共计 6838 个字符,预计需要花费 18 分钟才能阅读完成。
iSCSI 技术是一种由 IBM 公司研究开发的,是一个供硬件设备使用的可以在 IP 协议的上层运行的 SCSI 指令集,这种指令集合可以实现在 IP 网络上运行 SCSI 协议,使其能够在诸如高速千兆以太网上进行路由选择。iSCSI 技术是一种新储存技术,该技术是将现有 SCSI 接口与以太网络 (Ethernet) 技术结合,使服务器可与使用 IP 网络的储存装置互相交换资料。
1. 安装 iscsi 服务软件和添加一块共享硬盘
[root@node1 ~]# yum install scsi-target-utils – 安装软件
[root@node1 ~]# sfdisk -l /dev/sdb – 新添加的磁盘
Disk /dev/sdb: 66 cylinders, 255 heads, 63 sectors/track
[root@node1 ~]#
2. 服务器端修改配置文件
[root@node1 ~]# vim /etc/tgt/targets.conf – 修改配置文件, 添加以下行
<target iqn.2014-01.node1:server.target4> –2014-01 是日期,node1 是计算机名,server.target4 随意写
direct-store /dev/sdb – 要共享的硬盘, 也可以是分区, 块设备
write-cache off – 不写入缓存
initiator-address 2.2.2.0/24 – 允许哪个网段访问
</target>
[root@node1 ~]# /etc/init.d/tgtd restart
Stopping SCSI target daemon: [OK]
Starting SCSI target daemon: [OK]
[root@node1 ~]# netstat -lutnp |grep 3260
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3260 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1962/tgtd
tcp 0 0 :::3260 :::* LISTEN 1962/tgtd
[root@node1 ~]# tgt-admin –show | grep Target – 查看到共享有一个存储
Target 1: iqn.2014-01.node1:server.target4
[root@node1 ~]# iptables -I INPUT -p tcp -s 2.2.2.0/24 –dport 3260 -j ACCEPT – 放行包过滤
3. 客户端是 Windows 系统
(1) 下载 Windows 系统 iSCSI 客户端工具, 并安装
免费下载地址在 http://linux.linuxidc.com/
用户名与密码都是www.linuxidc.com
具体下载目录在 /2014 年资料 / 2 月 / 3 日 /CentOS 6.4 系统存储服务器之 iSCSI
下载方法见 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-07/87684.htm
(2)安装完后打开界面添
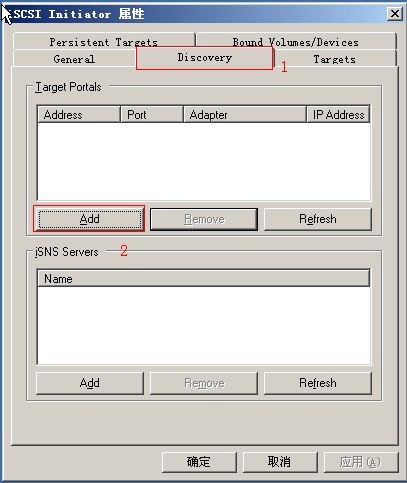
(3)写入服务器的 IP 地址

(4)查看服务器共享的磁盘, 如果没有请检查其它地方是否有错
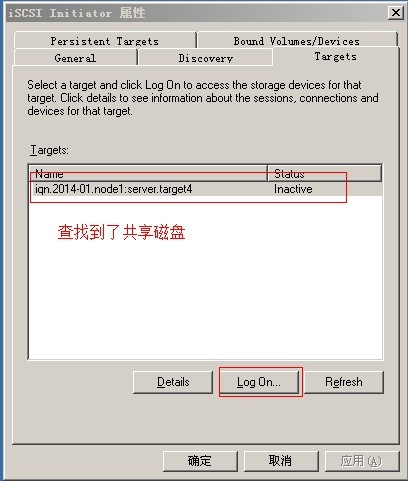
(5)登陆服务器的 scsi 服务

(6)在 windows 系统中可以看到新的磁盘了, 在中途需要安装驱动就下一步安装, 也要格式化新的磁盘
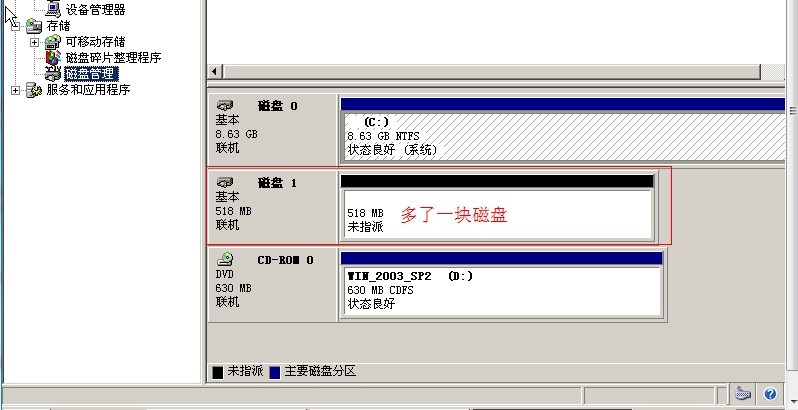
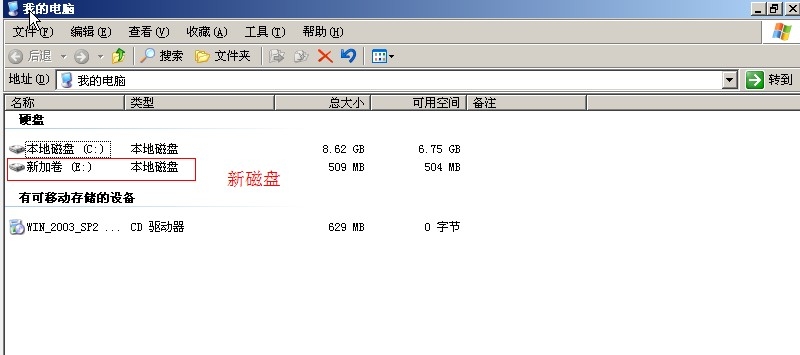
(7)在我的电脑中可以看到分区了
相关阅读:
基于 RHCS+iSCSI+CLVM 实现 Web 服务的共享存储集群架构 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-05/84888.htm
Linux 环境 iSCSI 存储及多路径功能配置 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-05/84635.htm
构建基于 IP SAN 的 iSCSI 存储系统 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-05/84570.htm
iSCSI 连接不上解决 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-01/78462.htm
Citrix XenServer 中安装 CentOS 6.0 并配置 iSCSI 服务 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-01/78461.htm
CentOS 5.3 使用 iSCSI 挂载存储磁盘柜 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2011-01/31529.htm
4. 客户端是 Linux 系统
[root@RedHat ~]# yum install iscsi-target-utils – 安装客户端软件
[root@redhat ~]# /etc/init.d/iscsid start – 启动服务
[root@redhat ~]# /etc/init.d/iscsi start – 启动服务
[root@redhat ~]# iscsiadm -m discovery -t sendtargets -p 2.2.2.27:3260 – 查找服务器的共享磁盘
2.2.2.27:3260,1 iqn.2014-01.node1:server.target4
[root@redhat ~]# iscsiadm -m node -T iqn.2014-01.node1:server.target4 –login – 登陆服务器
Logging in to [iface: default, target: iqn.2014-01.node1:server.target4, portal: 2.2.2.27,3260] (multiple)
Login to [iface: default, target: iqn.2014-01.node1:server.target4, portal: 2.2.2.27,3260] successful.
[root@redhat ~]# fdisk -l /dev/sdb – 查看磁盘
Disk /dev/sdb: 546 MB, 546308096 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 66 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x5ce268ef
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2 66 522112+ 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 2 66 522081 7 HPFS/NTFS
[root@redhat ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb – 格式化磁盘
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
/dev/sdb is entire device, not just one partition!
Proceed anyway? (y,n) y
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
33360 inodes, 133376 blocks
6668 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=138412032
5 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
6672 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (4096 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 37 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
[root@redhat ~]# mount /dev/sdb /mnt/ – 挂载目录
[root@redhat ~]# df -TH
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root
ext4 20G 833M 19G 5% /
tmpfs tmpfs 262M 0 262M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 ext4 508M 32M 451M 7% /boot
/dev/sr0 iso9660 538M 18M 494M 4% /mnt
/dev/sdb ext4 538M 18M 494M 4% /mnt
[root@redhat ~]# ll /mnt/ – 查看文件
total 16
drwx——. 2 root root 16384 Jan 16 13:55 lost+found
[root@redhat ~]#
5. 注销 iscsi 连接和退出
[root@redhat ~]# iscsiadm -m node -o delete -T iqn.2014-01.node1:server.target4 – 注销连接
iscsiadm: This command will remove the record [iface: default, target: iqn.2014-01.node1:server.target4, portal: 2.2.2.27,3260], but a session is using it. Logout session then rerun command to remove record.
iscsiadm: Could not execute operation on all records: session exists
[root@redhat ~]# iscsiadm -m node -U all – 断开所有连接
Logging out of session [sid: 1, target: iqn.2014-01.node1:server.target4, portal: 2.2.2.27,3260]
Logout of [sid: 1, target: iqn.2014-01.node1:server.target4, portal: 2.2.2.27,3260] successful.
[root@redhat ~]# sfdisk -l – 没有那个磁盘了
Disk /dev/sda: 2652 cylinders, 255 heads, 63 sectors/track
Units = cylinders of 8225280 bytes, blocks of 1024 bytes, counting from 0
Device Boot Start End #cyls #blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 0+ 63- 64- 512000 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 63+ 2652- 2589- 20794368 8e Linux LVM
/dev/sda3 0 – 0 0 0 Empty
/dev/sda4 0 – 0 0 0 Empty
Disk /dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root: 2457 cylinders, 255 heads, 63 sectors/track
Disk /dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_swap: 130 cylinders, 255 heads, 63 sectors/track
[root@redhat ~]#
更多 CentOS 相关信息见CentOS 专题页面 http://www.linuxidc.com/topicnews.aspx?tid=14
iSCSI 技术是一种由 IBM 公司研究开发的,是一个供硬件设备使用的可以在 IP 协议的上层运行的 SCSI 指令集,这种指令集合可以实现在 IP 网络上运行 SCSI 协议,使其能够在诸如高速千兆以太网上进行路由选择。iSCSI 技术是一种新储存技术,该技术是将现有 SCSI 接口与以太网络 (Ethernet) 技术结合,使服务器可与使用 IP 网络的储存装置互相交换资料。
1. 安装 iscsi 服务软件和添加一块共享硬盘
[root@node1 ~]# yum install scsi-target-utils – 安装软件
[root@node1 ~]# sfdisk -l /dev/sdb – 新添加的磁盘
Disk /dev/sdb: 66 cylinders, 255 heads, 63 sectors/track
[root@node1 ~]#
2. 服务器端修改配置文件
[root@node1 ~]# vim /etc/tgt/targets.conf – 修改配置文件, 添加以下行
<target iqn.2014-01.node1:server.target4> –2014-01 是日期,node1 是计算机名,server.target4 随意写
direct-store /dev/sdb – 要共享的硬盘, 也可以是分区, 块设备
write-cache off – 不写入缓存
initiator-address 2.2.2.0/24 – 允许哪个网段访问
</target>
[root@node1 ~]# /etc/init.d/tgtd restart
Stopping SCSI target daemon: [OK]
Starting SCSI target daemon: [OK]
[root@node1 ~]# netstat -lutnp |grep 3260
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3260 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1962/tgtd
tcp 0 0 :::3260 :::* LISTEN 1962/tgtd
[root@node1 ~]# tgt-admin –show | grep Target – 查看到共享有一个存储
Target 1: iqn.2014-01.node1:server.target4
[root@node1 ~]# iptables -I INPUT -p tcp -s 2.2.2.0/24 –dport 3260 -j ACCEPT – 放行包过滤
3. 客户端是 Windows 系统
(1) 下载 Windows 系统 iSCSI 客户端工具, 并安装
免费下载地址在 http://linux.linuxidc.com/
用户名与密码都是www.linuxidc.com
具体下载目录在 /2014 年资料 / 2 月 / 3 日 /CentOS 6.4 系统存储服务器之 iSCSI
下载方法见 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-07/87684.htm
(2)安装完后打开界面添

(3)写入服务器的 IP 地址

(4)查看服务器共享的磁盘, 如果没有请检查其它地方是否有错

(5)登陆服务器的 scsi 服务

(6)在 windows 系统中可以看到新的磁盘了, 在中途需要安装驱动就下一步安装, 也要格式化新的磁盘

(7)在我的电脑中可以看到分区了

相关阅读:
基于 RHCS+iSCSI+CLVM 实现 Web 服务的共享存储集群架构 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-05/84888.htm
Linux 环境 iSCSI 存储及多路径功能配置 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-05/84635.htm
构建基于 IP SAN 的 iSCSI 存储系统 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-05/84570.htm
iSCSI 连接不上解决 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-01/78462.htm
Citrix XenServer 中安装 CentOS 6.0 并配置 iSCSI 服务 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-01/78461.htm
CentOS 5.3 使用 iSCSI 挂载存储磁盘柜 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2011-01/31529.htm















