共计 6803 个字符,预计需要花费 18 分钟才能阅读完成。
1、ganglia 简介
Ganglia 是一款为 HPC(高性能计算)集群而设计的可扩展的分布式监控系统,它可以监视和显示集群中的节点的各种状态信息,它由运行在各个节点上的 gmond 守护进程来采集 CPU、内存、硬盘利用率、I/O 负载、网络流量情况等方面的数据,然后汇总到 gmetad 守护进程下,使用 rrdtool 存储数据,最后将历史数据以曲线方式通过 PHP 页面呈现。
Ganglia 的特点如下:
良好的扩展性,分层架构设计能够适应大规模服务器集群的需要
负载开销低,支持高并发
广泛支持各种操作系统(UNIX 等)和 cpu 架构,支持虚拟
2、ganglia 组成
Ganglia 监控系统有三部分组成,分别是 gmond、gmetad、webfrontend,作用如下。
gmond: 即为 ganglia monitoring daemon,是一个守护进程,运行在每一个需要监测的节点上,用于收集本节点的信息并发送到其他节点,同时也接收其他节点发过了的数据,默认的监听端口为 8649。
gmetad: 即为 ganglia meta daemon,是一个守护进程,运行在一个数据汇聚节点上,定期检查每个监测节点的 gmond 进程并从那里获取数据,然后将数据指标存储在本地 RRD 存储引擎中。
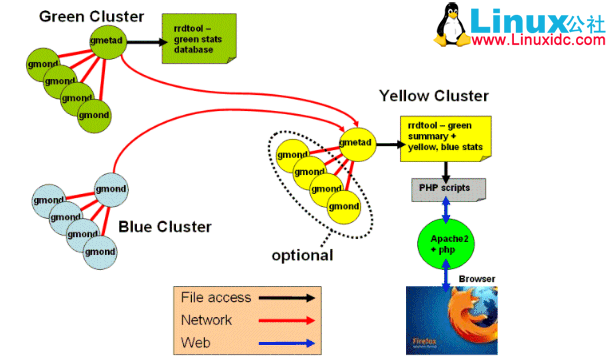
webfrontend: 是一个基于 web 的图形化监控界面,需要和 Gmetad 安装在同一个节点上,它从 gmetad 取数据,并且读取 RRD 数据库,通过 rrdtool 生成图表,用于前台展示,界面美观、丰富,功能强大。下图是其结构
环境规划(CentOS6.7)
服务器端 172.16.80.117
客户端 172.16.80.117 172.16.80.116
3、ganglia 的安装
[root@centos02 tools]# wget wget
[root@centos02 tools]# rpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
[root@centos02 tools]# yum install ganglia-gmetad.x86_64 ganglia-gmond.x86_64 ganglia-gmond-python.x86_64 -y
修改服务端配置文件
[root@centos02 tools]# vim /etc/ganglia/gmetad.conf
data_source “my cluster” 172.16.80.117 172.16.80.116
gridname “MyGrid”
ganglia web 的安装(基于 LNMP 环境)
[root@centos02 tools]# tar xf ganglia-web-3.7.2.tar.gz
[root@centos02 tools]# mv ganglia-web-3.7.2 /application/nginx/html/ganglia
修改 ganglia web 的 php 配置文件
[root@centos02 tools]# vim /application/nginx/html/ganglia/conf_default.php
$conf[‘gweb_confdir’] = “/application/nginx/html/ganglia”;
nginx 配置
[root@centos02 ganglia]# cat /application/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
worker_processes 2;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
log_format main ‘$remote_addr – $remote_user [$time_local] “$request” ‘
‘$status $body_bytes_sent “$http_referer” ‘
‘”$http_user_agent” “$http_x_forwarded_for”‘;
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.linuxidc.com martin.com;
location / {
root html/zabbix;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
}
location ~ .*\.(php|php5)?$ {
root html/zabbix;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi.conf;
}
access_log logs/access_zabbix.log main;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name ganglia.linuxidc.com;
location / {
root html/ganglia;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
}
location ~ .*\.(php|php5)?$ {
root html/ganglia;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi.conf;
}
access_log logs/access_bbs.log main;
}
###status
server{
listen 80;
server_name status.linuxidc.org;
location / {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
}
}
}
访问测试,报错如下
Fatal error:Errors were detected in your configuration.
DWOO compiled templates directory ‘/application/nginx/html/ganglia/dwoo/compiled’ is not writeable.
Please adjust $conf[‘dwoo_compiled_dir’].
DWOO cache directory ‘/application/nginx/html/ganglia/dwoo/cache’ is not writeable.
Please adjust $conf[‘dwoo_cache_dir’].
in /application/nginx-1.6.3/html/ganglia/eval_conf.php on line 126
解决办法:
[root@centos02 tools]# mkdir /application/nginx/html/ganglia/dwoo/compiled
[root@centos02 tools]# mkdir /application/nginx/html/ganglia/dwoo/cache
[root@centos02 tools]# chmod 777 /application/nginx/html/ganglia/dwoo/compiled
[root@centos02 tools]# chmod 777 /application/nginx/html/ganglia/dwoo/cache
[root@centos02 html]# chmod -R 777 /var/lib/ganglia/rrds
修改客户端配置文件(所有的客户端都需要做)
[root@centos02 tools]# vim /etc/ganglia/gmond.conf
cluster {
name = “my cluster” #这个名字要和服务器端定义的 data_source 后面的名字一样
owner = “unspecified”
latlong = “unspecified”
url = “unspecified”
}
udp_send_channel {
#bind_hostname = yes # Highly recommended, soon to be default.
# This option tells gmond to use a source address
# that resolves to the machine’s hostname. Without
# this, the metrics may appear to come from any
# interface and the DNS names associated with
# those IPs will be used to create the RRDs.
# mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
host = 172.16.80.117 #这里我们采用单播方式,默认是组播
port = 8649
# ttl = 1
}
udp_recv_channel {
# mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
port = 8649
# bind = 239.2.11.71
retry_bind = true
# Size of the UDP buffer. If you are handling lots of metrics you really
# should bump it up to e.g. 10MB or even higher.
# buffer = 10485760
}
4、再次访问测试
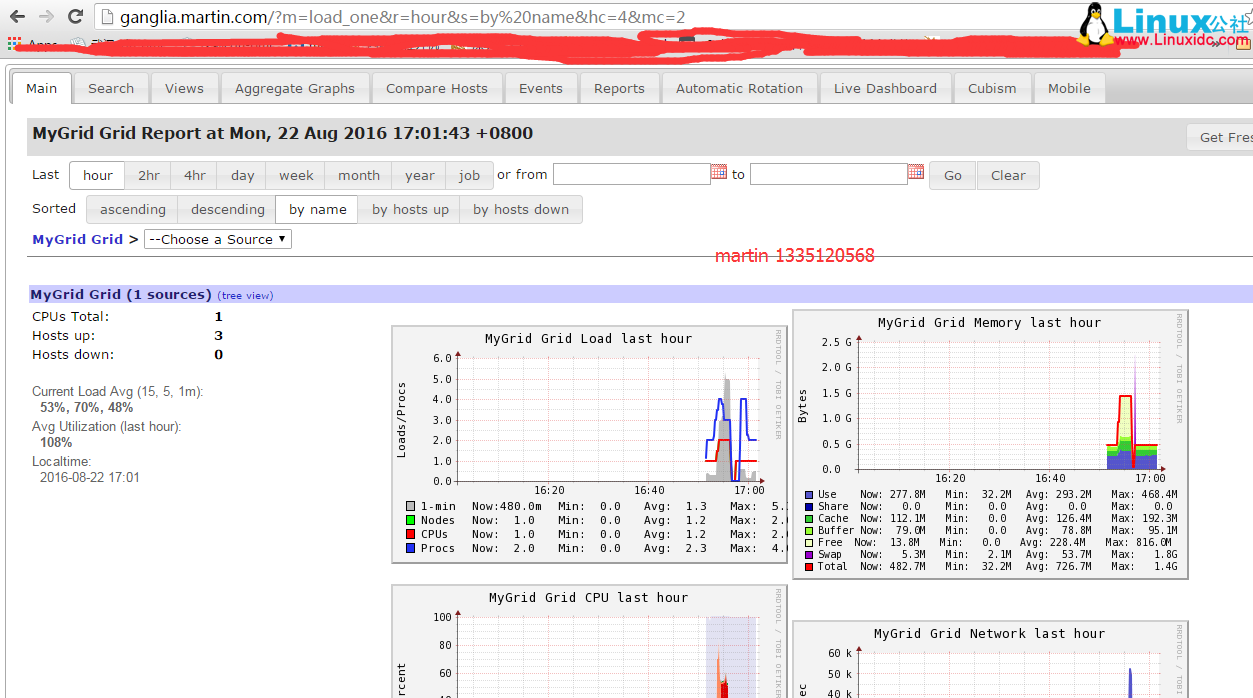
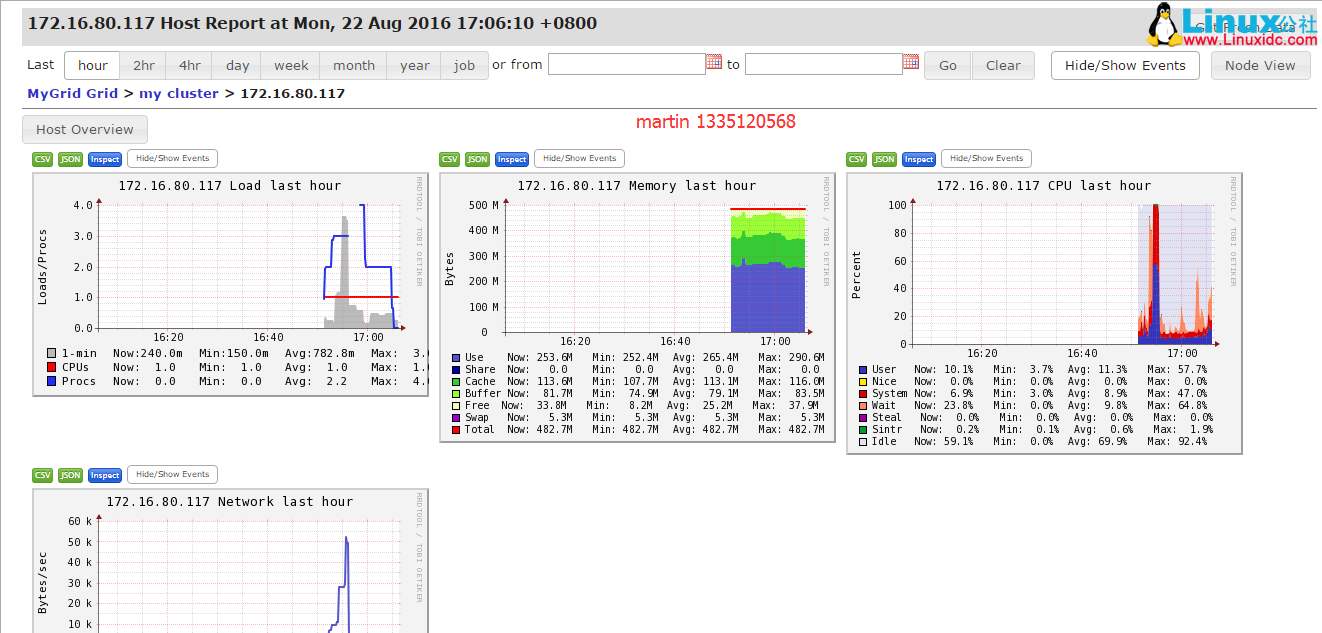
这里是整个集群的一个总的汇总图,而不是单台服务器的图,下面我们打开单台服务器的图看看
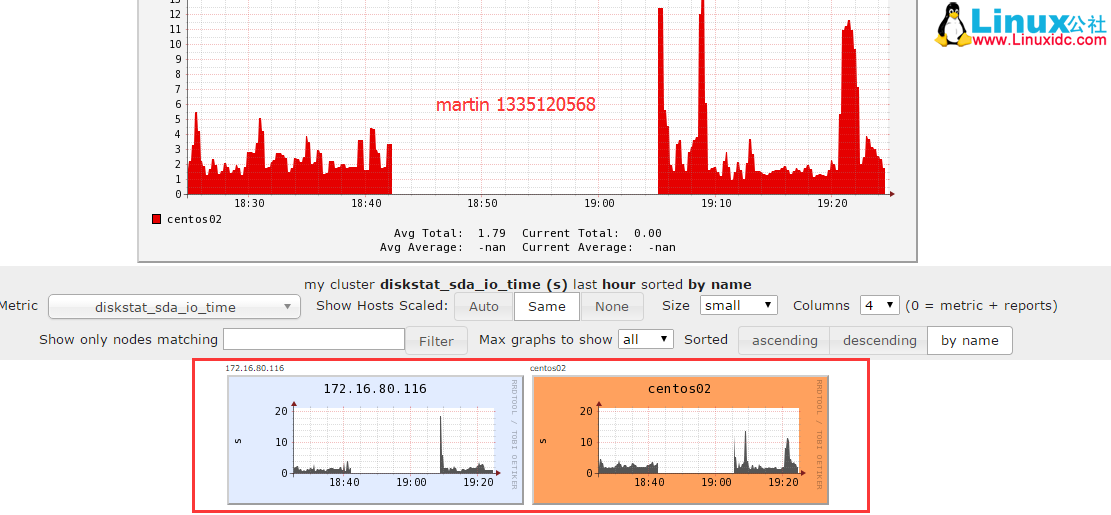
再来看看对同一指标,每台服务器一起显示的图
5、扩展 Ganglia 监控功能的方法
默认安装完成的 Ganglia 仅向我们提供基础的系统监控信息,通过 Ganglia 插件可以实现两种扩展 Ganglia 监控功能的方法。
1)添加带内(in-band)插件,主要是通过 gmetric 命令来实现。
这是通常使用的一种方法,主要是通过 crontab 方法并调用 Ganglia 的 gmetric 命令来向 gmond 输入数据,进而实现统一监控。这种方法简单,对于少量的监控可以采用,但是对于大规模自定义监控时,监控数据难以统一管理。
2)添加一些其他来源的带外(out-of-band)插件,主要是通过 C 或者 Python 接口来实现。
在 Ganglia3.1.x 版本以后,增加了 C 或 Python 接口,通过这个接口可以自定义数据收集模块,并且可以将这些模块直接插入到 gmond 中以监控用户自定义的应用。
这里我们举例通过带外扩展的方式 来监控 nginx 的运行状态
配置 ganglia 客户端,收集 nginx_status 数据
[root@centos02 nginx_status]# pwd
/tools/gmond_python_modules-master/nginx_status
[root@centos02 nginx_status]# cp conf.d/nginx_status.pyconf /etc/ganglia/conf.d/
[root@centos02 nginx_status]# cp python_modules/nginx_status.py /usr/lib64/ganglia/python_modules/
[root@centos02 nginx_status]# cp graph.d/nginx_* /application/nginx/html/ganglia/graph.d/
[root@centos02 mysql]# cat /etc/ganglia/conf.d/nginx_status.pyconf
#
modules {
module {
name = ‘nginx_status’
language = ‘python’
param status_url {
value = ‘http://status.linuxidc.org/’
}
param nginx_bin {
value = ‘/application/nginx/sbin/nginx’
}
param refresh_rate {
value = ’15’
}
}
}
collection_group {
collect_once = yes
time_threshold = 20
metric {
name = ‘nginx_server_version’
title = “Nginx Version”
}
}
collection_group {
collect_every = 10
time_threshold = 20
metric {
name = “nginx_active_connections”
title = “Total Active Connections”
value_threshold = 1.0
}
metric {
name = “nginx_accepts”
title = “Total Connections Accepted”
value_threshold = 1.0
}
metric {
name = “nginx_handled”
title = “Total Connections Handled”
value_threshold = 1.0
}
metric {
name = “nginx_requests”
title = “Total Requests”
value_threshold = 1.0
}
metric {
name = “nginx_reading”
title = “Connections Reading”
value_threshold = 1.0
}
metric {
name = “nginx_writing”
title = “Connections Writing”
value_threshold = 1.0
}
metric {
name = “nginx_waiting”
title = “Connections Waiting”
value_threshold = 1.0
}
}
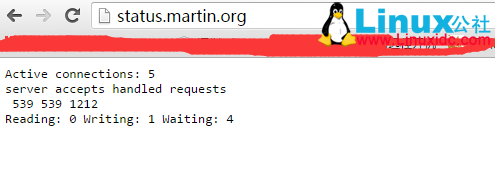
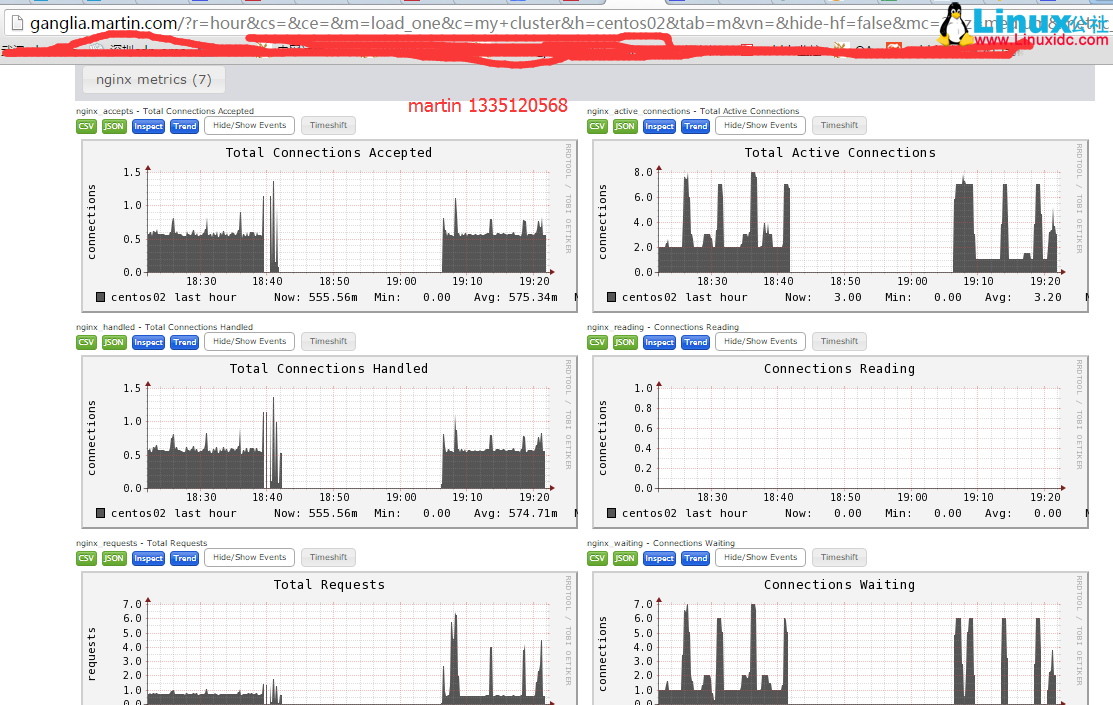
完成上面的所有步骤后,重启 Ganglia 客户端 gmond 服务,在客户端通过“gmond–m”
命令可以查看支持的模板,最后就可以在 Ganglia web 界面查看 Nginx 的运行状态
下面关于 Ganglia 的文章您也可能喜欢,不妨参考下:
Ganglia 3.1.x 下扩展 Python 模块(翻译自官方 wiki) http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2014-04/99565.htm
使用 Ganglia 监控 Hadoop 集群 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-05/61349.htm
在 VMware Workstation 的 Ubuntu 下安装和配置 Hadoop 与 Ganglia http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-06/85856.htm
Ganglia 安装部署之一建立 Grid http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-05/83673.htm
Ganglia 极其简单安装教程 yum 版 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-12/76536.htm
Ganglia 快速开始向导(翻译自官方 wiki)http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-11/92747.htm
CentOS 集群上安装 Ganglia-3.6.0 监控 Hadoop-2.2.0 和 HBase-0.96.0 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2014-01/95804.htm
Ganglia 在 CentOS 6.5 的安装 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2014-05/102024.htm
在 Ubuntu 14.04 Server 上安装 Ganglia http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2014-08/105838.htm
本文永久更新链接地址:http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2016-08/134668.htm
















