共计 16692 个字符,预计需要花费 42 分钟才能阅读完成。
上一篇 Web 服务(一)HTTP 基础详解详细介绍了 http 基础与 httpd 的安装(见 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2014-03/98952.htm);这篇详细介绍下 httpd-2.2 的部分配置参数
CentOS 6.5 编译安装 httpd-2.4.7 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2014-02/97265.htm
一、配置文件和基本格式
配置文件路径:/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
配置参数 值
1、配置指令不区分字符大小写;但是值有可能区分字符大小写
2、有些指令可以重复出现多次
配置文件格式:
1、全局配置
2、主机配置:用于仅提供一个站点
3、虚拟主机:用于提供多个站点(和主机配置不能同时生效)
配置文件语法测试:{service httpd configtest | httpd -t}
二、详细配置
1、监听套接字
# 配置文件事例
#Listen 12.34.56.78:80
Listen 80
Listen 8080
Listen 192.168.1.110:8082
此指令可以出现多次;用于指定监听多个不同的套接字:
[Linux]#httpd -t
Syntax OK
[Linux]#service httpd reload
Reloading httpd:
[Linux]#ss -tnl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 :::111 :::*
LISTEN 0 128 *:111 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 :::8080 :::*
LISTEN 0 128 :::80 :::*
LISTEN 0 128 192.168.1.186:8082 *:*
2、配置使用 Keep Alive
# KeepAlive: Whether or not to allow persistent connections (more than
# one request per connection). Set to “Off” to deactivate.
#
#KeepAlive On
KeepAlive Off
MaxKeepAliveRequests 100 #持久连接最大请求数
KeepAliveTimeout 15 #超时时间
3、多道处理模块 MPM
查看系统默认启用的模块
[Linux]#httpd -l
Compiled in modules:
core.c
prefork.c #默认启用 prefork 模块
http_core.c
mod_so.c
[Linux]#
# 如需启用 worker 模块;需要更改配置文件
[Linux]#vi /etc/sysconfig/httpd
#HTTPD=/usr/sbin/httpd.worker #启用该项后重启 httpd
配置模块信息
[Linux]#vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
# prefork MPM
# StartServers: number of server processes to start
# MinSpareServers: minimum number of server processes which are kept spare
# MaxSpareServers: maximum number of server processes which are kept spare
# ServerLimit: maximum value for MaxClients for the lifetime of the server
# MaxClients: maximum number of server processes allowed to start
# MaxRequestsPerChild: maximum number of requests a server process serves
prefork 稳定性较好,一个线程崩溃不会影响其他线程
<IfModule prefork.c> 判断 prefork 模块是否存在
StartServers 8 默认启动的工作进程数;不包含主进程
MinSpareServers 5 最少空闲进程数
MaxSpareServers 20 最大空闲进程数
ServerLimit 256 最大活动进程数
MaxClients 256 最多允许发起的请求的个数
MaxRequestsPerChild 4000 每个子进程在生命周期内所能够服务的最多请求个数
</IfModule>
# worker MPM
# StartServers: initial number of server processes to start
# MaxClients: maximum number of simultaneous client connections
# MinSpareThreads: minimum number of worker threads which are kept spare
# MaxSpareThreads: maximum number of worker threads which are kept spare
# ThreadsPerChild: constant number of worker threads in each server process
# MaxRequestsPerChild: maximum number of requests a server process serves
worker 多个进程;一个进程崩溃会影响其下的其他线程
<IfModule worker.c> 判断 worker 模块是否存在
StartServers 4 启动的子进程的个数
MaxClients 300 并发请求的最大个数
MinSpareThreads 25 最少空闲线程数
MaxSpareThreads 75 最大空闲线程数
ThreadsPerChild 25 每个子进程可生成的线程数
MaxRequestsPerChild 0 每个子进程在生命周期内所能够服务的最多请求个数;0 表示不做限定
</IfModule>
4、DSO 模块的加载方式
LoadModule module_name /path/to/module
可以使用相对路径和绝对路径;相对路径则对于 ServerRoot 所定义的位置而言;
更改完成后 service httpd reload 可生效
# LoadModule foo_module modules/mod_foo.so
#
LoadModule auth_basic_module modules/mod_auth_basic.so
LoadModule auth_digest_module modules/mod_auth_digest.so
LoadModule authn_file_module modules/mod_authn_file.so
LoadModule authn_alias_module modules/mod_authn_alias.so
LoadModule authn_anon_module modules/mod_authn_anon.so
#
#
[Linux]#httpd -M #可以查看系统所有装载模块
Loaded Modules:
core_module (static)
mpm_prefork_module (static)
http_module (static)
so_module (static)
auth_basic_module (shared)
auth_digest_module (shared)
authn_file_module (shared)
authn_alias_module (shared)
5、配置站点根目录和页面属性
# DocumentRoot: The directory out of which you will serve your
# documents. By default, all requests are taken from this directory, but
# symbolic links and aliases may be used to point to other locations.
#
DocumentRoot “/var/www/html”
DocumentRoot “/path/to/somewhere(站点路径)” #格式
# The Options directive is both complicated and important. Please see 下述站点有配置详细说明
# http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.2/mod/core.html#options
# for more information.
#
<Directory “/var/www/html”> #页面访问属性
#
#
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
#
#
#
Indexes 缺少默认页面时;允许将目录中的所有文件已列表形式返回给用户
FollowSymLinks 允许跟随符号链接所指向的原始文件;危险
None 所有都不启用
All 所有都启用
ExecCGI 是否允许使用 mod_cgi 模块执行 CGI 脚���
Includes 是否允许使用 mod_include 模块实现服务器端包含(SSI)
MultiViews 允许使用 mod_negotiation 实现内容协商
SymLinksIfOwnerMatch 在链接文件属主属组与原始文件的属主属组相同时;允许跟随符号链接所指向的原始文件
#
#
# AllowOverride controls what directives may be placed in .htaccess files.
# It can be “All”, “None”, or any combination of the keywords:
# Options FileInfo AuthConfig Limit
基于主机的访问控制
#
#
AllowOverride None 表示下面这些控制机制是否被禁用;None 表示不被禁用
#
# Controls who can get stuff from this server.
#
#allow 允许;deny 不允许
Order allow,deny #默认 deny;没有 allow 的都 deny;可以写多条;自上而下匹配
Allow from all 格式:from IP
Deny
#二者都匹配或二者都无匹配项时,则以后者为准;否则,则以匹配到的为准
</Directory>
# 最佳匹配:从列表中找出最小的能匹配到访问者的地址的条目为最终是生效的
# 详细参考 http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.2/mod/mod_authz_host.html#allow
6、定义默认主页面
# The index.html.var file (a type-map) is used to deliver content-
# negotiated documents. The MultiViews Option can be used for the
# same purpose, but it is much slower.
#
DirectoryIndex index.html index.html.var #自左而右依次查找
7、用户目录
# The path to the end user account ‘public_html’ directory must be
# accessible to the webserver userid. This usually means that ~userid
权限说明
# must have permissions of 711, ~userid/public_html must have permissions
# of 755, and documents contained therein must be world-readable.
# Otherwise, the client will only receive a “403 Forbidden” message.
#
# See also: http://httpd.apache.org/docs/misc/FAQ.html#forbidden
#
<IfModule mod_userdir.c>
#
# UserDir is disabled by default since it can confirm the presence
# of a username on the system (depending on home directory
# permissions).
#
UserDir disabled
disabled 禁止
UserDir public_html 用户家目录下的目录名称,所有位于此目录中的文件均可通过前述的访问路径进行访问;用户的家目录的赋予运行 httpd 进程的用户拥有执行权限;
#
# To enable requests to /~user/ to serve the user’s public_html
# directory, remove the “UserDir disabled” line above, and uncomment
# the following line instead:
#
#UserDir public_html
</IfModule>
8、配置日志功能
/var/log/httpd/access.log && error.log
access.log: 其需要记录的内容需要自定义
访问日志:
CustomLog “/path/to/access_log_file” Format_Name
LogFormat Format_String Format_Nam
# The following directives define some format nicknames for use with
# a CustomLog directive (see below).
#
LogFormat “%h %l %u %t \”%r\” %>s %b \”%{Referer}i\” \”%{User-Agent}i\”” combined
LogFormat “%h %l %u %t \”%r\” %>s %b” common
LogFormat “%{Referer}i -> %U” referer
LogFormat “%{User-agent}i” agent
#
#
#
%h:客户端地址
%l:远程登录名;通常为 -
%u:认证时的远程用户名;通常为 -
%t:接受到请求时的时间;
%r:请求报文的起始行;
%>s:响应状态码;
%b:响应报文的长度;单位字节;不包含 HTTP 首部
%{Header_Name}i:记录指定请求报文首部的内容(value)
%U:请求的 URL;不包含其他任何请求串
#
# 具体请参照 http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.2/mod/mod_log_config.html
#
# ErrorLog: The location of the error log file.
# If you do not specify an ErrorLog directive within a <VirtualHost>
# container, error messages relating to that virtual host will be
# logged here. If you *do* define an error logfile for a <VirtualHost>
# container, that host’s errors will be logged there and not here.
#
ErrorLog logs/error_log
9、路径别名和默认字符集
Alias /alias/ “/path/to/somewhere/” : 前面别名结尾有 / 后面结尾就一定得有 /
# We include the /icons/ alias for FancyIndexed directory listings. If you
# do not use FancyIndexing, you may comment this out.
#
Alias /icons/ “/var/www/icons/”
#
#
# 字符集
# Specify a default charset for all content served; this enables
# interpretation of all content as UTF-8 by default. To use the
# default browser choice (ISO-8859-1), or to allow the META tags
# in HTML content to override this choice, comment out this
# directive:
#
AddDefaultCharset UTF-8
10、CGI 脚本路径别名
URL –> FileSystem Directory
CGI:Common Gateway Interface
有很多机制需要 SUID 或 SGID 权限;
httpd 无法直接执行脚本;基于 CGI 协议调用脚本解释器;等待脚本解释器返回结果到 web 服务器
# ScriptAlias: This controls which directories contain server scripts.
# ScriptAliases are essentially the same as Aliases, except that
# documents in the realname directory are treated as applications and
# run by the server when requested rather than as documents sent to the client.
# The same rules about trailing “/” apply to ScriptAlias directives as to
# Alias.
#
ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ “/var/www/cgi-bin/”
ScriptAlias /URL/ “/path/to/somewhere/” #格式;路径需要执行权限
#
# 测试
cat << EOF
Content-Type: text/html
<pre>
The hostname is:`hostname`.
The time is:`date`.
</pre>
EOF
11、基于用户的访问控制
虚拟用户:不是系统的账号密码;
在配置文件 LoadModule 下 (auth) 开头的认证类型:
basic:基本认证;账号和密钥明文发送;
digest:摘要认证;hash 编程之后发送
认证提供者(authentication provider):账号和密钥的存放位置(authn)
授权机制(authentication):根据什么进行授权(authz)
1、编辑配置文件使用:
[Linux]#vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
# 在 <Directory> 网站附近下找一个位置新建一个
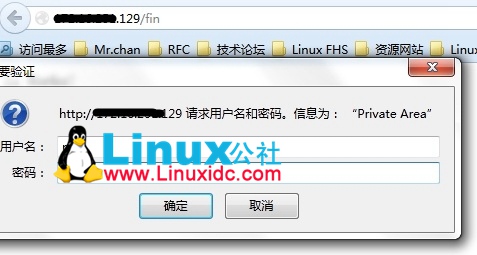
<Directory “/var/www/html/fin”> #指定目录文件
Options None #没有任何选项
AllowOverride AuthConfig #使用认证配置
AuthType Basic #认证类型
AuthName “Private Area” #质询时窗口标题
# AuthBasicProvider file #认证提供者;默认为文件
AuthUserFile /etc/httpd/conf/.htpasswd #指定文件存放用户账号
# AuthGroupFile /etc/httpd/conf/.htgroup #指定文件存放组
# Require group GroupName #指定组名
Require valid-user #所有的合法账户
</Directory>
2、使用 htpasswd 命令生成认证库
[Linux]#htpasswd -b /etc/httpd/conf/.htpasswd linuxidc linuxidc
Adding password for user linuxidc
[Linux]#
详细参数可以 man htpasswd
SYNOPSIS
htpasswd [-c] [-m] [-D] passwdfile username
htpasswd -b [-c] [-m | -d | -p | -s] [-D] passwdfile username password
htpasswd -n [-m | -d | -s | -p] username
htpasswd -nb [-m | -d | -s | -p] username password

12、虚拟主机
一个物理服务器提供多个站点;使用虚拟主机得先取消中心主机
1、基于不同的 IP 实现不同的虚拟
使用不同 IP;
2、基于不同的 port 实现不同的虚拟主机
使用不同端口
3、基于不同的 FQDN 实现不同的虚拟主机
使用不同的 ServerName 的值:FQDN
# DocumentRoot: The directory out of which you will serve your
# documents. By default, all requests are taken from this directory, but
# symbolic links and aliases may be used to point to other locations.
#
#DocumentRoot “/var/www/html” #这项需要先注释;中心主机
#
# 基于主机名不同进行测试;下面这项需要开启;IP 和 port 是不需要开启的
NameVirtualHost *:80
#
# NOTE: NameVirtualHost cannot be used without a port specifier
# (e.g. :80) if mod_ssl is being used, due to the nature of the
# SSL protocol.
#
# VirtualHost example:
# Almost any Apache directive may go into a VirtualHost container.
# The first VirtualHost section is used for requests without a known
# server name.
#
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@linuxidc.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/docs/linuxidc #指定站点路径
ServerName www.linuxidc.com #指定 FQDN
ErrorLog logs/linuxidc.com-error_log #指定错误日志路径及名称
CustomLog logs/linuxidc.com-access_log common #指定访问日志路径及名称
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@88181.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/docs/88181
ServerName www.88181.com
ErrorLog logs/88181.com-error_log
CustomLog logs/88181.com-access_log common
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@dark.net
DocumentRoot /www/docs/dark
ServerName www.dark.net
ErrorLog logs/dark.net-error_log
CustomLog logs/dark.net-access_log common
</VirtualHost>
#
# 配置完成后需要在对应的路径下建立相应的文件
[Linux]#httpd -t
Syntax OK
[Linux]#service httpd restart
Stopping httpd: [OK]
Starting httpd: [OK]
[Linux]#
配置完成后如在 linux 下测试则修改 /etc/hosts 文件;windows 下修改 C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts 文件
X.X.X.129 www.linuxidc.com
X.X.X.129 www.88181.com
X.X.X.129 www.dark.net
修改完成后直接访问即可。
# 查看日志文件
[Linux]#cd /var/log/httpd/
[Linux]#ls
access_log dark.net-access_log error_log linuxidc.com-access_log 88181.com-access_log
access_log-20140309 dark.net-error_log error_log-20140309 linuxidc.com-error_log 88181.com-error_log
[Linux]#
httpd 的部分参数介绍到这里;下一篇将介绍 https 的实现 httpd-2.4 的编译安装。http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2014-03/98761.htm
上一篇 Web 服务(一)HTTP 基础详解详细介绍了 http 基础与 httpd 的安装(见 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2014-03/98952.htm);这篇详细介绍下 httpd-2.2 的部分配置参数
CentOS 6.5 编译安装 httpd-2.4.7 http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2014-02/97265.htm
一、配置文件和基本格式
配置文件路径:/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
配置参数 值
1、配置指令不区分字符大小写;但是值有可能区分字符大小写
2、有些指令可以重复出现多次
配置文件格式:
1、全局配置
2、主机配置:用于仅提供一个站点
3、虚拟主机:用于提供多个站点(和主机配置不能同时生效)
配置文件语法测试:{service httpd configtest | httpd -t}
二、详细配置
1、监听套接字
# 配置文件事例
#Listen 12.34.56.78:80
Listen 80
Listen 8080
Listen 192.168.1.110:8082
此指令可以出现多次;用于指定监听多个不同的套接字:
[Linux]#httpd -t
Syntax OK
[Linux]#service httpd reload
Reloading httpd:
[Linux]#ss -tnl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 :::111 :::*
LISTEN 0 128 *:111 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 :::8080 :::*
LISTEN 0 128 :::80 :::*
LISTEN 0 128 192.168.1.186:8082 *:*
2、配置使用 Keep Alive
# KeepAlive: Whether or not to allow persistent connections (more than
# one request per connection). Set to “Off” to deactivate.
#
#KeepAlive On
KeepAlive Off
MaxKeepAliveRequests 100 #持久连接最大请求数
KeepAliveTimeout 15 #超时时间
3、多道处理模块 MPM
查看系统默认启用的模块
[Linux]#httpd -l
Compiled in modules:
core.c
prefork.c #默认启用 prefork 模块
http_core.c
mod_so.c
[Linux]#
# 如需启用 worker 模块;需要更改配置文件
[Linux]#vi /etc/sysconfig/httpd
#HTTPD=/usr/sbin/httpd.worker #启用该项后重启 httpd
配置模块信息
[Linux]#vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
# prefork MPM
# StartServers: number of server processes to start
# MinSpareServers: minimum number of server processes which are kept spare
# MaxSpareServers: maximum number of server processes which are kept spare
# ServerLimit: maximum value for MaxClients for the lifetime of the server
# MaxClients: maximum number of server processes allowed to start
# MaxRequestsPerChild: maximum number of requests a server process serves
prefork 稳定性较好,一个线程崩溃不会影响其他线程
<IfModule prefork.c> 判断 prefork 模块是否存在
StartServers 8 默认启动的工作进程数;不包含主进程
MinSpareServers 5 最少空闲进程数
MaxSpareServers 20 最大空闲进程数
ServerLimit 256 最大活动进程数
MaxClients 256 最多允许发起的请求的个数
MaxRequestsPerChild 4000 每个子进程在生命周期内所能够服务的最多请求个数
</IfModule>
# worker MPM
# StartServers: initial number of server processes to start
# MaxClients: maximum number of simultaneous client connections
# MinSpareThreads: minimum number of worker threads which are kept spare
# MaxSpareThreads: maximum number of worker threads which are kept spare
# ThreadsPerChild: constant number of worker threads in each server process
# MaxRequestsPerChild: maximum number of requests a server process serves
worker 多个进程;一个进程崩溃会影响其下的其他线程
<IfModule worker.c> 判断 worker 模块是否存在
StartServers 4 启动的子进程的个数
MaxClients 300 并发请求的最大个数
MinSpareThreads 25 最少空闲线程数
MaxSpareThreads 75 最大空闲线程数
ThreadsPerChild 25 每个子进程可生成的线程数
MaxRequestsPerChild 0 每个子进程在生命周期内所能够服务的最多请求个数;0 表示不做限定
</IfModule>
4、DSO 模块的加载方式
LoadModule module_name /path/to/module
可以使用相对路径和绝对路径;相对路径则对于 ServerRoot 所定义的位置而言;
更改完成后 service httpd reload 可生效
# LoadModule foo_module modules/mod_foo.so
#
LoadModule auth_basic_module modules/mod_auth_basic.so
LoadModule auth_digest_module modules/mod_auth_digest.so
LoadModule authn_file_module modules/mod_authn_file.so
LoadModule authn_alias_module modules/mod_authn_alias.so
LoadModule authn_anon_module modules/mod_authn_anon.so
#
#
[Linux]#httpd -M #可以查看系统所有装载模块
Loaded Modules:
core_module (static)
mpm_prefork_module (static)
http_module (static)
so_module (static)
auth_basic_module (shared)
auth_digest_module (shared)
authn_file_module (shared)
authn_alias_module (shared)
5、配置站点根目录和页面属性
# DocumentRoot: The directory out of which you will serve your
# documents. By default, all requests are taken from this directory, but
# symbolic links and aliases may be used to point to other locations.
#
DocumentRoot “/var/www/html”
DocumentRoot “/path/to/somewhere(站点路径)” #格式
# The Options directive is both complicated and important. Please see 下述站点有配置详细说明
# http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.2/mod/core.html#options
# for more information.
#
<Directory “/var/www/html”> #页面访问属性
#
#
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
#
#
#
Indexes 缺少默认页面时;允许将目录中的所有文件已列表形式返回给用户
FollowSymLinks 允许跟随符号链接所指向的原始文件;危险
None 所有都不启用
All 所有都启用
ExecCGI 是否允许使用 mod_cgi 模块执行 CGI 脚���
Includes 是否允许使用 mod_include 模块实现服务器端包含(SSI)
MultiViews 允许使用 mod_negotiation 实现内容协商
SymLinksIfOwnerMatch 在链接文件属主属组与原始文件的属主属组相同时;允许跟随符号链接所指向的原始文件
#
#
# AllowOverride controls what directives may be placed in .htaccess files.
# It can be “All”, “None”, or any combination of the keywords:
# Options FileInfo AuthConfig Limit
基于主机的访问控制
#
#
AllowOverride None 表示下面这些控制机制是否被禁用;None 表示不被禁用
#
# Controls who can get stuff from this server.
#
#allow 允许;deny 不允许
Order allow,deny #默认 deny;没有 allow 的都 deny;可以写多条;自上而下匹配
Allow from all 格式:from IP
Deny
#二者都匹配或二者都无匹配项时,则以后者为准;否则,则以匹配到的为准
</Directory>
# 最佳匹配:从列表中找出最小的能匹配到访问者的地址的条目为最终是生效的
# 详细参考 http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.2/mod/mod_authz_host.html#allow
6、定义默认主页面
# The index.html.var file (a type-map) is used to deliver content-
# negotiated documents. The MultiViews Option can be used for the
# same purpose, but it is much slower.
#
DirectoryIndex index.html index.html.var #自左而右依次查找
7、用户目录
# The path to the end user account ‘public_html’ directory must be
# accessible to the webserver userid. This usually means that ~userid
权限说明
# must have permissions of 711, ~userid/public_html must have permissions
# of 755, and documents contained therein must be world-readable.
# Otherwise, the client will only receive a “403 Forbidden” message.
#
# See also: http://httpd.apache.org/docs/misc/FAQ.html#forbidden
#
<IfModule mod_userdir.c>
#
# UserDir is disabled by default since it can confirm the presence
# of a username on the system (depending on home directory
# permissions).
#
UserDir disabled
disabled 禁止
UserDir public_html 用户家目录下的目录名称,所有位于此目录中的文件均可通过前述的访问路径进行访问;用户的家目录的赋予运行 httpd 进程的用户拥有执行权限;
#
# To enable requests to /~user/ to serve the user’s public_html
# directory, remove the “UserDir disabled” line above, and uncomment
# the following line instead:
#
#UserDir public_html
</IfModule>















