共计 3134 个字符,预计需要花费 8 分钟才能阅读完成。
linux 下可以通过 iostat 查看目前主机总的 io 使用情况,不过当通过 top 等命令查看时,发现 cpu wait 占多过多,想定位具体是哪些程序占用了 IO,本篇就通过一些常用的手段进行汇总下。
wa = I/O waiting,wa 指的是 CPU 等待磁盘写入完成的时间,就是说前提是要进行 IO 操作,在进行 IO 操作的时候,CPU 等待时间。如一个程序执行的最后,从系统空间到 dst 硬盘空间的时候,如果程序是阻塞的,那么这个时候 cpu 就要等待数据写入磁盘才能完成写操作了。所以这个时候 cpu 等待的时间就是 wa。
所以 wa 状态占比越高,证明 IO 越繁忙。
我们可以通过以下指令查看当前 io 的总终态:
| [root@361way ~]# sar -u 2 5 | |
| Linux 2.6.32-431.29.2.el6.x86_64 (361way) 01/25/2015 _x86_64_ (1 CPU) | |
| 06:59:58 PM CPU %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle | |
| 07:00:00 PM all 1.00 0.00 0.50 0.00 0.00 98.50 | |
| 07:00:02 PM all 5.05 0.00 1.52 1.01 0.00 92.42 | |
| 07:00:04 PM all 0.50 0.00 0.50 0.00 0.00 98.99 | |
| 07:00:06 PM all 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.00 | |
| 07:00:08 PM all 0.50 0.00 0.00 0.50 0.00 98.99 | |
| Average: all 1.41 0.00 0.50 0.30 0.00 97.79 | |
| [root@361way ~]# vmstat 2 5 | |
| procs -----------memory---------- ---swap-- -----io---- --system-- -----cpu----- | |
| r b swpd free buff cache si so bi bo in cs us sy id wa st | |
| 0 0 0 98488 209916 218256 0 0 8 28 11 10 5 0 95 0 0 | |
| 0 0 0 98480 209916 218256 0 0 0 0 155 198 0 0 100 0 0 | |
| 0 0 0 98496 209916 218256 0 0 0 0 141 191 1 0 99 0 0 | |
| 0 0 0 98496 209916 218256 0 0 0 0 142 189 0 1 99 0 0 | |
| 0 0 0 98512 209916 218256 0 0 0 0 152 189 0 0 100 0 0 | |
| [root@361way ~]# iostat -x 1 2 | |
| Linux 2.6.32-431.29.2.el6.x86_64 (361way) 01/25/2015 _x86_64_ (1 CPU) | |
| avg-cpu: %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle | |
| 4.71 0.00 0.42 0.24 0.00 94.63 | |
| Device: rrqm/s wrqm/s r/s w/s rsec/s wsec/s avgrq-sz avgqu-sz await svctm %util | |
| xvda 0.00 0.13 0.31 0.91 14.08 8.30 18.39 0.01 11.84 1.38 0.17 | |
| xvdb 0.00 2.12 0.05 3.90 1.52 48.10 12.57 0.05 11.84 0.57 0.22 | |
| avg-cpu: %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle | |
| 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.00 | |
| Device: rrqm/s wrqm/s r/s w/s rsec/s wsec/s avgrq-sz avgqu-sz await svctm %util | |
| xvda 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 | |
| xvdb 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 |
可以通过 linux 下最常用的两个命令 top、ps 找出目前正在占用 IO 的进程。在进行下一步之前我了解一下 D 状态,ps 命令中查看的状态有 D、R、S、Z、T,D 状态指不可中断睡眠 (通常是在 IO 操作) 收到信号不唤醒和不可运行, 进程必须等待直到有中断发生。
找出当前进程为 D 的状态:
while true; do date; ps auxf | awk '{if($8=="D") print $0;}'; sleep 1; don
上面的这个操作有一个缺点,就是一旦匹配到一个进程为 D 的,就开始重新执行下一个循环。而想查看所有当于 D 状态的进程,可以将其改为如下:
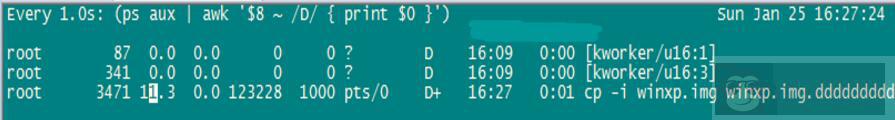
watch -d -n 1 “(ps aux | awk ‘\$8 ~ /D/ { print \$0}’)”
如下,是我在执行一个大文件的 cp 时,通过上面的指令查看到的结果:
除此之外,还可以通过专用工具去查看,如 iotop 或 latencytop。这里以 iotop 为例,执行后会显示当前的读写速度及每个进程占用的速度。执行后可以按 o 仅显示占用 IO 的进程:
| [root@361way ~]# iotop --help | |
| Usage: /usr/sbin/iotop [OPTIONS] | |
| DISK READ and DISK WRITE are the block I/O bandwidth used during the sampling | |
| period. SWAPIN and IO are the percentages of time the thread spent respectively | |
| while swapping in and waiting on I/O more generally. PRIO is the I/O priority at | |
| which the thread is running (set using the ionice command). | |
| Controls: left and right arrows to change the sorting column, r to invert the | |
| sorting order, o to toggle the --only option, p to toggle the --processes | |
| option, a to toggle the --accumulated option, q to quit, any other key to force | |
| a refresh. | |
| Options: | |
| --version show program's version number and exit | |
| -h, --help show this help message and exit | |
| -o, --only only show processes or threads actually doing I/O | |
| -b, --batch non-interactive mode | |
| -n NUM, --iter=NUM number of iterations before ending [infinite] | |
| -d SEC, --delay=SEC delay between iterations [1 second] | |
| -p PID, --pid=PID processes/threads to monitor [all] | |
| -u USER, --user=USER users to monitor [all] | |
| -P, --processes only show processes, not all threads | |
| -a, --accumulated show accumulated I/O instead of bandwidth | |
| -k, --kilobytes use kilobytes instead of a human friendly unit | |
| -t, --time add a timestamp on each line (implies --batch) | |
| -q, --quiet suppress some lines of header (implies --batch) |
















