共计 14623 个字符,预计需要花费 37 分钟才能阅读完成。
最近用 shell 写了个监控 haproxy 状态的脚本,记录一下以备后用。
1、首先明确需求。我们需要什么功能,常规方式是怎么实现的,使用脚本又该怎么实现。
只需要监控 5 个状态:当前连接数 Session rate 下的 Cur;错误状态 Errors 下的三种状态 Req,Conn,Resp;服务状态 Status。状态页面如图:
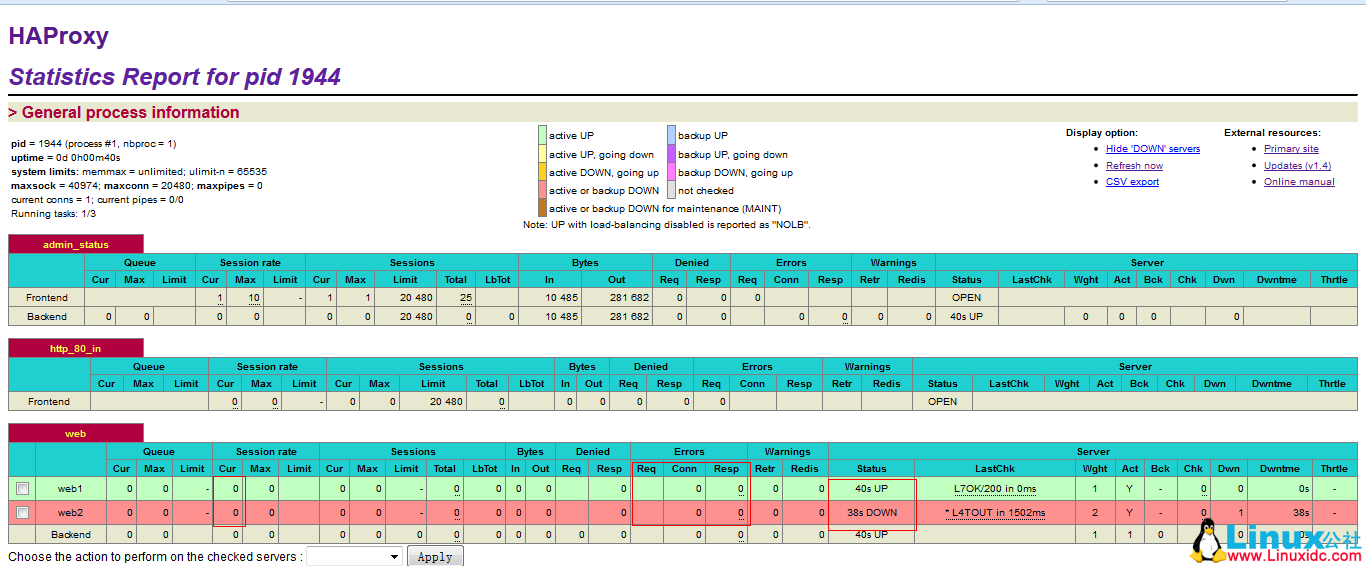
那么如何用脚本的形式把这些展示出来呢?重要的是,如何让 nagios 能够获取到这些数据?这就是接下来需要做的事情。
获取这些数据有两种方法:其一,通过 wget 或者 curl 来访问状态页面,然后筛选数据;其二,通过 sock 来获取状态,然后筛选。我先采用第二种方式来获取数据。
从 sock 获取数据,需要安装 socat 这个软件,具体使用省略。
echo “show stat” | socat /var/lib/haproxy/stats stdio
#/var/lib/haproxy/stats 是 haproxy 路径
可以看到以 csv 格式的状态
pxname,svname,qcur,qmax,scur,smax,slim,stot,bin,bout,dreq,dresp,ereq,econ,eresp,wretr,wredis,status,weight,act,bck,chkfail,chkdown,lastchg,downtime,qlimit,pid,iid,sid,throttle,lbtot,tracked,type,rate,rate_lim,rate_max,check_status,check_code,check_duration,hrsp_1xx,hrsp_2xx,hrsp_3xx,hrsp_4xx,hrsp_5xx,hrsp_other,hanafail,req_rate,req_rate_max,req_tot,cli_abrt,srv_abrt,
admin_status,FRONTEND,,,1,1,20480,31,12757,354568,0,0,0,,,,,OPEN,,,,,,,,,1,1,0,,,,0,1,0,10,,,,0,29,1,0,0,0,,1,10,31,,,
admin_status,BACKEND,0,0,0,0,20480,0,12757,354568,0,0,,0,0,0,0,UP,0,0,0,,0,773,0,,1,1,0,,0,,1,0,,0,,,,0,0,0,0,0,0,,,,,0,0,
http_80_in,FRONTEND,,,0,1,20480,4,348,848,0,0,0,,,,,OPEN,,,,,,,,,1,2,0,,,,0,0,0,1,,,,0,0,0,0,4,0,,0,1,4,,,
web,web1,0,0,0,0,,0,0,0,,0,,0,0,0,0,UP,1,1,0,0,0,773,0,,1,3,1,,0,,2,0,,0,L7OK,200,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,,,,0,0,
web,web2,0,0,0,0,,0,0,0,,0,,0,0,0,0,DOWN,2,1,0,0,1,771,771,,1,3,2,,0,,2,0,,0,L4TOUT,,1502,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,,,,0,0,
web,BACKEND,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,,0,0,0,0,UP,1,1,0,,0,773,0,,1,3,0,,0,,1,0,,0,,,,0,0,0,0,0,0,,,,,0,0,
需要的数据:当起连接数 rate 在第 34 域;err 相关的 ereq、econ、eresp 在第 13、14、15 域;状态 status 在第 18 域。用 awk 筛选数据:
rate=`echo “show stat” | socat /var/lib/haproxy/stats stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $34}’`
ereq=`echo “show stat” | socat /var/lib/haproxy/stats stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $34}’`
econ=`echo “show stat” | socat /var/lib/haproxy/stats stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $34}’`
eresp=`echo “show stat” | socat /var/lib/haproxy/stats stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $34}’`
status=`echo “show stat” | socat /var/lib/haproxy/stats stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $34}’`
数据现在已经可以获取了,接下来就要让 nagios 能够接受到数据。
2、了解插件规范。
nagios 的插件规范有两点:
(1)、需要一个返回值来确定状态
| 0 | OK |
| 1 | WARNING |
| 2 | CRITICAL |
| 3 | UNKNOWN |
(2)、在报警处输出定义的说明,默认大小 4K, 见红框位置:

了解了编写规范,现在就开始写脚本。
3、脚本实例
#########################################################################
# File Name: check_haproxy.sh
# Author: jc
# Created Time: 2014 年 03 月 01 日 星期六 14 时 36 分 23 秒
#########################################################################
#!/bin/bash
# 定义返回状态
ST_OK=0
ST_WR=1
ST_CR=2
ST_UK=3
#sock 的默认路径
sock_path=/var/lib/haproxy/stats
# 默认检查 sock 是否存在
#sock_check=1
# 帮助信息函数
print_help() {
echo ” –sock|-s)”
echo ” haproxy 的 sock 路径,默认路径:/var/lib/haproxy/stats”
echo ” -m/–mode)”
echo ” haproxy 的状态项, 目前只支持:rate,ereq,econ,eresp,status”
# echo ” -n/–no-check-sock)”
# echo ” 检查 sock 存在与否,1 检查,0 不检查 ”
exit $ST_UK
}
# 获取输入的选项
while test -n “$1”; do
case “$1” in
-help|-h)
print_help
exit $ST_UK
;;
–sock|-s)
sock=$2
shift
;;
–mode|-m)
mode=$2
shift
;;
–no-sock-check|-n)
sock_check=0
;;
–hostname|-H)
hostname=$2
shift
;;
–warning|-w)
warning=$2
shift
;;
–critical|-c)
critical=$2
shift
;;
*)
echo “Unknown argument: $1”
print_help
exit $ST_UK
;;
esac
shift
done
#sock 检测
#check_sock() {
#echo “show stat” | socat /var/lib/haproxy/stats stdio >/tmp/hap_sta.txt
#if [-s “/tmp/hap_sta.txt”]
#then
# con=1
#else
# con=2
#fi
#}
# 获取数据
get_val() {
case $mode in
rate)
val=`echo “show stat” | socat $sock_path stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $34}’`
;;
ereq)
val=`echo “show stat” | socat $sock_path stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $13}’`
if [-z $val]
then
val=0
fi
;;
econ)
val=`echo “show stat” | socat $sock_path stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $14}’`
;;
eresp)
val=`echo “show stat” | socat $sock_path stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $15}’`
;;
status)
val=`echo “show stat” | socat $sock_path stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $18}’`
;;
*)
echo “ 暂时不能检测此项,请重新输入 ”
;;
esac
}
# 显示的文字信息
out_pr() {
output=”haproxy is running. $mode’s key is $val”
}
# 开始执行
## 检查 sock 是否能够连上
#if [$sock_check = 1]
#then
# check_sock
# if [“$con” = 2]
# then
# echo “ERR!! 连接 haproxy 被拒绝,请确认服务已经开启,或者检查 sock 路径 / 权限是否正确!”
# exit $ST_CR
# fi
#fi
get_val
out_pr
#get_stat() {
if [“$val” -ge “$warning”] && [“$val” -lt “$critical”]
then
echo “WARNING – $output”
exit $ST_WR
elif [“$val” -ge “$critical”]
then
echo “CRITICAL – $output”
exit $ST_CR
else
echo “OK – $output”
exit $ST_OK
fi
脚本完成,先在命令行测试:
[root@webtest-250 libexec]# /opt/nagios/libexec/check_haproxy.sh -m rate -w 10 -c 20
OK – haproxy is running. rate’s key is 0
注意,以下两步相当重要,如果不给 nagios 用户添加权限,在页面会看不到值,如
(1)、更改 /etc/sudoers,把 nagios 启动用户添加进去
nagios ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_hap.sh
(2)、更改 /etc/sudoers 把这一行注释,否则在后台运行 sudo 会报错
#Defaults requiretty
现在切换到 nagios 的用户执行就正确了。
HAproxy 的详细介绍:请点这里
HAproxy 的下载地址:请点这里
推荐阅读:
Haproxy+Keepalived 搭建 Weblogic 高可用负载均衡集群 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-09/89732.htm
Keepalived+HAProxy 配置高可用负载均衡 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-03/56748.htm
CentOS 6.3 下 Haproxy+Keepalived+Apache 配置笔记 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-06/85598.htm
Haproxy + KeepAlived 实现 WEB 群集 on CentOS 6 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-03/55672.htm
Haproxy+Keepalived 构建高可用负载均衡 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-03/55880.htm
4、添加插件至 nagios
(1)、修改 commands.cfg,添加
##haproxy
define command{
command_name check_haproxy
command_line /opt/nagios/libexec/check_haproxy.sh -s $ARG1$ -m $ARG2$ -w $ARG3$ -C $ARG4$
}
(2)、修改服务配置文件,我是在本机监控故只改 localhost.cfg, 添加以下监控
##haproxy check
define service{
use local-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name localhost
service_description haproxy-Session-cur
check_command check_haproxy!/var/lib/haproxy/stats!rate!10!20
notifications_enabled 0
}
define service{
use local-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name localhost
service_description haproxy-Errors-req
check_command check_haproxy!/var/lib/haproxy/stats!ereq!3!5
notifications_enabled 0
}
define service{
use local-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name localhost
service_description haproxy-Errors-con
check_command check_haproxy!/var/lib/haproxy/stats!econ!3!5
notifications_enabled 0
}
define service{
use local-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name localhost
service_description haproxy-Errors-resp
check_command check_haproxy!/var/lib/haproxy/stats!eresp!3!5
notifications_enabled 0
}
(3)、添加进 nrpe.cfg, 这些报警阈值是为了方便测试设得比较小,根据实际应用更改
command[check_haproxy]=/usr/bin/sudo /opt/nagios/libexec/check_haproxy.sh -s /var/lib/haproxy/stats -m rate –warning 10 –critical 20
command[check_haproxy]=/usr/bin/sudo /opt/nagios/libexec/check_haproxy.sh -s /var/lib/haproxy/stats -m ereq –warning 3 –critical 5
command[check_haproxy]=/usr/bin/sudo /opt/nagios/libexec/check_haproxy.sh -s /var/lib/haproxy/stats -m econ –warning 3 –critical 5
command[check_haproxy]=/usr/bin/sudo /opt/nagios/libexec/check_haproxy.sh -s /var/lib/haproxy/stats -m eresp –warning 3 –critical 5
重启 nagios 服务,登陆 web 界面,已经可以看到监控项了:

现在来测试下是否能够正常报警,使用 siege 测试:
./bin/siege -c 50 -n 50 -t 30 http://192.168.1.250/stat.php
,等几分钟看界面,已经有报警了:
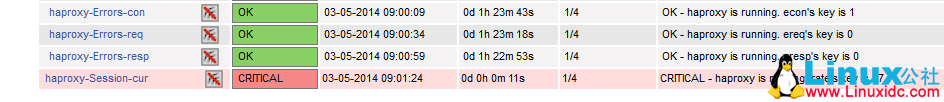
完毕
附:通过 curl 访问 haproxy 状态页面来获取数据脚本:
#########################################################################
# File Name: check_haproxy-url.sh
# Author: jc
# Created Time: 2014 年 03 月 01 日 星期六 17 时 27 分 03 秒
#########################################################################
#!/bin/bash
ST_OK=0
ST_WR=1
ST_CR=2
ST_UK=3
url_check=1
print_help() {
echo ” –url|-u)”
echo ” haproxy 监控页面的链接 ”
echo ” -m/–mode)”
echo ” haproxy 的状态项, 如:rate,ereq,econ,eresp,status”
echo ” -n/–no-url-check|)”
echo ” 是否检查 haproxy 的 url:1 检测(默认),0 不检查 ”
exit $ST_UK
}
while test -n “$1”; do
case “$1” in
-help|-h)
print_help
exit $ST_UK
;;
–mode|-m)
mode=$2
shift
;;
–no-url-check|-n)
url_check=0
;;
–url|-u)
hap_url=$2
shift
;;
–warning|-w)
warning=$2
shift
;;
–critical|-c)
critical=$2
shift
;;
*)
echo “Unknown argument: $1”
print_help
exit $ST_UK
;;
esac
shift
done
#check_url() {
#curl -o /tmp/stats.csv $url >/dev/null 2>&1
#if [-s stats.csv]
#then
#con=1
#else
#con=2
#fi
#}
curl -o /tmp/stats.csv $hap_url >/dev/null 2>&1
ch_val() {
if [-z $val]
then
val=0
else
val=$val
fi
}
get_val() {
case $mode in
rate)
val=`cat /tmp/stats.csv | grep web1 | awk -F ‘<tr class=’ ‘{print $3}’ | awk -F ‘</td><td>’ ‘{print $5}’`
ch_val
;;
ereq)
val=`cat /tmp/stats.csv | grep web1 | awk -F ‘<tr class=’ ‘{print $3}’ | awk -F ‘</td><td>’ ‘{print $16}’`
ch_val
;;
econ)
val=`cat /tmp/stats.csv | grep web1 | awk -F ‘<tr class=’ ‘{print $3}’ | awk -F ‘</td><td>’ ‘{print $17}’| awk -F ‘<‘ ‘{print $1}’`
ch_val
;;
eresp)
val=`cat /tmp/stats.csv | grep web1 | awk -F ‘<tr class=’ ‘{print $3}’ | awk -F ‘</td><td>’ ‘{print $18}’`
ch_val
;;
# status)
# val=`cat /tmp/stats.csv | grep web1 | awk -F ‘<tr class=’ ‘{print $3}’ | awk -F ‘</td><td>’ ‘{print $21}’`
# ch_val
# ;;
*)
echo “mode 输入错误,请重新输入 ”
;;
esac
}
out_pr() {
output=”haproxy is running. $mode: $val”
}
get_stat() {
if [$val -ge $warning] && [$val -lt $critical]
then
echo “WARNING – ${output}”
exit $ST_WR
elif [“$val” -ge “$critical”]
then
echo “CRITICAL – ${output}”
exit $ST_CR
else
echo “OK – ${output}”
exit $ST_OK
fi
}
#if [$url_check -eq 1]
#then
# check_url
# if [“$con” -eq 2]
# then
# echo “ERR!! 无法访问 haproxy 的状态页面,请确认 url 输入正确!”
# exit $ST_CR
# fi
#fi
get_val
out_pr
get_stat
Nagios 的详细介绍:请点这里
Nagios 的下载地址:请点这里
相关阅读:
网络监控器 Nagios 全攻略 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-07/87067.htm
Nagios 搭建与配置详解 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-05/84848.htm
Nginx 环境下构建 Nagios 监控平台 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2011-07/38112.htm
在 RHEL5.3 上配置基本的 Nagios 系统(使用 Nagios-3.1.2) http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2011-07/38129.htm
CentOS 5.5+Nginx+Nagios 监控端和被控端安装配置指南 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2011-09/44018.htm
Ubuntu 13.10 Server 安装 Nagios Core 网络监控运用 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-11/93047.htm
最近用 shell 写了个监控 haproxy 状态的脚本,记录一下以备后用。
1、首先明确需求。我们需要什么功能,常规方式是怎么实现的,使用脚本又该怎么实现。
只需要监控 5 个状态:当前连接数 Session rate 下的 Cur;错误状态 Errors 下的三种状态 Req,Conn,Resp;服务状态 Status。状态页面如图:

那么如何用脚本的形式把这些展示出来呢?重要的是,如何让 nagios 能够获取到这些数据?这就是接下来需要做的事情。
获取这些数据有两种方法:其一,通过 wget 或者 curl 来访问状态页面,然后筛选数据;其二,通过 sock 来获取状态,然后筛选。我先采用第二种方式来获取数据。
从 sock 获取数据,需要安装 socat 这个软件,具体使用省略。
echo “show stat” | socat /var/lib/haproxy/stats stdio
#/var/lib/haproxy/stats 是 haproxy 路径
可以看到以 csv 格式的状态
pxname,svname,qcur,qmax,scur,smax,slim,stot,bin,bout,dreq,dresp,ereq,econ,eresp,wretr,wredis,status,weight,act,bck,chkfail,chkdown,lastchg,downtime,qlimit,pid,iid,sid,throttle,lbtot,tracked,type,rate,rate_lim,rate_max,check_status,check_code,check_duration,hrsp_1xx,hrsp_2xx,hrsp_3xx,hrsp_4xx,hrsp_5xx,hrsp_other,hanafail,req_rate,req_rate_max,req_tot,cli_abrt,srv_abrt,
admin_status,FRONTEND,,,1,1,20480,31,12757,354568,0,0,0,,,,,OPEN,,,,,,,,,1,1,0,,,,0,1,0,10,,,,0,29,1,0,0,0,,1,10,31,,,
admin_status,BACKEND,0,0,0,0,20480,0,12757,354568,0,0,,0,0,0,0,UP,0,0,0,,0,773,0,,1,1,0,,0,,1,0,,0,,,,0,0,0,0,0,0,,,,,0,0,
http_80_in,FRONTEND,,,0,1,20480,4,348,848,0,0,0,,,,,OPEN,,,,,,,,,1,2,0,,,,0,0,0,1,,,,0,0,0,0,4,0,,0,1,4,,,
web,web1,0,0,0,0,,0,0,0,,0,,0,0,0,0,UP,1,1,0,0,0,773,0,,1,3,1,,0,,2,0,,0,L7OK,200,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,,,,0,0,
web,web2,0,0,0,0,,0,0,0,,0,,0,0,0,0,DOWN,2,1,0,0,1,771,771,,1,3,2,,0,,2,0,,0,L4TOUT,,1502,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,,,,0,0,
web,BACKEND,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,,0,0,0,0,UP,1,1,0,,0,773,0,,1,3,0,,0,,1,0,,0,,,,0,0,0,0,0,0,,,,,0,0,
需要的数据:当起连接数 rate 在第 34 域;err 相关的 ereq、econ、eresp 在第 13、14、15 域;状态 status 在第 18 域。用 awk 筛选数据:
rate=`echo “show stat” | socat /var/lib/haproxy/stats stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $34}’`
ereq=`echo “show stat” | socat /var/lib/haproxy/stats stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $34}’`
econ=`echo “show stat” | socat /var/lib/haproxy/stats stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $34}’`
eresp=`echo “show stat” | socat /var/lib/haproxy/stats stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $34}’`
status=`echo “show stat” | socat /var/lib/haproxy/stats stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $34}’`
数据现在已经可以获取了,接下来就要让 nagios 能够接受到数据。
2、了解插件规范。
nagios 的插件规范有两点:
(1)、需要一个返回值来确定状态
| 0 | OK |
| 1 | WARNING |
| 2 | CRITICAL |
| 3 | UNKNOWN |
(2)、在报警处输出定义的说明,默认大小 4K, 见红框位置:

了解了编写规范,现在就开始写脚本。
3、脚本实例
#########################################################################
# File Name: check_haproxy.sh
# Author: jc
# Created Time: 2014 年 03 月 01 日 星期六 14 时 36 分 23 秒
#########################################################################
#!/bin/bash
# 定义返回状态
ST_OK=0
ST_WR=1
ST_CR=2
ST_UK=3
#sock 的默认路径
sock_path=/var/lib/haproxy/stats
# 默认检查 sock 是否存在
#sock_check=1
# 帮助信息函数
print_help() {
echo ” –sock|-s)”
echo ” haproxy 的 sock 路径,默认路径:/var/lib/haproxy/stats”
echo ” -m/–mode)”
echo ” haproxy 的状态项, 目前只支持:rate,ereq,econ,eresp,status”
# echo ” -n/–no-check-sock)”
# echo ” 检查 sock 存在与否,1 检查,0 不检查 ”
exit $ST_UK
}
# 获取输入的选项
while test -n “$1”; do
case “$1” in
-help|-h)
print_help
exit $ST_UK
;;
–sock|-s)
sock=$2
shift
;;
–mode|-m)
mode=$2
shift
;;
–no-sock-check|-n)
sock_check=0
;;
–hostname|-H)
hostname=$2
shift
;;
–warning|-w)
warning=$2
shift
;;
–critical|-c)
critical=$2
shift
;;
*)
echo “Unknown argument: $1”
print_help
exit $ST_UK
;;
esac
shift
done
#sock 检测
#check_sock() {
#echo “show stat” | socat /var/lib/haproxy/stats stdio >/tmp/hap_sta.txt
#if [-s “/tmp/hap_sta.txt”]
#then
# con=1
#else
# con=2
#fi
#}
# 获取数据
get_val() {
case $mode in
rate)
val=`echo “show stat” | socat $sock_path stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $34}’`
;;
ereq)
val=`echo “show stat” | socat $sock_path stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $13}’`
if [-z $val]
then
val=0
fi
;;
econ)
val=`echo “show stat” | socat $sock_path stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $14}’`
;;
eresp)
val=`echo “show stat” | socat $sock_path stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $15}’`
;;
status)
val=`echo “show stat” | socat $sock_path stdio | awk -F, ‘$2==”web1″ {print $18}’`
;;
*)
echo “ 暂时不能检测此项,请重新输入 ”
;;
esac
}
# 显示的文字信息
out_pr() {
output=”haproxy is running. $mode’s key is $val”
}
# 开始执行
## 检查 sock 是否能够连上
#if [$sock_check = 1]
#then
# check_sock
# if [“$con” = 2]
# then
# echo “ERR!! 连接 haproxy 被拒绝,请确认服务已经开启,或者检查 sock 路径 / 权限是否正确!”
# exit $ST_CR
# fi
#fi
get_val
out_pr
#get_stat() {
if [“$val” -ge “$warning”] && [“$val” -lt “$critical”]
then
echo “WARNING – $output”
exit $ST_WR
elif [“$val” -ge “$critical”]
then
echo “CRITICAL – $output”
exit $ST_CR
else
echo “OK – $output”
exit $ST_OK
fi
脚本完成,先在命令行测试:
[root@webtest-250 libexec]# /opt/nagios/libexec/check_haproxy.sh -m rate -w 10 -c 20
OK – haproxy is running. rate’s key is 0
注意,以下两步相当重要,如果不给 nagios 用户添加权限,在页面会看不到值,如
(1)、更改 /etc/sudoers,把 nagios 启动用户添加进去
nagios ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_hap.sh
(2)、更改 /etc/sudoers 把这一行注释,否则在后台运行 sudo 会报错
#Defaults requiretty
现在切换到 nagios 的用户执行就正确了。
HAproxy 的详细介绍:请点这里
HAproxy 的下载地址:请点这里
推荐阅读:
Haproxy+Keepalived 搭建 Weblogic 高可用负载均衡集群 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-09/89732.htm
Keepalived+HAProxy 配置高可用负载均衡 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-03/56748.htm
CentOS 6.3 下 Haproxy+Keepalived+Apache 配置笔记 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-06/85598.htm
Haproxy + KeepAlived 实现 WEB 群集 on CentOS 6 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-03/55672.htm
Haproxy+Keepalived 构建高可用负载均衡 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-03/55880.htm















