共计 12882 个字符,预计需要花费 33 分钟才能阅读完成。
1. 搭建一个测试集群,集群有 4 台机器,配置集群中每一台机器的 /etc/hosts 文件:
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
172.28.3.40 nn nn.Hadoop.plat
172.28.3.41 dn1 dn0.hadoop.plat
172.28.3.42 dn2 dn1.hadoop.plat
172.28.3.43 dn3 dn2.hadoop.plat
2. 配置 namenode 到 datanode ssh 免密码登陆:
在 nn 上执行,ssh-keygen –t rsa
cd ~/.ssh
cat id_rsa.put >> authorized_keys
对集群中每一台 data node 执行: ssh-copy-id root@dn1 ssh-copy-id root@dn2 ssh-copy-id root@dn13
这样就可以保证,nn 节点可以免密码登陆到 dn1, dn2, dn3
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr00:1A:4A:C6:6B:A0
inet addr:172.28.3.40 Bcast:172.28.7.255 Mask:255.255.248.0
inet6 addr: fe80::21a:4aff:fec6:6ba0/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:1064845 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:557212 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:1578655986 (1.4 GiB) TX bytes:647178854 (617.1 MiB)
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:103276 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:103276 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:58108687 (55.4 MiB) TX bytes:58108687 (55.4 MiB)
[root@nn .ssh]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
172.28.3.40 nn nn.hadoop.plat
172.28.3.41 dn1 dn0.hadoop.plat
172.28.3.42 dn2 dn1.hadoop.plat
172.28.3.43 dn3 dn2.hadoop.plat
[root@nn .ssh]# ssh dn1
SIOCADDRT: File exists
3. 关闭 iptables
chkconfig iptables off
/etc/init.d/iptables stop
4. 关闭 seLinux
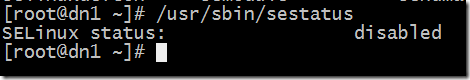
查看 selinux 状态:
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/sbin/sestatus –v
/usr/sbin/setenforce 0 #使 SELinux 工作模式变成 permissive 模式
/usr/sbin/setenforce 1 #使 SELinux 工作模式变成 enforcing 模式
这样就可以实时控制 SELinux 的启用和不启用了。
三个参数介绍介绍
- enforcing — The SELinux security policy is enforced.
- permissive — The SELinux system prints warnings but does not enforce policy.
- disabled — SELinux is fully disabled. SELinux hooks are disengaged from the kernel and the pseudo-file system is unregistered.
永久关闭 SELinux
编辑 /etc/selinux/config,找到 SELINUX 行修改成为:SELINUX=disabled:
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing – SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive – SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled – No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=disabled
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values:
# targeted – Only targeted network daemons are protected.
# strict – Full SELinux protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
如果重启系统,就会发现 SELinux 的状态变成 disabled
5. 关闭 linux 内核 huge_page:
| Add the following lines in /etc/rc.local and reboot the server: | |
| echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/RedHat_transparent_hugepage/enabled | |
| echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/redhat_transparent_hugepage/defrag |
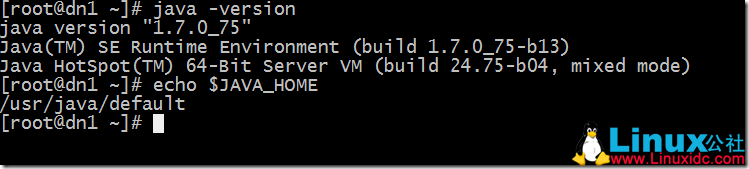
6. 安装 java,配置 JAVA_HOME
cd/usr/java
rz–be
/usr/java/jdk1.7.0_75
ln -s /usr/java/jdk1.7.0_75 /usr/java/default
vim/etc/profile
route add default gw172.28.0.1
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/default
export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
编辑好 /etc/profile,执行 source /etc/profile 使配置生效,保证每一台机器上的 java 版本都是一致的,并且 JAVA_HOME 环境变量是有效的:
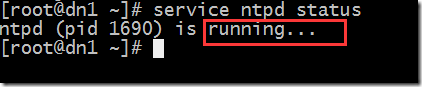
7. 每台机器上安装 ntpd
| rpm -aq | grep ntpd | |
| yum install ntpd | |
| chkconfig ntpd on | |
| service ntpd start |
确保每台机器的 ntpd 服务都处于运行状态:
8. 确保机器上安装了 openssh-server,并且升级 openssl 到最新:
| rpm -qa | grep ssh | |
| yum install openssh-server | |
| service sshd restart | |
| chkconfig sshd on |
确保 openssl 最新:
yum install openssl-devel-1.0.1e-42.el6.x86_64
9. yum 源确保可以用,本次安装采用了 163 的 yum 源,先将 /etc/yum.repos.d/ 中,所有的文件都删掉,然后新建文件 CentOS6-Base-163.repo,填入如下内容:
#
# The mirror system uses the connecting IP address of the client and the
# update status of each mirror to pick mirrors that are updated to and
# geographically close to the client. You should use thisfor CentOS updates
# unless you are manually picking other mirrors.
#
# If the mirrorlist= does not work for you, as a fall back you can try the
# remarked out baseurl= line instead.
#
#
[base]
name=CentOS-$releasever – Base – 163.com
baseurl=http://mirrors.163.com/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=os
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
#released updates
[updates]
name=CentOS-$releasever – Updates – 163.com
baseurl=http://mirrors.163.com/centos/$releasever/updates/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=updates
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
#additional packages that may be useful
[extras]
name=CentOS-$releasever – Extras – 163.com
baseurl=http://mirrors.163.com/centos/$releasever/extras/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=extras
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
#additional packages that extend functionality of existing packages
[centosplus]
name=CentOS-$releasever – Plus – 163.com
baseurl=http://mirrors.163.com/centos/$releasever/centosplus/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=centosplus
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
#contrib– packages by Centos Users
[contrib]
name=CentOS-$releasever – Contrib – 163.com
baseurl=http://mirrors.163.com/centos/$releasever/contrib/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=contrib
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
配置 ambari 的 yum 源,本配置源是部署在本地局域网中的一台 apache 服务器上的:
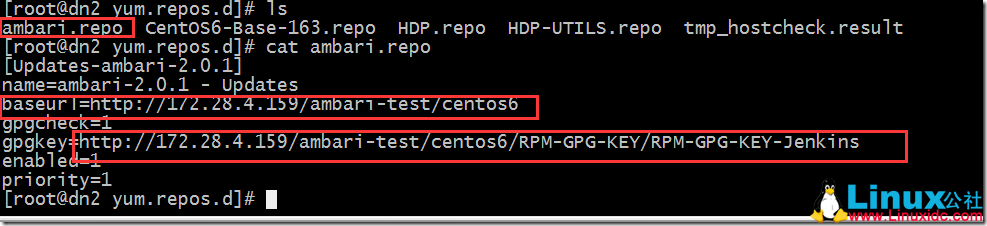
[Updates-ambari-2.0.1]
name=ambari-2.0.1 – Updates
baseurl=http://172.28.4.159/ambari-test/centos6
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://172.28.4.159/ambari-test/centos6/RPM-GPG-KEY/RPM-GPG-KEY-Jenkins
enabled=1
priority=1
[root@hdp159yum.repos.d]#
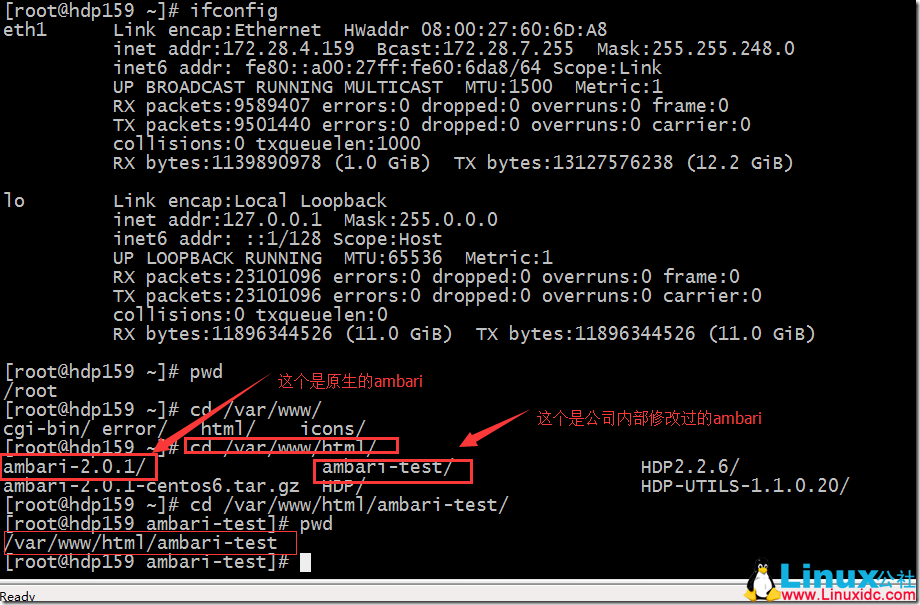
将 yum 源配置好好了后,执行如下命令:
| yum clean all | |
| yum repolist |
10. 在 nn 机器上,安装 ambari-servier,执行如下命令,之所以加—nogpgcheck 参数,是因为此处安装的是公司修改后的 ambari,如果是安装原生的 ambari,不用加该选项:
yum install --nogpgcheck ambari-server
11. 配置和启动 ambari-server, setup –j 配置 ambari-server 要使用的 java 环境:
| ambari-server setup -j /usr/java/default | |
| ambari-server start |
12. 在浏览器中,输入 nn:8080 进入 ambari 的登陆页面,用户名和密码都是 admin:
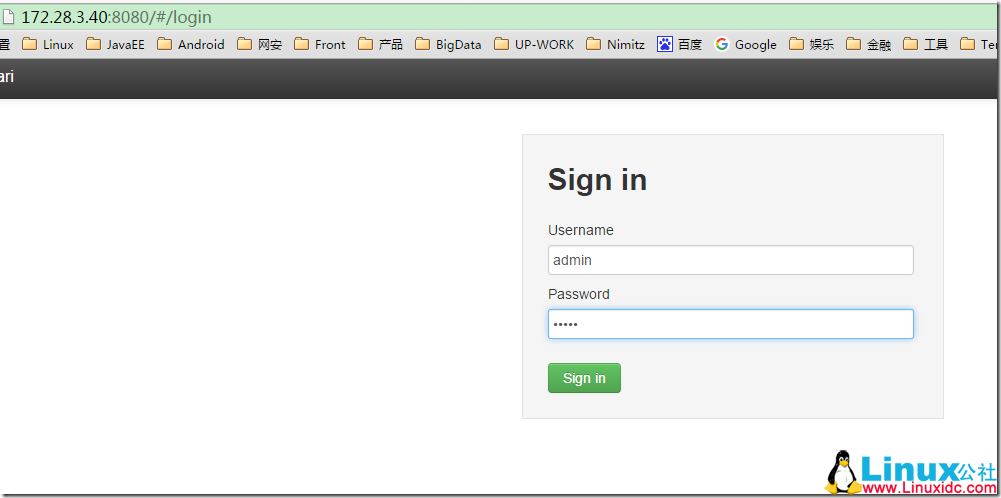
更多详情见请继续阅读下一页的精彩内容 :http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2017-03/141297p2.htm
13. 配置 HDP 的 RedHat6 的 baseURL, 此处使用的是本地局域网中的 HDP 安装源:
http://172.28.4.159/HDP2.2.6/HDP/CentOS6/2.x/updates/2.2.6.0/
http://172.28.4.159/HDP2.2.6/HDP-UTILS-1.1.0.20/repos/centos6/

14. 将 nn 节点下,/root/.ssh/id_rsa 文件上传到 ambari 中,配置好 Target Hosts:
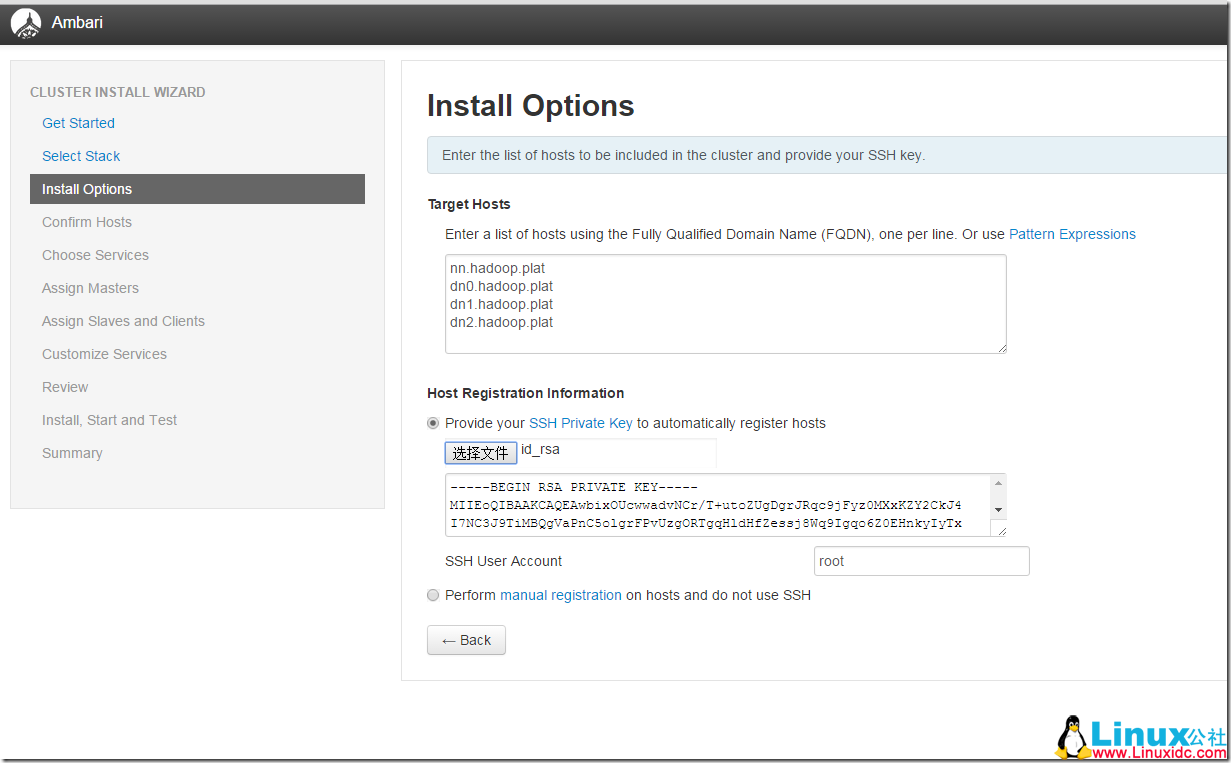
15. 发现一个警告消息,在每一台机器上执行如下命令,消除警告:
INFO:HostCleanup:
Killing pid‘s: [”]
INFO:HostCleanup:Deleting packages: [”]
INFO:HostCleanup:
Deleting directories: [”]
INFO:HostCleanup:Path doesn‘t exists:
INFO:HostCleanup:
Deleting additional directories: [”]
INFO:HostCleanup:
Deleting repo files: []
INFO:HostCleanup:
Erasing alternatives:{‘symlink_list‘: [”], ‘target_list‘: [”]}
INFO:HostCleanup:Path doesn‘t exists:
INFO:HostCleanup:Clean-up completed. The output is at /var/lib/ambari-agent/data/hostcleanup.result

16. 分配 slaves 和 clients:
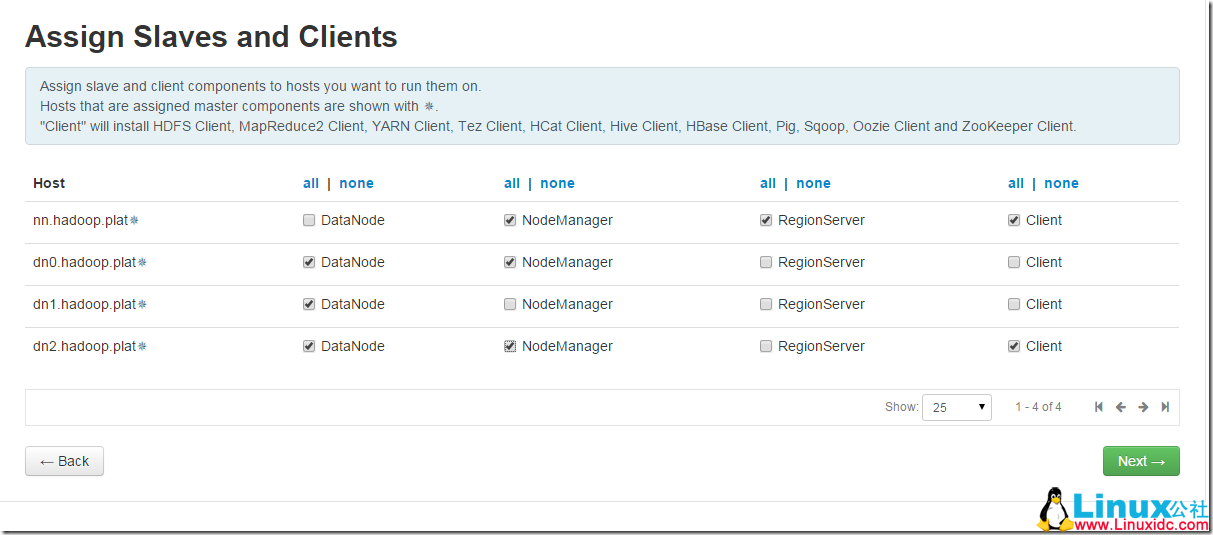
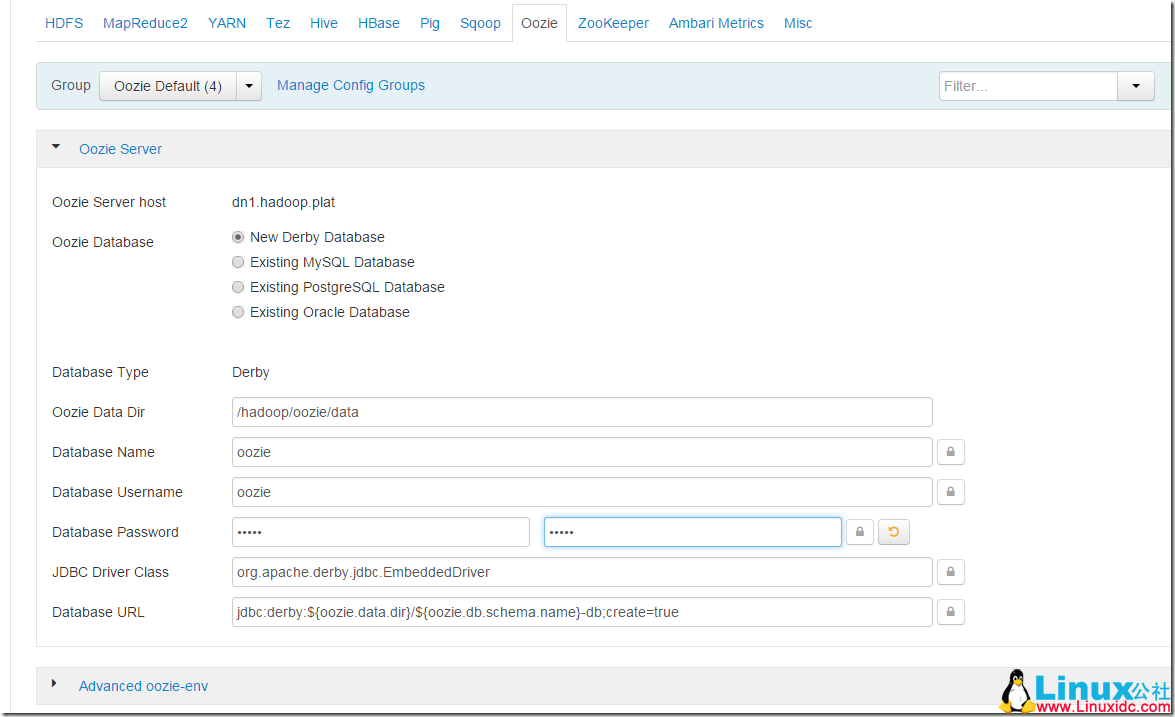
设置好,hive 和 oozie 数据库的用户名和密码:
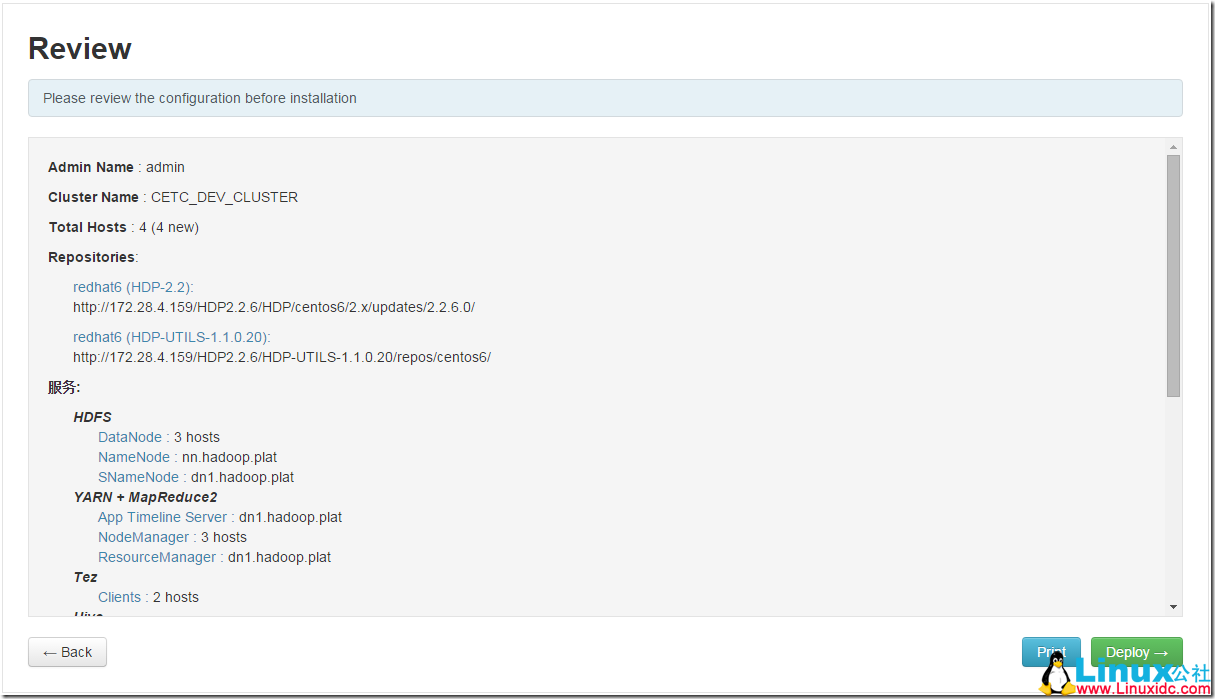
查看总结信息:
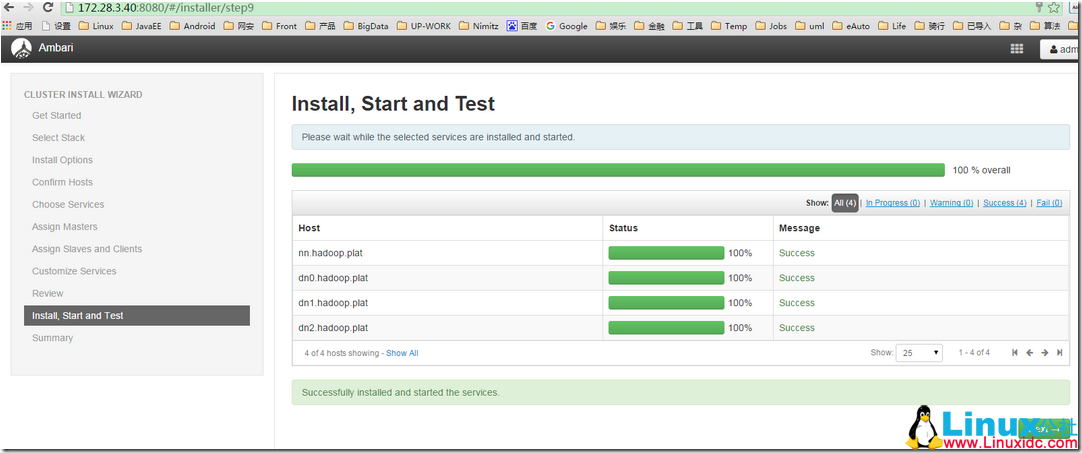
17. 进入安装流程,最后安装成功:
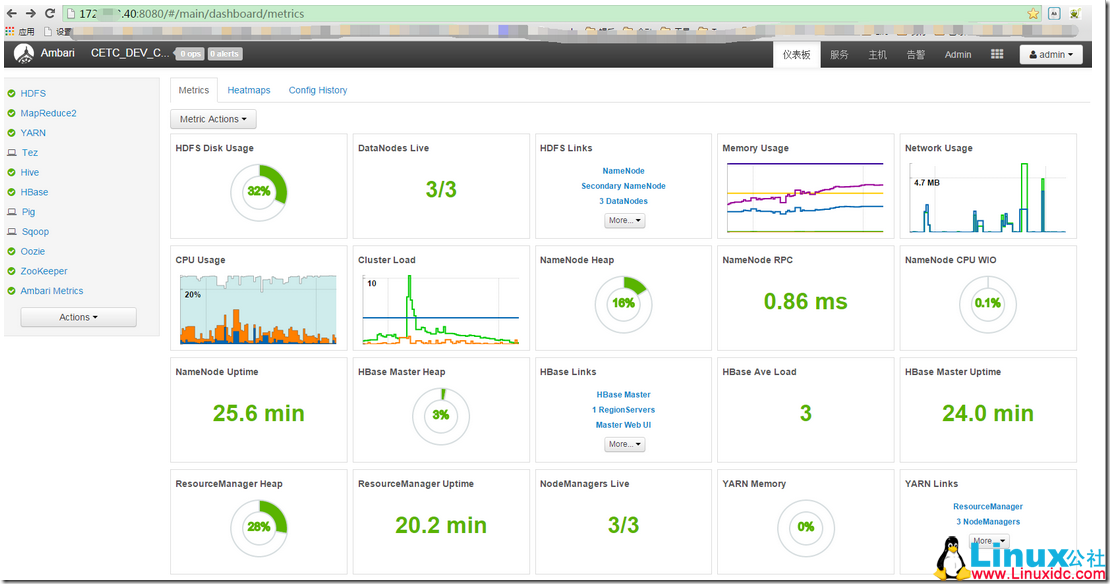
本文永久更新链接地址 :http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2017-03/141297.htm
1. 搭建一个测试集群,集群有 4 台机器,配置集群中每一台机器的 /etc/hosts 文件:
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
172.28.3.40 nn nn.Hadoop.plat
172.28.3.41 dn1 dn0.hadoop.plat
172.28.3.42 dn2 dn1.hadoop.plat
172.28.3.43 dn3 dn2.hadoop.plat
2. 配置 namenode 到 datanode ssh 免密码登陆:
在 nn 上执行,ssh-keygen –t rsa
cd ~/.ssh
cat id_rsa.put >> authorized_keys
对集群中每一台 data node 执行: ssh-copy-id root@dn1 ssh-copy-id root@dn2 ssh-copy-id root@dn13
这样就可以保证,nn 节点可以免密码登陆到 dn1, dn2, dn3
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr00:1A:4A:C6:6B:A0
inet addr:172.28.3.40 Bcast:172.28.7.255 Mask:255.255.248.0
inet6 addr: fe80::21a:4aff:fec6:6ba0/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:1064845 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:557212 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:1578655986 (1.4 GiB) TX bytes:647178854 (617.1 MiB)
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:103276 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:103276 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:58108687 (55.4 MiB) TX bytes:58108687 (55.4 MiB)
[root@nn .ssh]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
172.28.3.40 nn nn.hadoop.plat
172.28.3.41 dn1 dn0.hadoop.plat
172.28.3.42 dn2 dn1.hadoop.plat
172.28.3.43 dn3 dn2.hadoop.plat
[root@nn .ssh]# ssh dn1
SIOCADDRT: File exists
3. 关闭 iptables
chkconfig iptables off
/etc/init.d/iptables stop
4. 关闭 seLinux
查看 selinux 状态:
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/sbin/sestatus –v
/usr/sbin/setenforce 0 #使 SELinux 工作模式变成 permissive 模式
/usr/sbin/setenforce 1 #使 SELinux 工作模式变成 enforcing 模式
这样就可以实时控制 SELinux 的启用和不启用了。
三个参数介绍介绍
- enforcing — The SELinux security policy is enforced.
- permissive — The SELinux system prints warnings but does not enforce policy.
- disabled — SELinux is fully disabled. SELinux hooks are disengaged from the kernel and the pseudo-file system is unregistered.
永久关闭 SELinux
编辑 /etc/selinux/config,找到 SELINUX 行修改成为:SELINUX=disabled:
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing – SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive – SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled – No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=disabled
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values:
# targeted – Only targeted network daemons are protected.
# strict – Full SELinux protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
如果重启系统,就会发现 SELinux 的状态变成 disabled

5. 关闭 linux 内核 huge_page:
| Add the following lines in /etc/rc.local and reboot the server: | |
| echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/RedHat_transparent_hugepage/enabled | |
| echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/redhat_transparent_hugepage/defrag |
6. 安装 java,配置 JAVA_HOME
cd/usr/java
rz–be
/usr/java/jdk1.7.0_75
ln -s /usr/java/jdk1.7.0_75 /usr/java/default
vim/etc/profile
route add default gw172.28.0.1
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/default
export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
编辑好 /etc/profile,执行 source /etc/profile 使配置生效,保证每一台机器上的 java 版本都是一致的,并且 JAVA_HOME 环境变量是有效的:

7. 每台机器上安装 ntpd
| rpm -aq | grep ntpd | |
| yum install ntpd | |
| chkconfig ntpd on | |
| service ntpd start |
确保每台机器的 ntpd 服务都处于运行状态:

8. 确保机器上安装了 openssh-server,并且升级 openssl 到最新:
| rpm -qa | grep ssh | |
| yum install openssh-server | |
| service sshd restart | |
| chkconfig sshd on |
确保 openssl 最新:
yum install openssl-devel-1.0.1e-42.el6.x86_64
9. yum 源确保可以用,本次安装采用了 163 的 yum 源,先将 /etc/yum.repos.d/ 中,所有的文件都删掉,然后新建文件 CentOS6-Base-163.repo,填入如下内容:
#
# The mirror system uses the connecting IP address of the client and the
# update status of each mirror to pick mirrors that are updated to and
# geographically close to the client. You should use thisfor CentOS updates
# unless you are manually picking other mirrors.
#
# If the mirrorlist= does not work for you, as a fall back you can try the
# remarked out baseurl= line instead.
#
#
[base]
name=CentOS-$releasever – Base – 163.com
baseurl=http://mirrors.163.com/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=os
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
#released updates
[updates]
name=CentOS-$releasever – Updates – 163.com
baseurl=http://mirrors.163.com/centos/$releasever/updates/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=updates
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
#additional packages that may be useful
[extras]
name=CentOS-$releasever – Extras – 163.com
baseurl=http://mirrors.163.com/centos/$releasever/extras/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=extras
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
#additional packages that extend functionality of existing packages
[centosplus]
name=CentOS-$releasever – Plus – 163.com
baseurl=http://mirrors.163.com/centos/$releasever/centosplus/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=centosplus
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
#contrib– packages by Centos Users
[contrib]
name=CentOS-$releasever – Contrib – 163.com
baseurl=http://mirrors.163.com/centos/$releasever/contrib/$basearch/
#mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=contrib
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=http://mirror.centos.org/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6
配置 ambari 的 yum 源,本配置源是部署在本地局域网中的一台 apache 服务器上的:

[Updates-ambari-2.0.1]
name=ambari-2.0.1 – Updates
baseurl=http://172.28.4.159/ambari-test/centos6
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://172.28.4.159/ambari-test/centos6/RPM-GPG-KEY/RPM-GPG-KEY-Jenkins
enabled=1
priority=1
[root@hdp159yum.repos.d]#

将 yum 源配置好好了后,执行如下命令:
| yum clean all | |
| yum repolist |
10. 在 nn 机器上,安装 ambari-servier,执行如下命令,之所以加—nogpgcheck 参数,是因为此处安装的是公司修改后的 ambari,如果是安装原生的 ambari,不用加该选项:
yum install --nogpgcheck ambari-server
11. 配置和启动 ambari-server, setup –j 配置 ambari-server 要使用的 java 环境:
| ambari-server setup -j /usr/java/default | |
| ambari-server start |
12. 在浏览器中,输入 nn:8080 进入 ambari 的登陆页面,用户名和密码都是 admin:

更多详情见请继续阅读下一页的精彩内容 :http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2017-03/141297p2.htm
















