共计 9451 个字符,预计需要花费 24 分钟才能阅读完成。
概述
Oracle-procedure 解读
Oracle 存储过程和自定义函数
PL/SQL 中的过程和函数(通常称为子程序)是 PL/SQL 块的一种特殊的类型,这种类型的子程序可以以编译的形式存放在数据库中,并为后续的程序块调用。
相同点:完成特定功能的程序
不同点:是否用 return 语句返回值。
举个例子:
| create or replace procedure PrintStudents(p_staffName in xgj_test.username%type) as | |
| cursor c_testData is | |
| select t.sal, t.comm from xgj_test t where t.username = p_staffName; | |
| begin | |
| for v_info in c_testData loop | |
| DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(v_info.sal || ' ' || v_info.comm); | |
| end loop; | |
| end PrintStudents; |
一旦创建了改程序并将其存储在数据库中,就可以使用如下的方式调用该过程
| begin | |
| PrintStudents('Computer Science'); | |
| PrintStudents('Match'); | |
| end; | |
| / |
或者
| exec PrintStudents('Computer Science'); | |
| exec PrintStudents('Match'); |
在命令窗口中: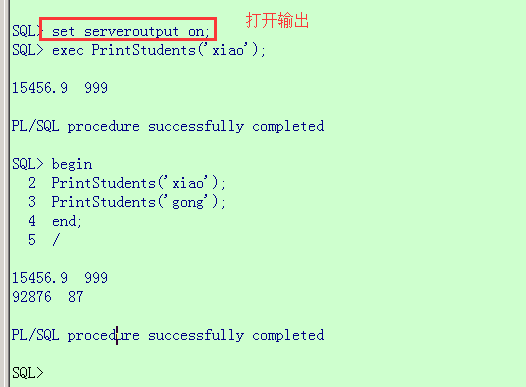
在 pl/sql 工具的 sql 窗口中: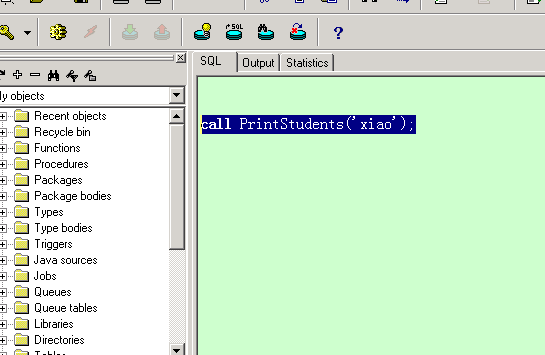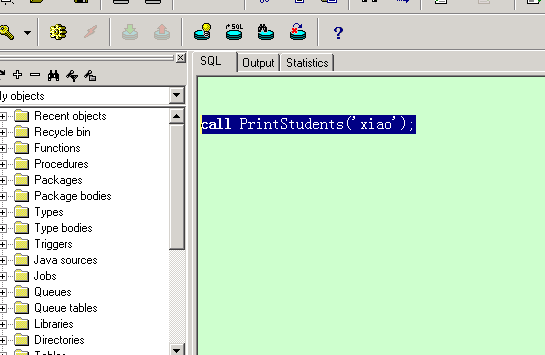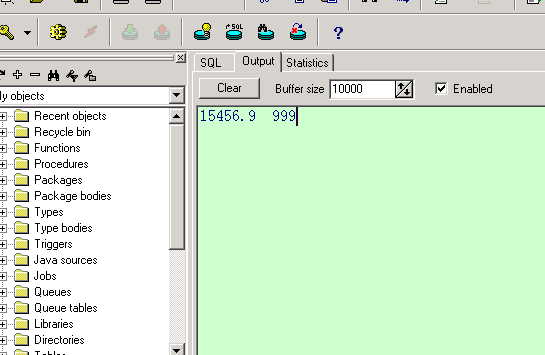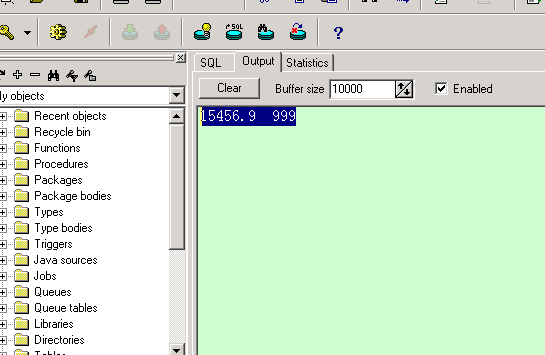
存储过程的创建和调用
基本语法
| create [or replace] procedure procedure_name | |
| [(argument [ {IN | OUT | IN OUT }] type, | |
| ...... | |
| argument [{IN | OUT | IN OUT }] type ) ] {IS | AS} | |
| procedure_body |
无参的存储过程
| /** | |
| 无参数的存过 | |
| 打印 hello world | |
| 调用存储过程:1. exec sayhelloworld(); | |
| 2 begin | |
| sayhelloworld(); | |
| end; | |
| / | |
| */ | |
| create or replace procedure sayhelloworld | |
| as | |
| -- 说明部分 | |
| begin | |
| dbms_output.put_line('hello world'); | |
| end sayhelloworld; |
调用过程:
| SQL> set serveroutput on ; | |
| SQL> exec sayhelloworld(); | |
| hello world | |
| PL/SQL procedure successfully completed | |
| SQL> begin | |
| 2 sayhelloworld(); | |
| 3 sayhelloworld(); | |
| 4 end; | |
| 5 / | |
| hello world | |
| hello world | |
| PL/SQL procedure successfully completed |
带参数的存储过程
| /** | |
| 创建一个带参数的存储过程 | |
| 给指定的员工增加工资,并打印增长前后的工资 | |
| */ | |
| create or replace procedure addSalary(staffName in xgj_test.username%type ) | |
| as | |
| -- 定义一个变量保存调整之前的薪水 | |
| oldSalary xgj_test.sal%type; | |
| begin | |
| -- 查询员工涨之前的薪水 | |
| select t.sal into oldSalary from xgj_test t where t.username=staffName; | |
| -- 调整薪水 | |
| update xgj_test t set t.sal = sal+1000 where t.username=staffName ; | |
| -- 输出 | |
| dbms_output.put_line('调整之前的薪水:'|| oldSalary || ', 调整之后的薪水:' || (oldSalary + 1000)); | |
| end addSalary; |
可以看到,update 语句之后并没有 commit 的操作。
一般来讲为了保证事务的一致性,由调用者来提交比较合适,当然了是需要区分具体的业务需求的~
| begin | |
| addSalary('xiao'); | |
| addSalary('gong'); | |
| commit ; | |
| end ; | |
| / |
存储函数
基本语法
| create [or replace] function function_name | |
| [(argument [ {IN | OUT | IN OUT }] type, | |
| ...... | |
| argument [{IN | OUT | IN OUT }] type ) ] | |
| RETURN {IS | AS} | |
| function_body |
其中 return 子句是必须存在的,一个函数如果没有执行 return 就结束将发生错误,这一点和存过有说不同。
存储函数
准备的数据如下: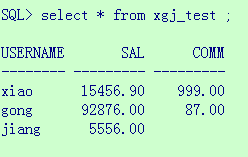
| /** | |
| 查询员工的年薪(月工资 *12 + 奖金)*/ | |
| create or replace function querySalaryInCome(staffName in varchar2) | |
| return number as | |
| -- 定义变量保存员工的工资和奖金 | |
| pSalary xgj_test.sal%type; | |
| pComm xgj_test.comm%type; | |
| begin | |
| -- 查询员工的工资和奖金 | |
| select t.sal, t.comm | |
| into pSalary, pComm | |
| from xgj_test t | |
| where t.username = staffName; | |
| -- 直接返回年薪 | |
| return pSalary * 12 + pComm; | |
| end querySalaryInCome; |
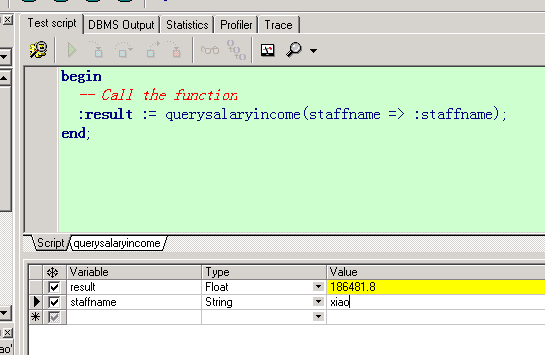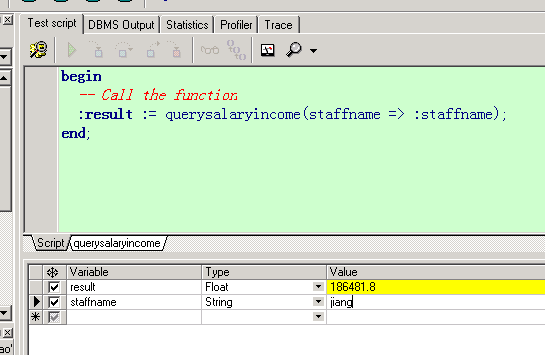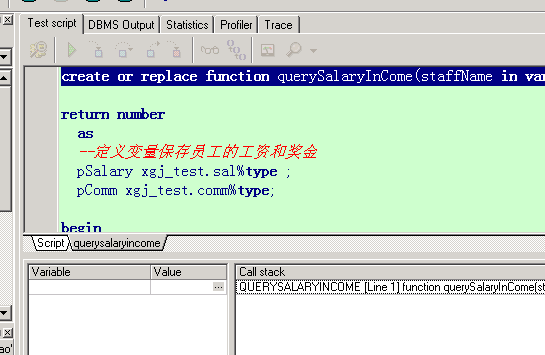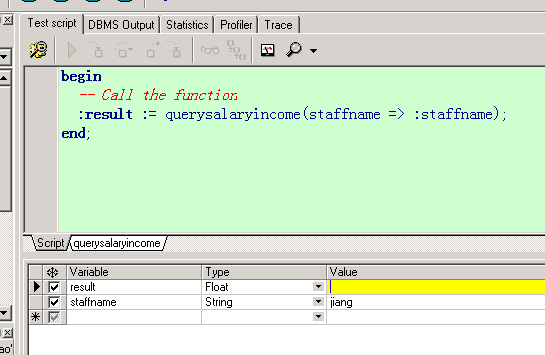
存在一个问题,当奖金为空的时候,算出来的年收入竟然是空的。
因为 如果一个表达式中有空值,那么这个表达式的结果即为空值。
所以我们需要对空值进行处理,使用 nvl 函数即可。
最后修改后的 function 为
| create or replace function querySalaryInCome(staffName in varchar2) | |
| return number as | |
| -- 定义变量保存员工的工资和奖金 | |
| pSalary xgj_test.sal%type; | |
| pComm xgj_test.comm%type; | |
| begin | |
| -- 查询员工的工资和奖金 | |
| select t.sal, t.comm | |
| into pSalary, pComm | |
| from xgj_test t | |
| where t.username = staffName; | |
| -- 直接返回年薪 | |
| return pSalary * 12 + nvl(pComm,0); | |
| end querySalaryInCome; |
out 参数
out 参数
一般来讲,存储过程和存储函数的区别在于存储函数可以有一个返回值,而存储过程没有返回值。
- 存储过程和存储函数都可以有 out 参数
- 存储过程和存储函数都可以有多个 out 参数
- 存储过程可以通过 out 参数实现返回值
那我们如何选择存储过程和存储函数呢?
原则:
如果只有一个返回值,用存储函数,否则(即没有返回值或者有多个返回值)使用存储过程。
| /** | |
| 根据员工姓名,查询员工的全部信息 | |
| */ | |
| create or replace procedure QueryStaffInfo(staffName in xgj_test.username%type, | |
| pSal out number, | |
| pComm out xgj_test.comm%type, | |
| pJob out xgj_test.job%type) | |
| is | |
| begin | |
| -- 查询该员工的薪资,奖金和职位 | |
| select t.sal,t.comm,t.job into pSal,pComm,pJob from xgj_test t where t.username=staffName; | |
| end QueryStaffInfo; |
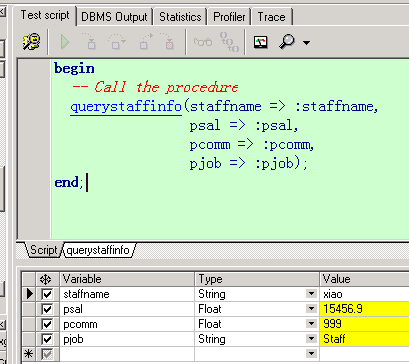
先抛出两个思考问题:
- 查询员工的所有信息–> out 参数太多怎么办?
- 查询某个部门中所有员工的信息–> out 中返回集合?
后面会讲到如何解决?总不能一个个的写 out 吧~
在应用中访问存储过程和存储函数
概述
我们使用 JAVA 程序连接 Oracle 数据库。
使用 jar: ojdbc14.jar
关于 oracle 官方提供的几个 jar 的区别
classes12.jar (1,600,090 bytes) – for use with JDK 1.2 and JDK 1.3
classes12_g.jar (2,044,594 bytes) – same as classes12.jar, except that classes were compiled with“javac -g”and contain some tracing information.
classes12dms.jar (1,607,745 bytes) – same as classes12.jar, except that it contains additional code`to support Oracle Dynamic Monitoring Service.
classes12dms_g.jar (2,052,968 bytes) – same as classes12dms.jar except that classes were compiled with“javac -g”and contain some tracing information.
ojdbc14.jar (1,545,954 bytes) – classes for use with JDK 1.4 and 1.5
ojdbc14_g.jar (1,938,906 bytes) – same as ojdbc14.jar, except that classes were compiled with“javac -g”and contain some tracing information.
ojdbc14dms.jar (1,553,561 bytes) – same as ojdbc14.jar, except that it contains additional code`to support Oracle Dynamic Monitoring Service.
ojdbc14dms_g.jar (1,947,136 bytes) – same as ojdbc14dms.jar, except that classes were compiled with“javac -g”and contain some tracing information.
工程目录如下: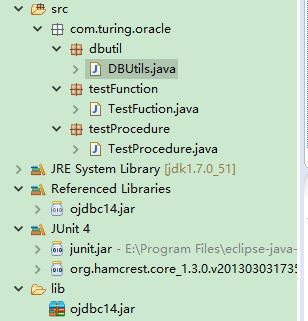
简单的写下获取数据库连接的工具类
| import java.sql.Connection; | |
| import java.sql.DriverManager; | |
| import java.sql.ResultSet; | |
| import java.sql.SQLException; | |
| import java.sql.Statement; | |
| public class DBUtils { | |
| // 设定数据库驱动,数据库连接地址端口名称,用户名,密码 | |
| private static final String driver = "oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"; | |
| private static final String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@ip:xxxx"; | |
| private static final String username = "xxxx"; | |
| private static final String password = "xxxx"; | |
| /** | |
| * 注册数据库驱动 | |
| */ | |
| static {try {Class.forName(driver); | |
| } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e.getMessage()); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * 获取数据库连接 | |
| */ | |
| public static Connection getConnection() {try {Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password); | |
| // 成功,返回 connection | |
| return connection; | |
| } catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } | |
| // 获取失败,返回 null | |
| return null; | |
| } | |
| /** | |
| * 释放连接 | |
| */ | |
| public static void cleanup(Connection conn, Statement st, ResultSet rs) {if (rs != null) {try {rs.close(); | |
| } catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } finally {rs = null; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| if (st != null) {try {st.close(); | |
| } catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } finally {st = null; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| if (conn != null) {try {conn.close(); | |
| } catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace(); | |
| } finally {conn = null; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
在应用程序中访问存储过程
根据官方提供的 API,我们可以看到:
| import java.sql.CallableStatement; | |
| import java.sql.Connection; | |
| import java.sql.SQLException; | |
| import org.junit.Test; | |
| import com.turing.oracle.dbutil.DBUtils; | |
| import oracle.jdbc.OracleTypes; | |
| public class TestProcedure { | |
| public void callProcedure(){// {call <procedure-name>[(<arg1>,<arg2>, ...)]} | |
| Connection conn = null ; | |
| CallableStatement callableStatement = null ; | |
| /** | |
| * | |
| 根据员工姓名,查询员工的全部信息 | |
| create or replace procedure QueryStaffInfo(staffName in xgj_test.username%type, | |
| pSal out number, | |
| pComm out xgj_test.comm%type, | |
| pJob out xgj_test.job%type) | |
| is | |
| begin | |
| -- 查询该员工的薪资,奖金和职位 | |
| select t.sal,t.comm,t.job into pSal,pComm,pJob from xgj_test t where t.username=staffName; | |
| end QueryStaffInfo; | |
| */ | |
| // 我们可以看到该存过 4 个参数 1 个入参 3 个出参 | |
| String sql = "{call QueryStaffInfo(?,?,?,?)}"; | |
| try {// 获取连接 | |
| conn = DBUtils.getConnection(); | |
| // 通过连接获取到 CallableStatement | |
| callableStatement = conn.prepareCall(sql); | |
| // 对于 in 参数,需要赋值 | |
| callableStatement.setString(1, "xiao"); | |
| // 对于 out 参数,需要声明 | |
| callableStatement.registerOutParameter(2, OracleTypes.NUMBER); // 第二个? | |
| callableStatement.registerOutParameter(3, OracleTypes.NUMBER);// 第三个? | |
| callableStatement.registerOutParameter(4, OracleTypes.VARCHAR);// 第四个? | |
| // 执行调用 | |
| callableStatement.execute(); | |
| // 取出结果 | |
| int salary = callableStatement.getInt(2); | |
| int comm = callableStatement.getInt(3); | |
| String job = callableStatement.getString(3); | |
| System.out.println(salary + "\t" + comm + "\t" + job); | |
| } catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace(); | |
| }finally {DBUtils.cleanup(conn, callableStatement, null); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
在应用程序中访问存储函数
| import java.sql.CallableStatement; | |
| import java.sql.Connection; | |
| import org.junit.Test; | |
| import com.turing.oracle.dbutil.DBUtils; | |
| import oracle.jdbc.OracleTypes; | |
| public class TestFuction { | |
| public void callFuction(){//{?= call <procedure-name>[(<arg1>,<arg2>, ...)]} | |
| Connection conn = null; | |
| CallableStatement call = null; | |
| /** | |
| * create or replace function querySalaryInCome(staffName in varchar2) | |
| return number as | |
| -- 定义变量保存员工的工资和奖金 | |
| pSalary xgj_test.sal%type; | |
| pComm xgj_test.comm%type; | |
| begin | |
| -- 查询员工的工资和奖金 | |
| select t.sal, t.comm | |
| into pSalary, pComm | |
| from xgj_test t | |
| where t.username = staffName; | |
| -- 直接返回年薪 | |
| return pSalary * 12 + nvl(pComm,0); | |
| end querySalaryInCome; | |
| */ | |
| String sql = "{?=call querySalaryInCome(?)}"; | |
| try {// 获取连接 | |
| conn = DBUtils.getConnection(); | |
| // 通过 conn 获取 CallableStatement | |
| call = conn.prepareCall(sql); | |
| // out 参数,需要声明 | |
| call.registerOutParameter(1, OracleTypes.NUMBER); | |
| // in 参数,需要赋值 | |
| call.setString(2, "gong"); | |
| // 执行 | |
| call.execute(); | |
| // 取出返回值 第一个?的值 | |
| double income = call.getDouble(1); | |
| System.out.println("该员工的年收入:" + income); | |
| } catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace(); | |
| }finally {DBUtils.cleanup(conn, call, null); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
在 out 参数中访问光标
在 out 参数中使用光标
我们之前抛出的两个思考问题:
- 查询员工的所有信息–> out 参数太多怎么办?
- 查询某个部门中所有员工的信息–> out 中返回集合?
我们可以通过返回 Cursor 的方式来实现。
在 out 参数中使用光标 的步骤:
- 申明包结构
- 包头
- 包体
包头:
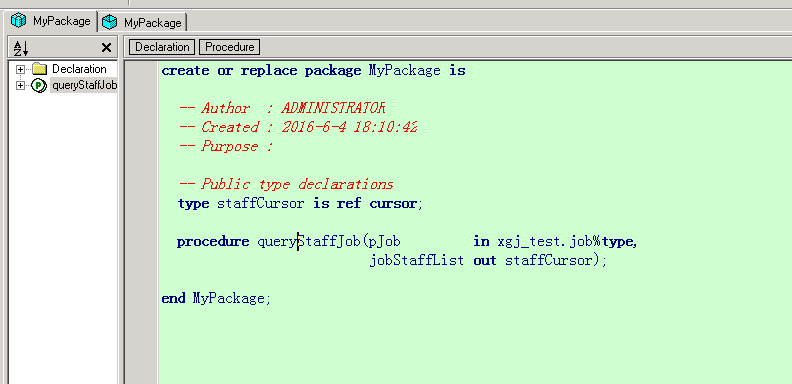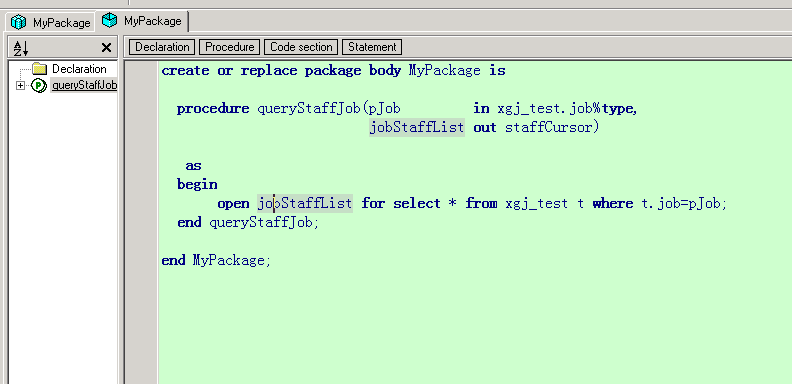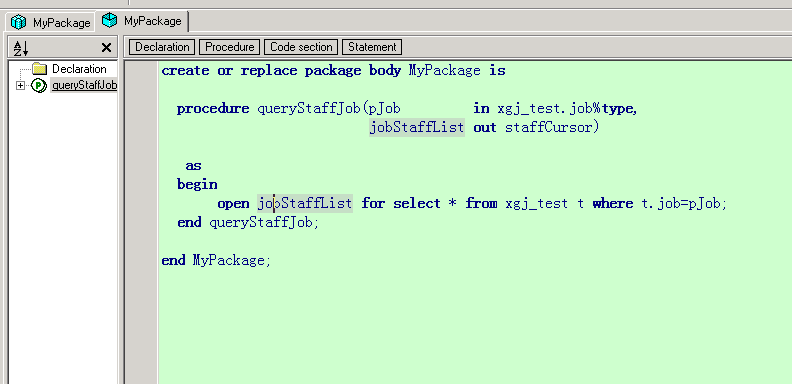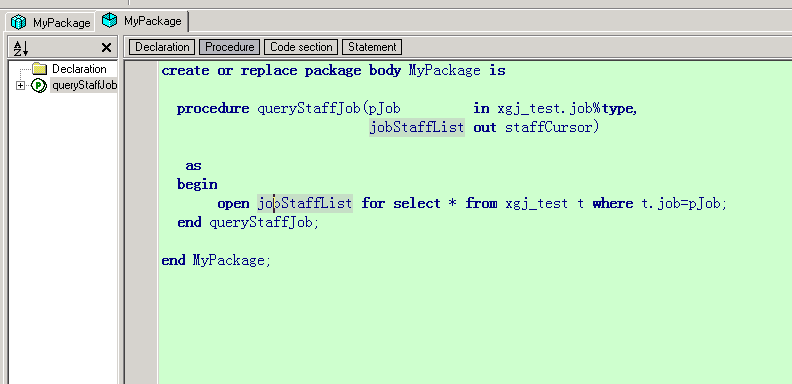
| create or replace package MyPackage is | |
| -- Author : ADMINISTRATOR | |
| -- Created : 2016-6-4 18:10:42 | |
| -- Purpose : | |
| -- 使用 type 关键字 is ref cursor 说明是 cursor 类型 | |
| type staffCursor is ref cursor; | |
| procedure queryStaffJob(pJob in xgj_test.job%type, | |
| jobStaffList out staffCursor); | |
| end MyPackage; |
创建完包头之后,创建包体,包体需要实现包头中声明的所有方法。
包体
| create or replace package body MyPackage is | |
| procedure queryStaffJob(pJob in xgj_test.job%type, | |
| jobStaffList out staffCursor) | |
| as | |
| begin | |
| open jobStaffList for select * from xgj_test t where t.job=pJob; | |
| end queryStaffJob; | |
| end MyPackage; |
事实上,通过 plsql 工具创建包头,编译后,包体的框架就会自动的生成了。
在应用程序中访问包下的存储过程
在应用程序中访问包下的存储过程
在应用程序中访问包下的存储过程,需要带包名
| import java.sql.CallableStatement; | |
| import java.sql.Connection; | |
| import java.sql.ResultSet; | |
| import org.junit.Test; | |
| import com.turing.oracle.dbutil.DBUtils; | |
| import oracle.jdbc.OracleTypes; | |
| import oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleCallableStatement; | |
| public class TestCursor { | |
| public void testCursor(){/** | |
| * | |
| * create or replace package MyPackage is | |
| type staffCursor is ref cursor; | |
| procedure queryStaffJob(pJob in xgj_test.job%type, | |
| jobStaffList out staffCursor); | |
| end MyPackage; | |
| */ | |
| String sql = "{call MyPackage.queryStaffJob(?,?)}" ; | |
| Connection conn = null; | |
| CallableStatement call = null ; | |
| ResultSet rs = null; | |
| try { | |
| // 获取数据库连接 | |
| conn = DBUtils.getConnection(); | |
| // 通过 conn 创建 CallableStatemet | |
| call = conn.prepareCall(sql); | |
| // in 参数 需要赋值 | |
| call.setString(1, "Staff"); | |
| // out 参数需要声明 | |
| call.registerOutParameter(2, OracleTypes.CURSOR); | |
| // 执行调用 | |
| call.execute(); | |
| // 获取返回值 | |
| rs = ((OracleCallableStatement)call).getCursor(2); | |
| while(rs.next()){ | |
| // 取出值 | |
| String username = rs.getString("username"); | |
| double sal = rs.getDouble("sal"); | |
| double comm = rs.getDouble("comm"); | |
| System.out.println("username:" + username + "\t sal:" + sal + "\t comm:" + comm); | |
| } | |
| } catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace(); | |
| }finally {DBUtils.cleanup(conn, call, rs); | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } |
更多 Oracle 相关信息见Oracle 专题页面 http://www.linuxidc.com/topicnews.aspx?tid=12
本文永久更新链接地址:http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2016-11/136851.htm















