共计 1303 个字符,预计需要花费 4 分钟才能阅读完成。
Oracle 数据库中,数据的增、删、改、查,通过 SQL 语句实现
SQL:结构化查询语言;
特点:不区分大小写;字符串用单引号引起来;语句结束用分号表示结束;
行注释,在语句的最前面加“–”
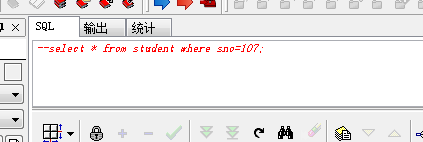
块注释,分别在语句的前后加 /* 和 */
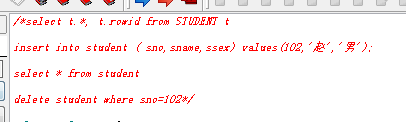
SQL 中常用的几类:
一、数据定义语言 DDL:创建、修改、删除数据库语言。
create table Student
(sno varchar2(3) not null,
sname varchar2(8) not null,
ssex varchar2(2) not null,
sbirthday date,
sclass varchar2(5)
)
;
-- Add comments to the table
comment on table Student
is '学生表';
-- Add comments to the columns
comment on column Student.sno
is '学号(主建)';
comment on column Student.sname
is '学生姓名';
comment on column Student.ssex
is '性别';
comment on column Student.sbirthday
is '生日';
comment on column Student.sclass
is '班级'; 二、数据操作语言 DML:添加(insert into)、修改(update set)、删除表中的数据。(delete)
1. 数据的添加:
-- 增加数据
insert into student(sno,sname,ssex) values('102','张三','男');
-- 或者这样写
insert into student values('102','张三','男',sysdate,'95033');
select * from student2. 数据的修改:
-- 数据的修改
update student set ssex='女' where sno='102';
-- 如果不加 where,便是修改整个表某列的属性
-- 对某一列数据的加减
update student set sclass=sclass+1;
update 表名 set 列名 = 列名 +1 where 条件
-- 日期的加减 1 为日的加减 1 3. 数据的删除:
-- 数据的删除
delete student where sno=102;
delete 表名 where 条件;
-- 不加 where,即删除整个表,但是效率低,可用 truncate table 表名来删除(先删表,再建表)例:truncate table student;三、数据查询语言 DQL:从表中获取数据(查询数据)。
-- 数据查询
select * from student;
select * from 表名;
-- 根据条件找字段
select sno,sname from student where sclass='95031';
select 字段名 from 表名 where 条件 更多 Oracle 相关信息见 Oracle 专题页面 http://www.linuxidc.com/topicnews.aspx?tid=12
本文永久更新链接地址 :http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2016-12/138280.htm
正文完
星哥玩云-微信公众号
















