共计 3018 个字符,预计需要花费 8 分钟才能阅读完成。
| 导读 | 今天的分享是再批 json, 去年分享过因为 mysql json 导致的故障,今天的 case 其实是去年的姊妹篇,原理一模一样。上一篇弱智的 MySQL NULL, 居然有小伙伴留言说,在业务中依赖 NULL 使联合索引不唯一的特性,比如有的用户就要多条记录,有的仅一条。我看了差点一口老血喷出来,把业务逻辑耦合在 DB 中这样真的合适嘛? 要是外包另当别论,正常项目谁接手谁倒霉。 |

今天的分享是再批 json, 去年分享过因为 mysql json 导致的故障,今天的 case 其实是去年的姊妹篇,原理一模一样。有两个原因不建议用 json:
上面提到的两点有争议? 有争议就对了,一致认同是垃圾的东西谁会讨论它呢?
JSON 有两种表示方法:文本可读的在 mysql 中对应 json_dom.cc, binary 二进制表示的对应 json_binary.cc
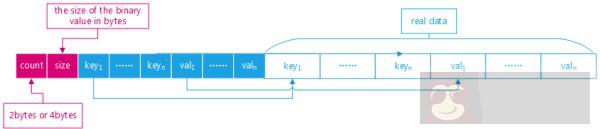
| If the value is a JSON object, its binary representation will have a | |
| header that contains: | |
| - the member count | |
| - the size of the binary value in bytes | |
| - a list of pointers to each key | |
| - a list of pointers to each value | |
| The actual keys and values will come after the header, in the same | |
| order as in the header. | |
| Similarly, if the value is a JSON array, the binary representation | |
| will have a header with | |
| - the element count | |
| - the size of the binary value in bytes | |
| - a list of pointers to each value |
源码中注释也写的比较清楚,二进制分成两部分 header + element. 实际上 mysql 只是 server 识别了 json, 各个存储引擎仍存储的二进制 blob
换句话说,底层引擎对 json 是无感知的,就是一条数据而己
json-function-reference[1] 官方有好多在 server 层操作 json 的方法,感兴趣的可以看一下
MySQL Client 读取 json 时是 json_dom 调用 wrapper_to_string 方法,序列化成可读格式数据
写入 json 时,是由 json_binary 调用 serialize_json_value 方法,序列化成上面图表示的 binary 数据,然后由引擎层存储成 blob 格式
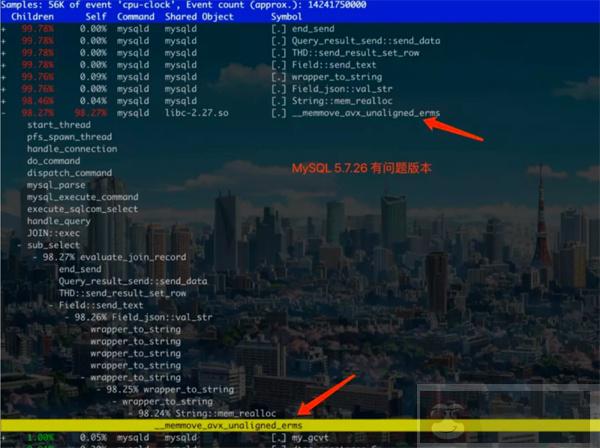
去年故障也有服务端的问题:加载单条数据失败主动 panic, 坑人不浅 (理由是数据不一致,宁可不对外提供服务,问题是那条数据恰好是重不重要的一类)。所以这个故事告诉我们: 在线服务的可用性,远高于数据一致性
慢的原因是 wrapper_to_string 遇到 json array 特别多的情况下反复 mem_realloc 创建内存空间,导致性能下降
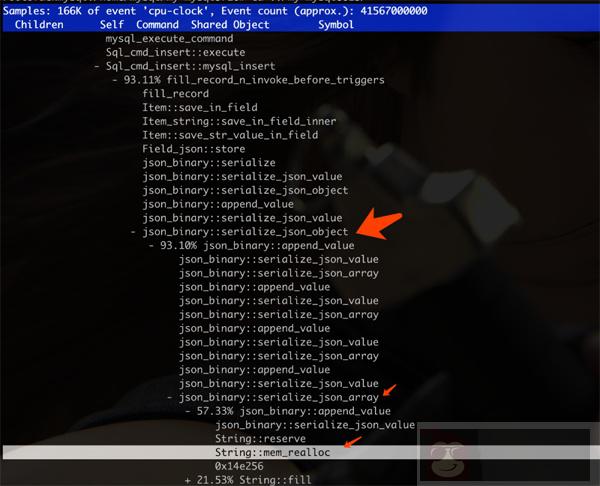
其实去年没有 fix 完整,最近发现写入也有类似问题,只不过是 serialize_json_value 写入存储引擎前反复 mem_realloc 造成超时。这时前端页面发现写入超时了,(人工) 重试继续写入 json 数据
恰好赶上联合索引中有 NULL 字段,由此引出了唯一索引不唯一的现象。那怎么解决呢? 前端按钮 cooldown 治标不治本,sql 执行 12s 前端肯定又点击提交了,治本还得升级 mysql 8.0 并且移除 NULL 字段, 那会不会又引入其它问题呢?
项目初期做了错误的决定,后人很容易买单。希望我们踩到的坑,能让你决定使用 json 前犹豫几秒钟 ^^
在测试机上发现 8.0 是 ok 的,没有性能问题,查看提交的 commit, 2016 年就有人发现并 fix 了,不知道有没有 back port 到 mysql 5.7 那几个版本
| commit a2f9ea422e4bdfd65da6dd0c497dc233629ec52e | |
| Author: Knut Anders Hatlen | |
| Date: Fri Apr 1 12:56:23 2016 +0200 | |
| Bug#23031146: INSERTING 64K SIZE RECORDS TAKE TOO MUCH TIME | |
| If a JSON value consists of a large sub-document which is wrapped in | |
| many levels of JSON arrays or objects, serialization of the JSON value | |
| may take a very long time to complete. | |
| This is caused by how the serialization switches between the small | |
| storage format (used by documents that need less than 64KB) and the | |
| large storage format. When it detects that the large storage format | |
| has to be used, it redoes the serialization of the current | |
| sub-document using the large format. But this re-serialization has to | |
| be redone again when the parent of the sub-document is switched from | |
| small format to large format. For deeply nested documents, the inner | |
| parts end up getting re-serializing again and again. | |
| This patch changes how the switch between the formats is done. Instead | |
| of starting with re-serializing the inner parts, it now starts with | |
| the outer parts. If a sub-document exceeds the maximum size for the | |
| small format, we know that the parent document will exceed it and need | |
| to be re-serialized too. Re-serializing an inner document is therefore | |
| a waste of time if we haven't already expanded its parent. By starting | |
| with expanding the outer parts of the JSON document, we avoid the | |
| wasted work and speed up the serialization. |
参考资料
[1]json-function-reference: https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/json-function-reference.html
















