共计 3044 个字符,预计需要花费 8 分钟才能阅读完成。
使用 Spring MVC 开发 Web 应用程序的主要工作就是编写 Controller 逻辑。在 Web 应用中,除了需要使用 MVC 给用户显示页面外,还有一类 API 接口,我们称之为 REST,通常输入输出都是 JSON,便于第三方调用或者使用页面 JavaScript 与之交互。
直接在 Controller 中处理 JSON 是可以的,因为 Spring MVC 的 @GetMapping 和@PostMapping都支持指定输入和输出的格式。如果我们想接收 JSON,输出 JSON,那么可以这样写:
| (value = "/rest", | |
| consumes = "application/json;charset=UTF-8", | |
| produces = "application/json;charset=UTF-8") | |
| public String rest( User user) {return "{\"restSupport\":true}"; | |
| } |
对应的 Maven 工程需要加入 Jackson 这个依赖:com.fasterxml.jackson.core:jackson-databind:2.14.0
注意到 @PostMapping 使用 consumes 声明能接收的类型,使用 produces 声明输出的类型,并且额外加了 @ResponseBody 表示返回的 String 无需额外处理,直接作为输出内容写入 HttpServletResponse。输入的 JSON 则根据注解@RequestBody 直接被 Spring 反序列化为 User 这个 JavaBean。
使用 curl 命令测试一下:
| curl -v -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"email":"[email protected]"}' http://localhost:8080/rest | |
| POST /rest HTTP/1.1 | |
| Host: localhost:8080 | |
| User-Agent: curl/7.64.1 | |
| Accept: */* | |
| Content-Type: application/json | |
| Content-Length: 27 | |
| < HTTP/1.1 200 | |
| < Content-Type: application/json;charset=utf-8 | |
| < Content-Length: 20 | |
| < Date: Sun, 10 May 2020 09:56:01 GMT | |
| < | |
| {"restSupport":true} |
输出正是我们写入的字符串。
直接用 Spring 的 Controller 配合一大堆注解写 REST 太麻烦了,因此,Spring 还额外提供了一个 @RestController 注解,使用 @RestController 替代 @Controller 后,每个方法自动变成 API 接口方法。我们还是以实际代码举例,编写 ApiController 如下:
| ("/api") | |
| public class ApiController { | |
| UserService userService; | |
| ("/users") | |
| public List<User> users() {return userService.getUsers();} | |
| ("/users/{id}") | |
| public User user(("id") long id) {return userService.getUserById(id); | |
| } | |
| ("/signin") | |
| public Map<String, Object> signin( SignInRequest signinRequest) {try {User user = userService.signin(signinRequest.email, signinRequest.password); | |
| return Map.of("user", user); | |
| } catch (Exception e) {return Map.of("error", "SIGNIN_FAILED", "message", e.getMessage()); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| public static class SignInRequest {public String email; | |
| public String password; | |
| } | |
| } |
编写 REST 接口只需要定义@RestController,然后,每个方法都是一个 API 接口,输入和输出只要能被 Jackson 序列化或反序列化为 JSON 就没有问题。我们用浏览器测试 GET 请求,可直接显示 JSON 响应:
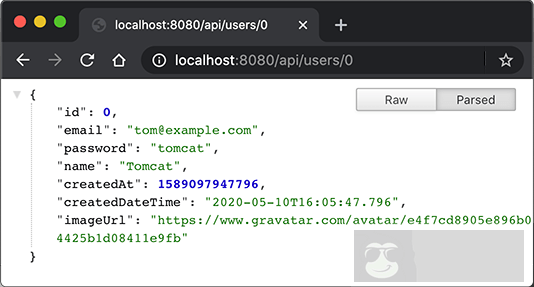
要测试 POST 请求,可以用 curl 命令:
| $ curl -v -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"email":"[email protected]","password":"bob123"}' http://localhost:8080/api/signin | |
| > POST /api/signin HTTP/1.1 | |
| > Host: localhost:8080 | |
| > User-Agent: curl/7.64.1 | |
| > Accept: */* | |
| > Content-Type: application/json | |
| > Content-Length: 47 | |
| > | |
| < HTTP/1.1 200 | |
| < Content-Type: application/json | |
| < Transfer-Encoding: chunked | |
| < Date: Sun, 10 May 2020 08:14:13 GMT | |
| < | |
| {"user":{"id":1,"email":"[email protected]","password":"bob123","name":"Bob",... |
注意观察上述 JSON 的输出,User能被正确地序列化为 JSON,但暴露了 password 属性,这是我们不期望的。要避免输出 password 属性,可以把 User 复制到另一个 UserBean 对象,该对象只持有必要的属性,但这样做比较繁琐。另一种简单的方法是直接在 User 的password属性定义处加上 @JsonIgnore 表示完全忽略该属性:
| public class User { | |
| ... | |
| public String getPassword() {return password; | |
| } | |
| ... | |
| } |
但是这样一来,如果写一个 register(User user) 方法,那么该方法的 User 对象也拿不到注册时用户传入的密码了。如果要允许输入password,但不允许输出password,即在 JSON 序列化和反序列化时,允许写属性,禁用读属性,可以更精细地控制如下:
| public class User { | |
| ... | |
| (access = Access.WRITE_ONLY) | |
| public String getPassword() {return password; | |
| } | |
| ... | |
| } |
同样的,可以使用 @JsonProperty(access = Access.READ_ONLY) 允许输出,不允许输入。
练习
使用 REST 实现 API。
下载练习
小结
使用 @RestController 可以方便地编写 REST 服务,Spring 默认使用 JSON 作为输入和输出。
要控制序列化和反序列化,可以使用 Jackson 提供的 @JsonIgnore 和@JsonProperty注解。
















