共计 2890 个字符,预计需要花费 8 分钟才能阅读完成。
| 导读 | Systemctl 是 systemd 用于管理系统和管理服务的工具。许多现代 Linux 发行版,如 Ubuntu、Debian、Fedora、Linux Mint、OpenSuSE、Redhat 都采用 systemd 作为默认的 init 系统。 |
使用 systemctl,可以启动、停止、重新加载、重启服务、列出服务单元、检查服务状态、启用 / 禁用服务、管理运行级别和电源管理。在本文中将展示如何在 Linux 中使用 systemctl 命令来管理 systemd 服务。
使用 systemctl 启动服务时,命令格式:systemctl start [service-name]。例如,启动 firewalld 服务:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start firewalld
与以前老版本的 linux 中的 service 命令相反,systemctl start 命令不输出任何内容。
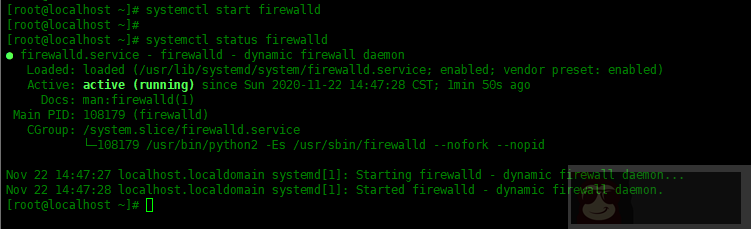
要停止服务,请使用systemctl stop [service-name]。例如,停止 firewalld 服务:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
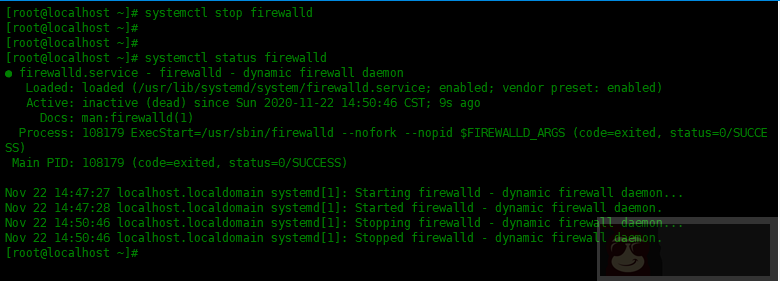
要重新启动服务,请使用systemctl restart [service-name],例如:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart firewalld
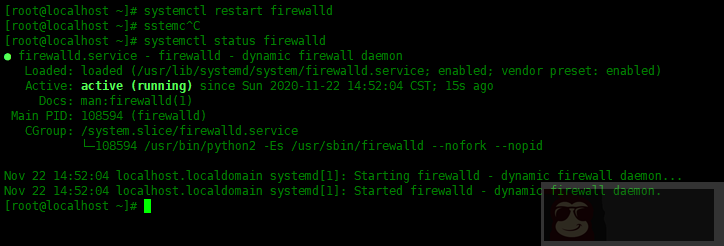
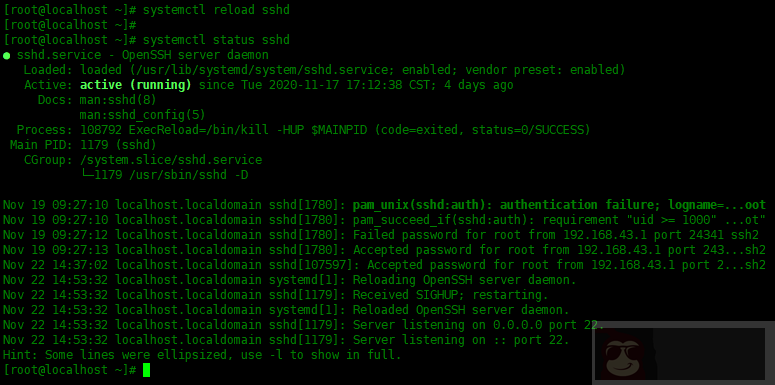
要重新加载服务的配置(例如 ssh)而不重新启动它,请使用systemctl reload [service-name],例如:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl reload sshd
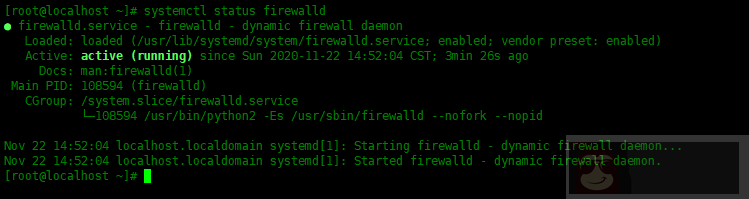
为了查看服务是否正在运行,我们可以使用 systemctl status [service-name] 来查看。
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl status firewalld
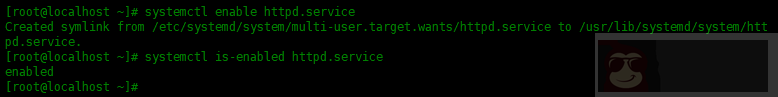
要在引导时启用服务,请使用systemctl enable [service-name],例如:
| [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable httpd.service | |
| Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service. |
同样,disable 时取消引导时启用服务:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl disable httpd.service
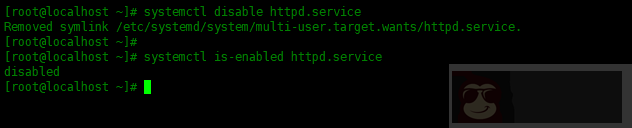
可以使用 is-enabled 选项检查开机是否启动该服务,请运行:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl is-enabled httpd.service
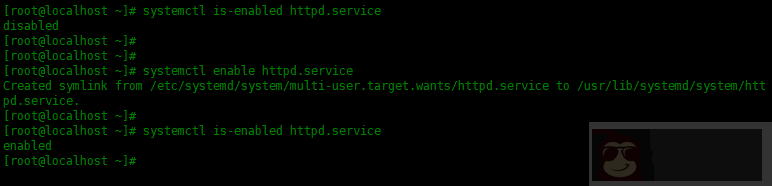
输出的内容 enabled 表示开机时启动该服务,disabled表示开机时不启动该服务。
要列出所有激活的单元,使用 list-units 选项。
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl list-units
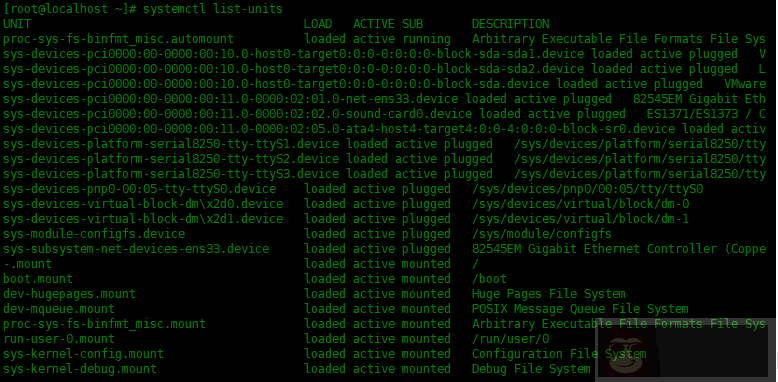
要列出所有活动的服务,请运行:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl list-units -t service
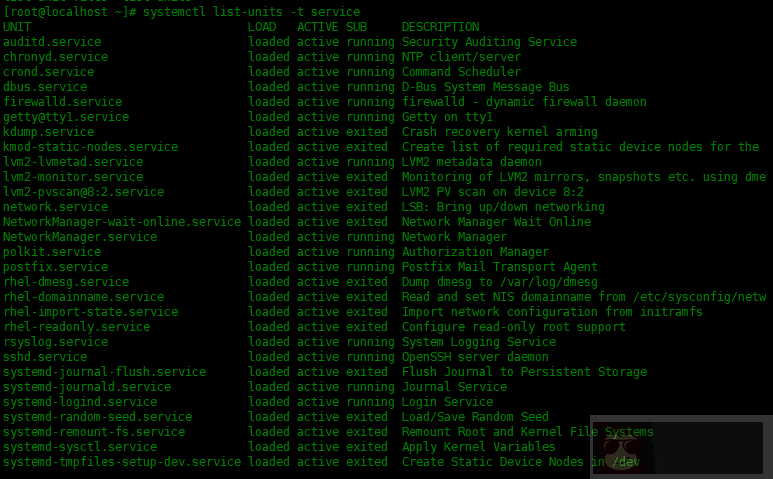
像 poweroff、shutdown 命令一样,systemctl 命令可以关闭系统,重启或进入休眠状态。
关机:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl poweroff
重启:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl reboot
系统休眠:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl hibernate
通常,上述所有 systemctl 命令都可以用于通过 systemctl 命令本身管理远程主机。这将使用 ssh 与远程主机进行通信。如下所示:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl status httpd -H root@192.168.0.12
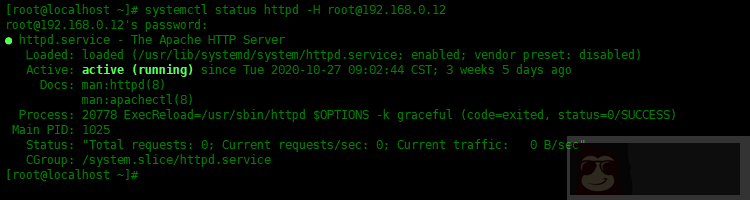
-H选项,指定远程主机的用户名和密码。
Systemd 具有 Targets 的概念,这些 Targets 的目的与 sysVinit 系统中的运行级别相似。sysVinit 中的运行级别主要是数字(0,1,2,-6)。以下是 sysVinit 中的运行级别及其对应的 systemd 中的 target:
| 0 runlevel0.target, poweroff.target | |
| 1 runlevel1.target, rescue.target | |
| 2,3,4 runlevel2.target, runlevel3.target,runlevel4.target, multi-user.target | |
| 5 runlevel5.target, graphical.target | |
| 6 runlevel6.target, reboot.target |
如果想要查看当前的运行级别,可以使用如下命令:
| [root@localhost ~]# systemctl get-default | |
| multi-user.target |
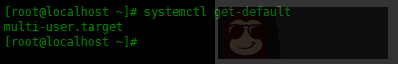
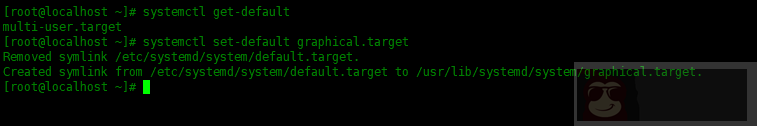
设置默认的运行级别为 graphical,命令如下:
| [root@localhost ~]# systemctl set-default graphical.target | |
| Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/default.target. | |
| Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/default.target to /usr/lib/systemd/system/graphical.target. |
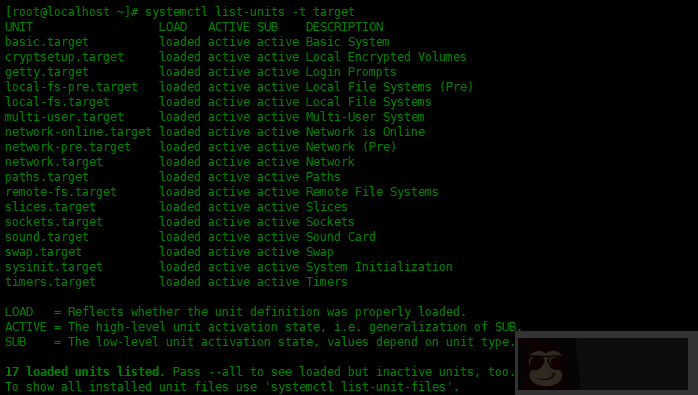
想要列出所有激活的 target,可以使用下面命令:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl list-units -t target
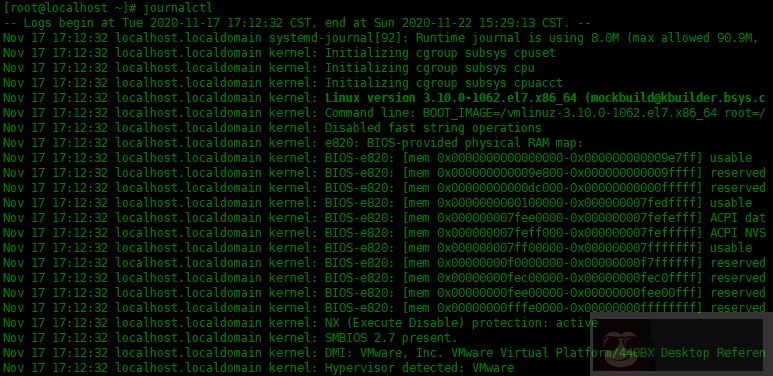
systemd 有自己的日志系统,称为 journald。它替换了 sysVinit 中的 syslogd。
[root@localhost ~]# journalctl
要查看所有引导消息,请运行命令journalctl -b
[root@localhost ~]# journalctl -b
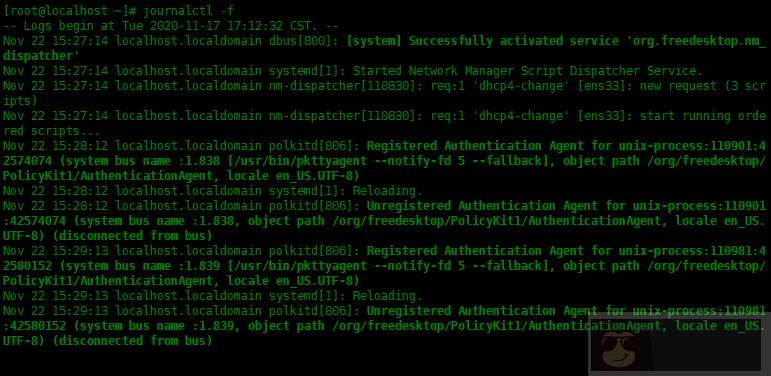
以下命令实时跟踪系统日志(类似于 tail -f):
[root@localhost ~]# journalctl -f
| [] | |
| Startup finished in 497ms (kernel) + 1.836s (initrd) + 6.567s (userspace) = 8.901s |
![]()
最后显示系统启动时间为 8.901 秒。
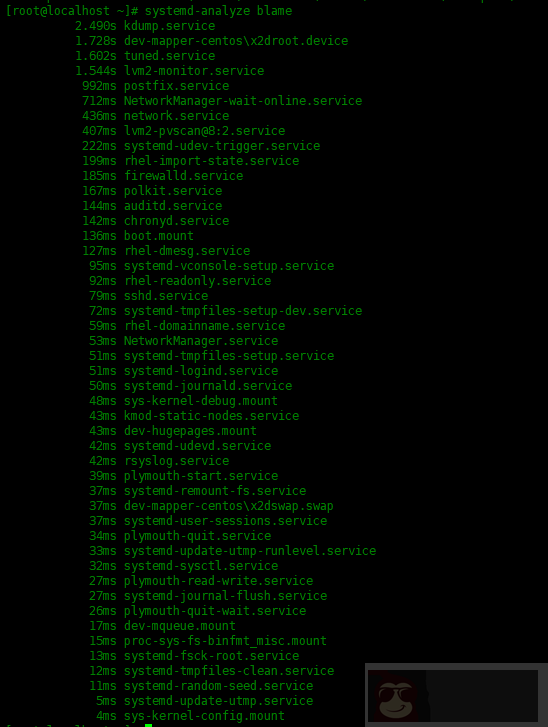
查看服务的启动时间:
[root@localhost ~]# systemd-analyze blame
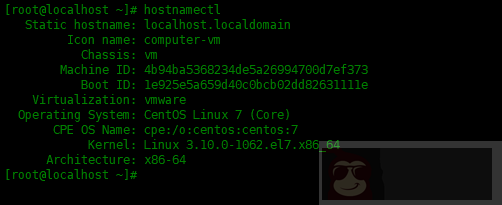
查看主机名称:
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl
在本文学习了 systemctl 命令来管理 Linux 发行版中的系统服务。
















