共计 12111 个字符,预计需要花费 31 分钟才能阅读完成。
ngx_http_stub_status 监控连接信息
nginx 现已成为目前使用最广泛的 web 服务器和反向代理服务器,我们线上的 Tomcat 服务器一般都会由 nginx 进行代理,以此实现负载均衡的效果。既然 nginx 被应用得那么广泛,我们自然也得学习如何去对 nginx 做性能监控。本小节将介绍如何使用 nginx 的 ngx_http_stub_status 模块来对连接信息进行监控。本文默认读者有 nginx 的基础,所以一些基础性的东西不会过多介绍。
关于该模块的官方文档地址如下:
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_stub_status_module.html
如果你的 nginx 是使用 yum 进行安装的,那么一般会自带这个模块,可以忽略以下这段为了安装 ngx_http_stub_status 模块而重新编译安装 nginx 的部分。因为我的 nginx 是编译安装的,当时并没有加上这个模块进行编译,所以现在还需要重新去编译安装一次。过程如下:
| [root@01server ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -V # 列出安装了哪些模块,可以看到我这里没有安装任何模块 | |
| nginx version: nginx/1.12.1 | |
| built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-11) (GCC) | |
| configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx | |
| [root@01server ~]# rm -rf /usr/local/nginx/ # 删除原本的 nginx | |
| [root@01server ~]# cd /usr/local/src/ # 进入存放安装包的路径 | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/src]# ls | |
| nginx-1.12.1 nginx-1.12.1.tar.gz | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/src]# cd nginx-1.12.1 # 进入之前已经解压好的目录 | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/src/nginx-1.12.1]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_stub_status_module # 加入编译参数,指定需要安装的模块 | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/src/nginx-1.12.1]# make && make install # 编译安装 | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/src/nginx-1.12.1]# cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin/ | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/nginx/sbin]# ./nginx -V # 可以已经把模块安装好了 | |
| nginx version: nginx/1.12.1 | |
| built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-11) (GCC) | |
| configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_stub_status_module | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/nginx/sbin]# |
安装好之后,还需要编辑一下配置文件,不使用 nginx 默认的配置文件:
| [root@01server /usr/local/nginx/sbin]# cd ../conf/ | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/nginx/conf]# mv nginx.conf nginx.conf.bak # 不使用 nginx 自带的配置文件 | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/nginx/conf]# vim nginx.conf # 将以下内容粘贴进去 | |
| user nobody nobody; | |
| worker_processes 2; | |
| error_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx_error.log crit; | |
| pid /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid; | |
| worker_rlimit_nofile 51200; | |
| events | |
| { | |
| use epoll; | |
| worker_connections 1024; | |
| } | |
| http | |
| { | |
| include mime.types; | |
| default_type application/octet-stream; | |
| server_names_hash_bucket_size 3526; | |
| server_names_hash_max_size 4096; | |
| log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local]"$request" ' | |
| '$status $body_bytes_sent"$http_referer" ' | |
| '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; | |
| access_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log main; | |
| sendfile on; | |
| tcp_nopush on; | |
| keepalive_timeout 30; | |
| client_header_timeout 3m; | |
| client_body_timeout 3m; | |
| send_timeout 3m; | |
| connection_pool_size 256; | |
| client_header_buffer_size 1k; | |
| large_client_header_buffers 8 4k; | |
| request_pool_size 4k; | |
| output_buffers 4 32k; | |
| postpone_output 1460; | |
| client_max_body_size 10m; | |
| client_body_buffer_size 256k; | |
| client_body_temp_path /usr/local/nginx/client_body_temp; | |
| proxy_temp_path /usr/local/nginx/proxy_temp; | |
| fastcgi_temp_path /usr/local/nginx/fastcgi_temp; | |
| fastcgi_intercept_errors on; | |
| tcp_nodelay on; | |
| gzip on; | |
| gzip_min_length 1k; | |
| gzip_buffers 4 8k; | |
| gzip_comp_level 5; | |
| gzip_http_version 1.1; | |
| gzip_types text/plain application/x-Javascript text/css text/htm | |
| application/xml; | |
| include vhost/*.conf; | |
| } | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/nginx/conf]# mkdir vhost | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/nginx/conf]# vim vhost/default.conf # 虚拟主机配置文件,将以下内容粘贴进去 | |
| server{ | |
| listen 80; | |
| server_name localhost; | |
| index index.html index.htm index.php; | |
| root /usr/local/nginx/html; | |
| location = /nginx_status{# 配置访问路径,即 uri | |
| stub_status on; # 开启该模块 | |
| access_log off; # 关闭日志 | |
| allow 101.106.102.129; # 允许访问的 ip,即白名单 ip | |
| allow 127.0.0.1; | |
| deny all; # 拒绝白名单 ip 以外的 ip 访问 | |
| } | |
| } | |
| [root@01server ~]# |
启动 nginx:
| [root@01server /usr/local/nginx/conf]# cd ../sbin/ | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/nginx/sbin]# ./nginx -t # 检查 nginx 的配置文件是否正常 | |
| nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok | |
| nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/nginx/sbin]# ./nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf # 启动 nginx | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/nginx/sbin]# netstat -lntp |grep nginx | |
| tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 22713/nginx: master | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/nginx/sbin]# |
启动成功后,使用浏览器访问 /nginx_status,访问成功响应的信息如下: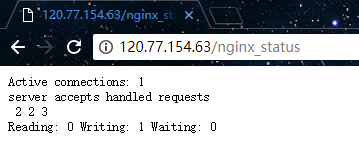
说明:
- Active connections 当前活动的连接数量(包括等待的)
- accepts 已接收的连接总数
- handled 已处理的连接总数
- requests 当前的请求总数
- Reading nginx 正在读取的连接数量
- Writing nginx 正在响应的连接数量
- Waiting 当前空闲的连接数量
如上,通过这些简单的参数可以看到 nginx 当前的连接信息。在高并发场景下,可以根据 Active connections 参数判断当前的一个并发数量,Reading 参数则可以告诉我们当前 nginx 是否繁忙。当然,这只是最简单的一个 nginx 的监控方式,参数也就只有那么几个。但这些都是其他更高级的监控工具的基础,所以了解这些基础监控也是有必要的。
ngxtop 监控请求信息
在上一小节中,我们介绍了如何利用 ngx_http_stub_status 模块去监控 nginx 的连接信息。本小节将介绍如何使用 ngxtop 工具来监控 nginx 的请求信息。
ngxtop 可以实时解析 nginx 访问日志,并且将处理结果输出到终端,功能类似于系统命令 top,所以这个软件起名 ngxtop。有了 ngxtop,你可以实时了解到当前 nginx 的访问状况,再也不需要 tail 日志看屏幕刷新。
ngxtop 项目地址:
https://github.com/lebinh/ngxtop
安装 ngxtop:
由于 ngxtop 是 Python 编写的,我们可以使用 pip 进行安装。如果你的机器上没有安装 pip,需要先把 pip 装上,安装命令如下:
| [] | |
| [] |
然后通过 pip 安装 ngxtop,命令如下:
[root@01server ~]# pip install ngxtop
ngxtop 使用说明:
| [root@01server ~]# ngxtop --help | |
| ngxtop - ad-hoc query for nginx access log. | |
| Usage: | |
| ngxtop [options] | |
| ngxtop [options] (print|top|avg|sum) <var> ... | |
| ngxtop info | |
| ngxtop [options] query <query> ... | |
| Options: | |
| -l <file>, --access-log <file> # 需要分析的访问日志 | |
| -f <format>, --log-format <format> # log_format 指令指定的日志格式 [默认: combined] | |
| --no-follow ngxtop default behavior is to ignore current lines in log | |
| and only watch for new lines as they are written to the access log. | |
| Use this flag to tell ngxtop to process the current content of the access log instead. # 简而言之,对历史信息进行统计 | |
| -t <seconds>, --interval <seconds> report interval when running in follow mode [default: 2.0] # 指定监控信息刷新的间隔,单位为秒 [默认: 2.0] | |
| -g <var>, --group-by <var> # 根据变量分组 [默认: request_path] | |
| -w <var>, --having <expr> # 具备子句 [默认: 1] having clause [default: 1] | |
| -o <var>, --order-by <var> # 排序 [默认: count] | |
| -n <number>, --limit <number> # 显示的条数 [默认: 10] | |
| -a <exp> ..., --a <exp> ... add exp (must be aggregation exp: sum, avg, min, max, etc.) into output # 添加聚合表达式到输出信息中 | |
| -v, --verbose # 更多的输出 | |
| -d, --debug # 打印所有行和解析记录,debug | |
| -h, --help # 当前帮助信息. | |
| --version # 输出版本信息. |
高级选项:
| -c <file>, --config <file> # 运行 ngxtop 解析 nginx 配置文件 | |
| -i <filter-expression>, --filter <filter-expression> filter in, records satisfied given expression are processed. # 根据指定的表达式进行过滤,仅显示过滤后的信息 | |
| -p <filter-expression>, --pre-filter <filter-expression> in-filter expression to check in pre-parsing phase. # 在筛选器表达式中检查预解析阶段 |
范例:
| All examples read nginx config file for access log location and format. | |
| If you want to specify the access log file and / or log format, use the -f and -a options. | |
| "top" like view of nginx requests | |
| 指定配置文件启动 ngxtop: | |
| $ ngxtop -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf | |
| 404 前十的请求: | |
| $ ngxtop top request_path --filter 'status == 404' | |
| 总流量前十的请求: | |
| $ ngxtop --order-by 'avg(bytes_sent) * count' | |
| 访问量前十的 ip 地址: | |
| $ ngxtop --group-by remote_addr | |
| 输出 400 以上状态码的请求以及请求来源: | |
| $ ngxtop -i 'status >= 400' print request status http_referer | |
| Average body bytes sent of 200 responses of requested path begin with 'foo': | |
| $ ngxtop avg bytes_sent --filter 'status == 200 and request_path.startswith("foo")' |
指定 nginx 的配置文件进行启动:
[root@01server ~]# ngxtop -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
启动后如下: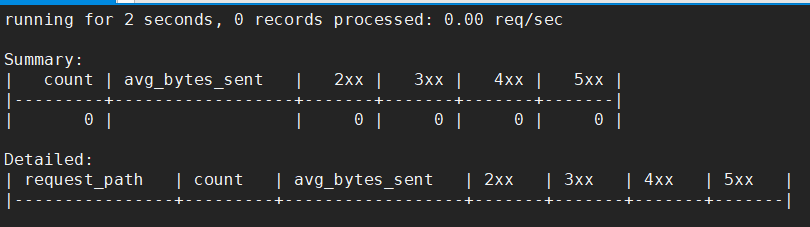
注:Summary 相当于请求的概览信息,Detailed 就自然是请求的详细信息了。2xx、3xx、4xx 以及 5xx,都是表示的 http 状态。avg_bytes_sent 表示请求所发送的字节数平均值,request_path 则是请求路径,count 表示请求的总次数。
默认情况下,ngxtop 不会显示启动 ngxtop 之前的请求信息,只会显示 ngxtop 启动之后新的请求信息。所以我们可以到浏览器上刷新一下,随便访问一些页面,人为制造一些请求。如下图,这时就可以看到 ngxtop 成功监控到了请求信息: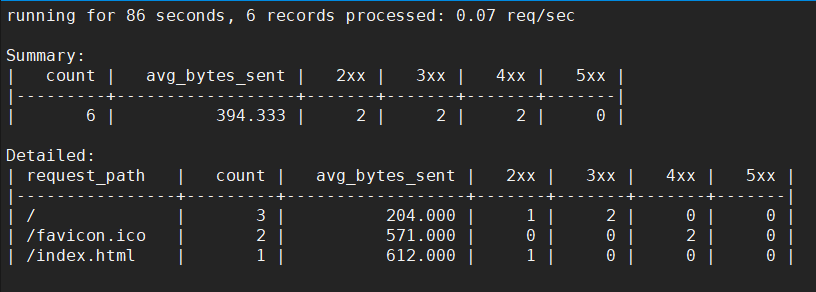
我们可以通过选项来指定一些条件,例如我希望只显示 http 状态是 200 的,就可以使用 - i 进行指定:
[root@01server ~]# ngxtop -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf -i 'status == 200'
如下: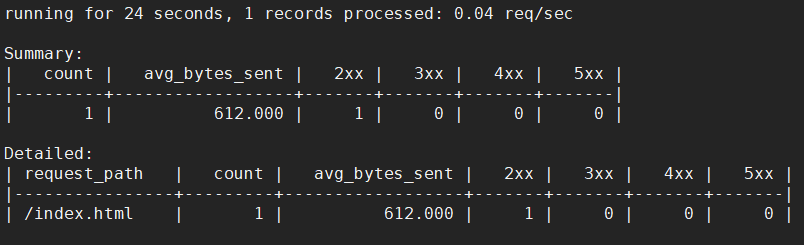
例如我希望显示访问最多的 ip,就可以使用 - g 进行指定:
[root@01server ~]# ngxtop -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf -g remote_addr
如下: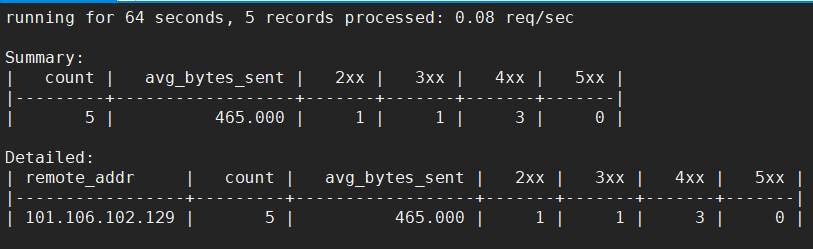
如果想要查看之前的请求信息可以使用 –no-follow 选项,相当于是对历史的请求信息做了一个统计,如下: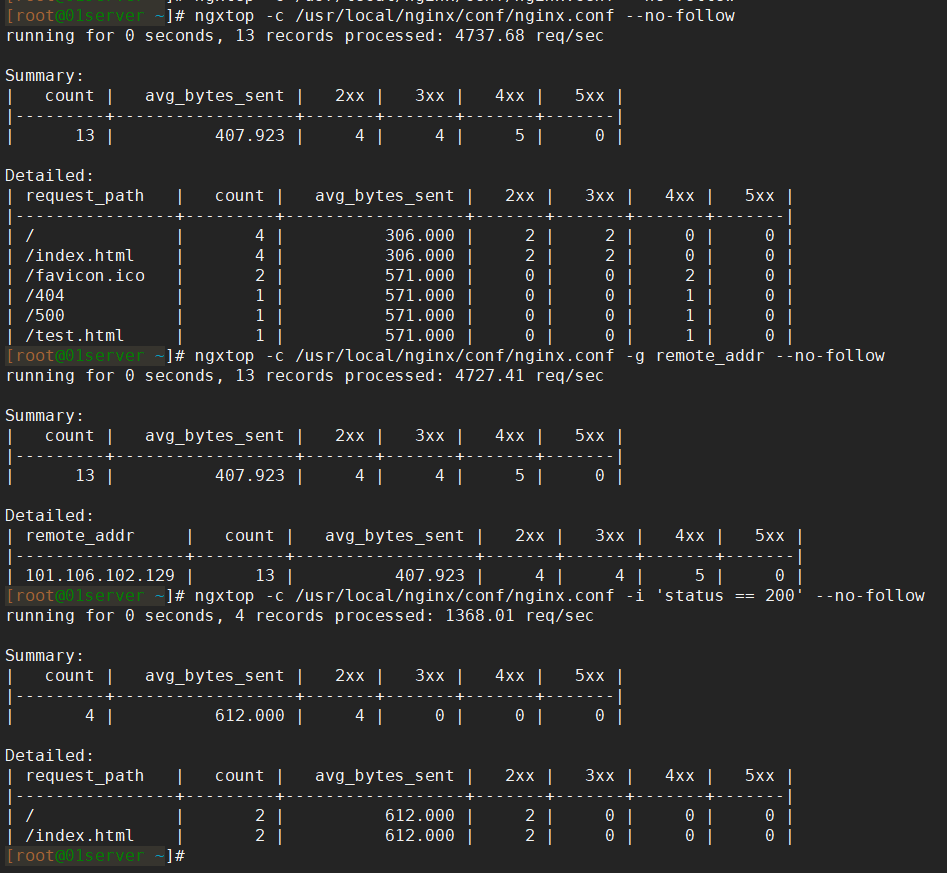
关于 ngxtop 常用操作就先简单介绍到这,希望详细了解最直接的就是查阅该项目在 github 上的文档。
nginx-rrd 图形化监控
在上两小节中,我们介绍了两个基础的 nginx 工具,能够监控连接信息和请求信息,它们都是基于命令行的。本小节则介绍一个图形化的 nginx 监控工具,该工具就是 nginx-rrd。nginx-rrd 也是 Nginx 官方推荐的一款 Nginx 监控工具,利用 nginx-rrd 可以很方便的生成图表,它可以监控连接信息和请求信息。
nginx-rrd 官网地址如下:
https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/modules/rrd_graph/
那么我们接下来就看看如何安装并使用 nginx-rrd 吧。nginx-rrd 部分功能是基于上两小节所介绍的工具实现的,所以在安装 nginx-rrd 之前需要根据上两节的介绍安装好所需的工具。由于 nginx-rrd 是使用 php 实现的,所以在此之前,我们得先安装好 php 的运行环境,以及安装 rrdtool 的相关依赖。我这里使用 yum 进行安装,命令如下:
| [root@01server ~]# yum install -y php php-gd php-soap php-mbstring php-xmlrpc php-dom php-fpm | |
| [root@01server ~]# yum install -y perl rrdtool perl-libwww-perl libwww-perl perl-rrdtool |
安装好 php 运行环境以及 rrdtool 后,我们还需要把 nginx 和 php-fpm 进行一个整合。修改 php-fpm 的配置文件,将文件中的 user 和 group 修改为与 nginx.conf 中的 user 一致:
| [root@01server ~]# vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf | |
| user = nobody | |
| group = nobody | |
| [root@01server ~]# |
还需要让 nginx 支持解析 php,在虚拟主机配置文件中,增加如下内容:
| [root@01server ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/vhost/default.conf # 添加以下内容 | |
| location ~ \.php$ | |
| { | |
| include fastcgi_params; | |
| fastcgi_pass unix:/tmp/php-fcgi.sock; | |
| fastcgi_index index.php; | |
| fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /usr/local/nginx/html$fastcgi_script_name; | |
| } | |
| [root@01server ~]# |
配置好后,启动 php-fpm 服务,并且重新加载 nginx:
| [root@01server ~]# systemctl start php-fpm | |
| [root@01server ~]# netstat -lntp |grep 9000 | |
| tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:9000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 24418/php-fpm: mast | |
| [root@01server ~]# nginx -s reload |
然后在虚拟主机配置文件中所指向的网站根目录下,新建一个简单的 php 文件,用于测试 nginx 是否已经能够正常解析 php 代码:
| [root@01server ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/html/index.php # 文件内容如下 | |
| phpinfo(); | |
| [root@01server ~]# |
接着到浏览器上进行访问,如下则是代表 nginx 已经能够支持解析 php 了: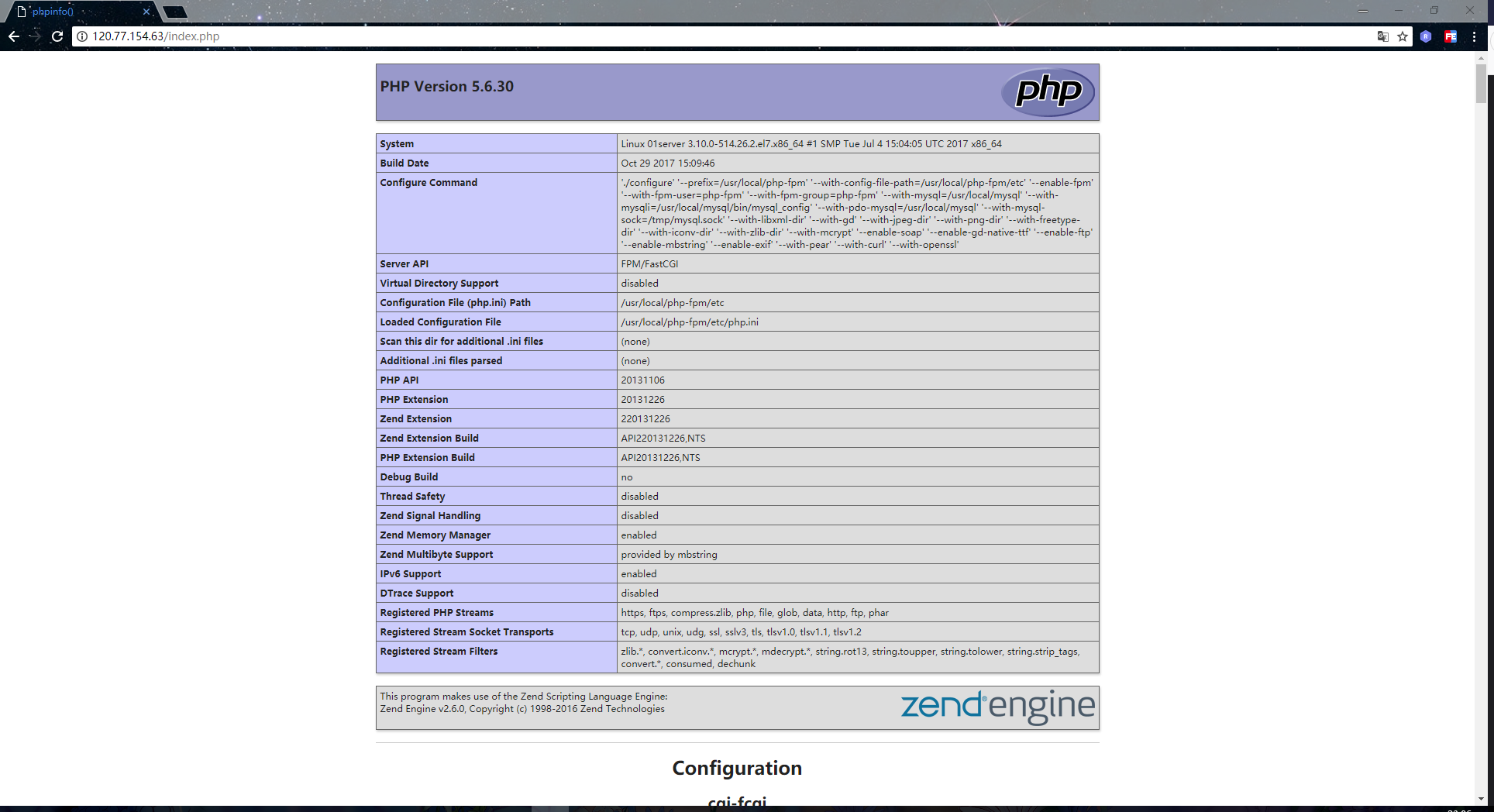
现在我们就可以开始安装 nginx-rrd 了,首先使用如下命令,下载 nginx-rrd 的压缩包:
| [root@01server ~]# cd /usr/local/src/ | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/src]# wget http://soft.vpser.net/status/nginx-rrd/nginx-rrd-0.1.4.tgz |
然后解压,并且拷贝一些脚本文件及配置文件到相应的系统目录下:
| [root@01server /usr/local/src]# tar -zvxf nginx-rrd-0.1.4.tgz | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/src]# cd nginx-rrd-0.1.4 | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/src/nginx-rrd-0.1.4]# ls | |
| etc html usr | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/src/nginx-rrd-0.1.4]# cp etc/nginx-rrd.conf /etc | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/src/nginx-rrd-0.1.4]# cp usr/sbin/* /usr/sbin | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/src/nginx-rrd-0.1.4]# rm -rf /usr/local/nginx/html/index.php # 删除之前测试用的 php 文件 | |
| [root@01server /usr/local/src/nginx-rrd-0.1.4]# cp html/index.php /usr/local/nginx/html/ |
修改 nginx-rrd 配置文件,配置数据存储目录以及图片存储目录,如下:
| [root@01server ~]# vim /etc/nginx-rrd.conf | |
| # dir where rrd databases are stored | |
| RRD_DIR="/usr/local/nginx/html/nginx-rrd"; # 数据存储目录 | |
| # dir where png images are presented | |
| WWW_DIR="/usr/local/nginx/html"; # 图片存储目录 | |
| [root@01server ~]# |
配置完之后,我们还需要使用 crontab 新建定时任务,用于定时执行 nginx-rrd 的两个脚本,因为 nginx-rrd 需要定时去采集数据才能实现一个监控的效果:
| [root@01server ~]# crontab -e | |
| * * * * * /bin/sh /usr/sbin/nginx-collect # 采集数据脚本 | |
| */1 * * * * /bin/sh /usr/sbin/nginx-graph # 生成图片脚本 | |
| [root@01server ~]# |
我们这里设定的定时任务是每一分钟执行一次,可以使用如下命令查看定时任务是否有在执行:
[root@01server ~]# tail -f /var/log/cron
确认定时任务有正常执行后,我们来安装 apache 的一个压测工具,方便于我们生成大量的请求数据:
[root@01server ~]# yum -y install httpd-tools
安装完成后,使用以下命令,对 nginx 进行压测,可以多执行几次:
[root@01server ~]# ab -n 10000 -c 10 http://127.0.0.1/index.html
命令说明:
- -n 指定总共发送多少个请求
- -c 指定同时发送多少个请求
使用压测工具产生了一些请求数据后,到浏览器上访问 nginx-rrd 的 index.php 文件,效果如下: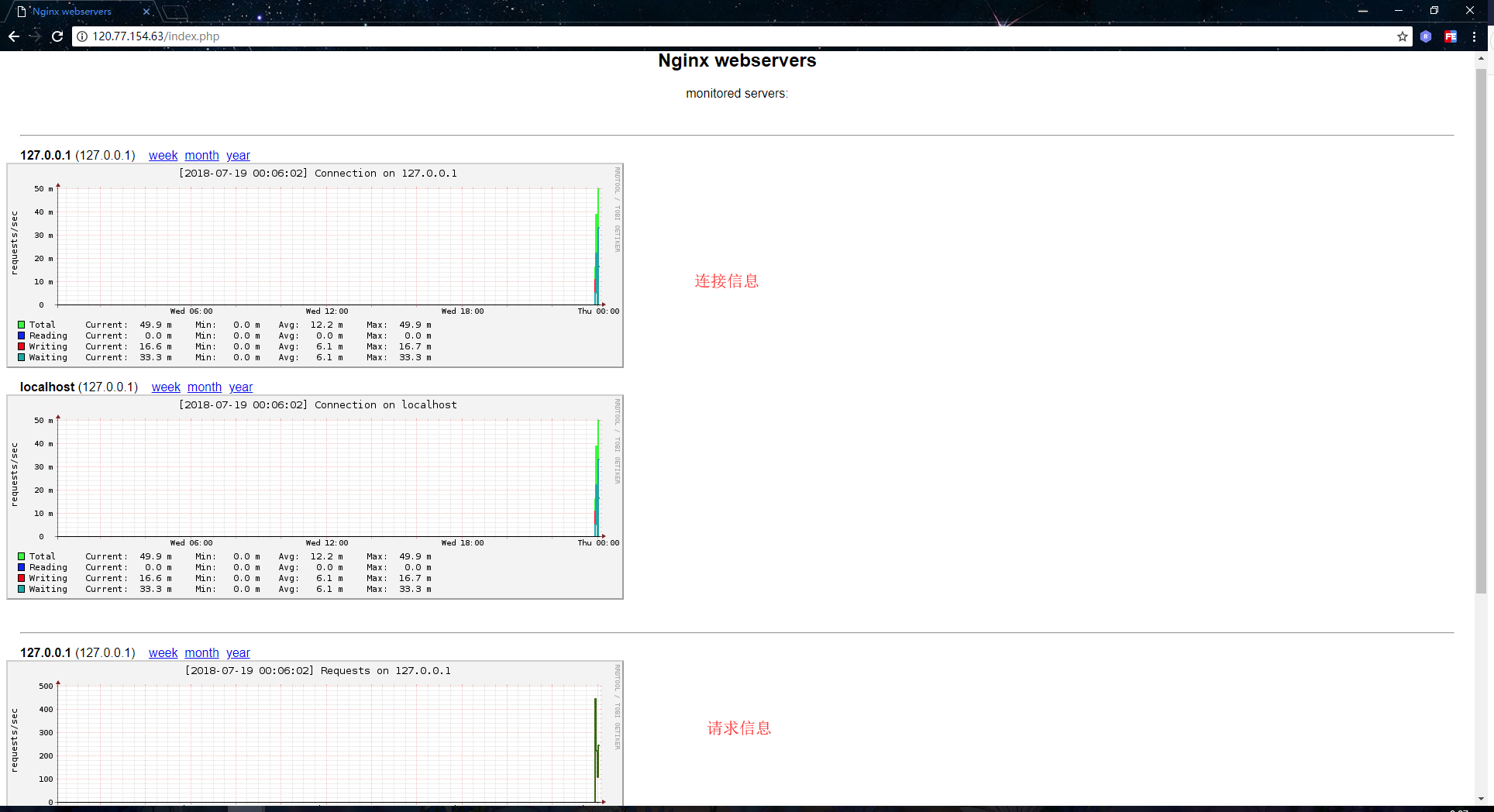
nginx 优化
在以上小节中,我们介绍了一些 nginx 的监控工具。知道了如何对 nginx 进行性能监控后,我们自然就需要知道一些 nginx 的常用优化参数和配置,所以本小节就是介绍一些 nginx 的常见优化方式。
1. 配置工作进程数和并发连接数。
默认情况下,nginx 只有一个工作进程,1024 个并发连接数。当我们需要提高 nginx 的并发负载能力时,可以适当的增加工作进程数和并发连接数。在 nginx.conf 里进行配置:
| [] | |
| worker_processes 2; | |
| events | |
| {use epoll; | |
| multi_accept on; | |
| worker_connections 10240; | |
| } | |
| [] |
2. 配置反向代理(后端 Server)的长连接
Nginx upstream 与后端的连接默认为短连接,通过 HTTP/1.0 向后端发起连接,并把请求的 ”Connection” header 设为 ”close”。Nginx 与前端的连接默认为长连接,一个用户跟 Nginx 建立连接之后,通过这个长连接发送多个请求。如果 Nginx 只是作为 reverse proxy 的话,可能一个用户连接就需要多个向后端的短连接。如果后端的服务器(源站或是缓存服务器)处理并发连接能力不强的话,就可能导致瓶颈的出现。所以我们才需要配置反向代理的长连接,以此缓解瓶颈的问题。示例配置如下:
| [root@01server ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/vhost/default.conf | |
| upstream server_pool{ | |
| server localhost:8080 weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30s; | |
| server localhost:9080 weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30s; | |
| keepalive 300; # 设置 300 个长连接,长连接能够大大提高请求转换的效率 | |
| } | |
| location / {proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; | |
| proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade"; | |
| proxy_pass http://server_pool/; | |
| } | |
| [root@01server ~]# |
3. 配置 gzip 压缩
我们都知道 http 传输的基本都是文本数据,对文本数据进行压缩后,能够减小数据的体积。这样就能够大幅提高访问效率,与页面的加载速度,并且还能够降低带宽资源的消耗。示例配置如下:
| [] | |
| gzip on; | |
| gzip_http_version 1.1; | |
| gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\.(?!.*SV1)"; | |
| gzip_proxied any; | |
| gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css application/xml application/json application/x-font-ttf application/sfg+xml application/x-icon text/javascript application/x-httpd-php image/jpeg image/gif image/png; | |
| gzip_vary on; | |
| gzip_static on; | |
| [] |
4. 操作系统优化
在 Linux 操作系统中,我们可以通过修改 /etc/sysctl.conf 系统配置文件,以此来设置 tcp/ip 连接的相关参数,可以在操作系统层面上提高网络连接的效率。示例配置如下:
| [root@01server ~]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf | |
| net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1 # 防止一个套接字在有过多试图连接到达时引起过载 | |
| net.core.somaxconn = 1024 # 连接队列的长度,默认值为 128, | |
| net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 10 # timewait 的超时时间,设置短一些 | |
| net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1 # os 直接使用 timewait 的连接 | |
| net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 0 # 回收禁用,不回收 timewait 连接 | |
| [root@01server ~]# |
还可以在 /etc/security/limits.conf 配置文件中,配置一个进程可以打开的最大文件数量。示例配置如下:
| [] | |
| * hard nofile 204800 | |
| * soft nofile 204800 | |
| * soft core unlimited | |
| * soft stack 204800 | |
| [] |
5. 其他优化:
示例配置如下:
| [] | |
| sendfile on; | |
| tcp_nopush on; | |
| tcp_nodelay off; | |
| [] |
:
















