes by'-' into cnum array and company array. | |
| Dim index_dict As Byte | |
| Dim arr_cnum() | |
| Dim arr_Company() | |
| For index_dict = 0 To UBound(dict_cnum_company.keys) | |
| ReDim Preserve arr_cnum(1 To UBound(dict_cnum_company.keys) + 1) | |
| ReDim Preserve arr_Company(1 To UBound(dict_cnum_company.keys) + 1) | |
| arr_cnum(index_dict + 1) = Split(dict_cnum_company.keys()(index_dict), "-")(0) | |
| arr_Company(index_dict + 1) = Split(dict_cnum_company.keys()(index_dict), "-")(1) | |
| Debug.Print index_dict | |
| Next | |
| 'assigns the value of the arrays to the celles. | |
| sht_out.Range("A1", "A" & UBound(arr_cnum)) = Application.WorksheetFunction.Transpose(arr_cnum) | |
| sht_out.Range("B1", "B" & UBound(arr_Company)) = Application.WorksheetFunction.Transpose(arr_Company) | |
| 'add 6 columns to output csv file: | |
| Dim arr_columns() As Variant | |
| arr_columns = Array("C_col", "D_col", "E_col", "F_col", "G_col", "H_col") 'sht_out.Range("C1:H1") = arr_columns | |
| Call checkAndCloseWorkbook(str_file_path, False) | |
| Call checkAndCloseWorkbook(str_new_file_path, True) | |
| Exit Sub | |
| error_handling: | |
| Call checkAndCloseWorkbook(str_file_path, False) | |
| Call checkAndCloseWorkbook(str_new_file_path, False) | |
| End Sub | |
| '辅助函数:'Get last row of Column N in a Worksheet | |
| Function getLastValidRow(in_ws As Worksheet, in_col As String) | |
| getLastValidRow = in_ws.Cells(in_ws.Rows.count, in_col).End(xlUp).Row | |
| End Function | |
| Function checkAndAttachWorkbook(in_wb_path As String) As Workbook | |
| Dim wb As Workbook | |
| Dim mywb As String | |
| mywb = in_wb_path | |
| For Each wb In Workbooks | |
| If LCase(wb.FullName) = LCase(mywb) Then | |
| Set checkAndAttachWorkbook = wb | |
| Exit Function | |
| End If | |
| Next | |
| Set wb = Workbooks.Open(in_wb_path, UpdateLinks:=0) | |
| Set checkAndAttachWorkbook = wb | |
| End Function | |
| Function checkAndCloseWorkbook(in_wb_path As String, in_saved As Boolean) | |
| Dim wb As Workbook | |
| Dim mywb As String | |
| mywb = in_wb_path | |
| For Each wb In Workbooks | |
| If LCase(wb.FullName) = LCase(mywb) Then | |
| wb.Close savechanges:=in_saved | |
| Exit Function | |
| End If | |
| Next | |
| End Function |
三,输出结果:
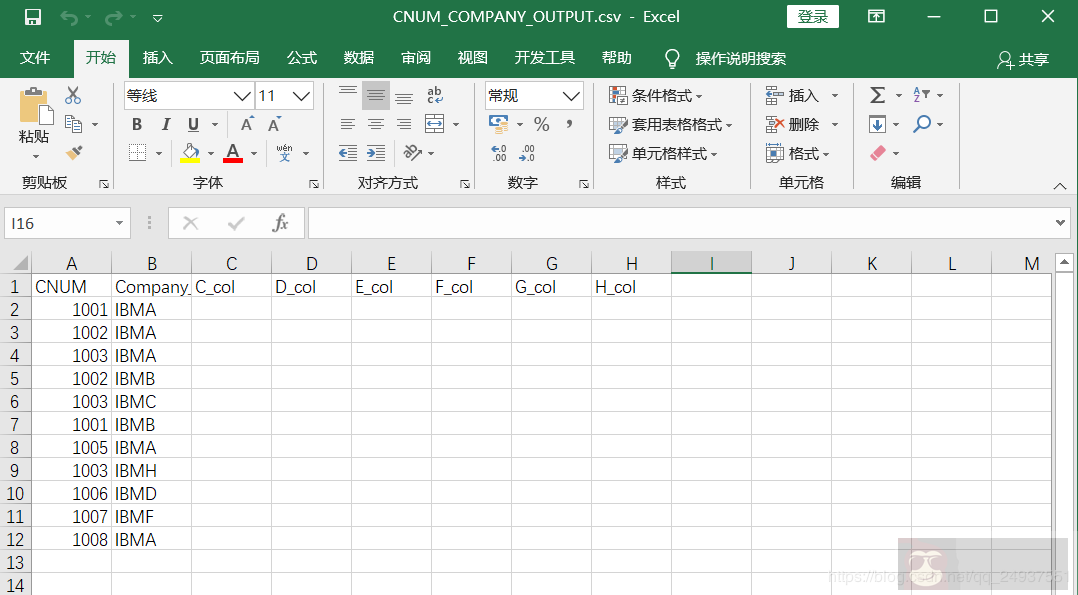
两种方法输出结果相同:
四,比较总结:
Python pandas 内置了大量处理数据的方法,我们不需要重复造轮子,用起来很方便,代码简洁的多。
Excel VBA 处理这个需求,使用了 数组,字典等数据结构(实际需求中,数据量往往很大,所以一些地方没有直接使用遍历单元格的方法),以及处理字符串,数组和字典的很多方法,对文件的操作也很复杂,一旦出错,调试起来比 python 也较困难,代码已经尽量优化,但还是远比 Python 要多。
到此这篇关于 VBA 处理数据与 Python Pandas 处理数据案例比较分析的文章就介绍到这了
正文完
星哥玩云-微信公众号
















